写在前面的话
上一节主要谈谈 MySQL 是怎么安装的以及最简单的初始化我们应该做哪些配置。其中也用到了一些简单的用户操作 SQL,所以这一节主要学习常用的 SQL 使用。
SQL 介绍
在了解 SQL 之前,对于 SQL 需要有以下简单的认知:
1. 主流的来个标准,SQL92 和 SQL99,在 MySQL 5.7 以后采用的是 SQL92。
2. 在 5.7 中新增了 sql_mode,作用在于限制哪些 SQL 能够使用,一个很明显的例子是 group by 的使用。
在上一节简单说过常用的 SQL 分类(主要前 3 个):
DDL:数据定义语言
DCL:数据控制语言
DML:数据操作语言
DQL:数据查询语言
数据类型
这算是数据定义过程中的一个重点,针对不同的数据我们给定不同的数据类型,作用在于保证数据的准确性和标准性。
数值类型:
| 类 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| tinyint | 整数 | 很小,0 - 255 |
| smallint | 整数 | 较小,-2^15 - 2^15 |
| mediumint | 整数 | 中等,很少用 |
| int | 整数 | 常规,-2^31 - 2^31 |
| bigint | 整数 | 较大,-2^63 - 2^63 |
| float | 浮点数 | 小型单精度浮点数,四个字节 |
| double | 浮点数 | 常规单精度浮点数,八个字节 |
| decimal | 定点数 | 包含整数部分,小数部分或者同时包含二者精确数值 |
| bit | BIT | 位字段值 |
字符类型:
| 类 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| char | 文本 | 固定长度字符串,最多 255 个字符 |
| varchar | 文本 | 可变长度字符串,最多 65535 个字符 |
| tinytext | 文本 | 可变长度字符串,最多 255 个字符 |
| text | 文本 | 可变长度字符串,最多 65535 个字符 |
| mediumtext | 文本 | 可变长度字符串,最多 1600万+ 个字符 |
| longtext | 文本 | 可变长字符串,最多 42亿+ 字符 |
| enum | 整数 | 一组固定合法值组成的枚举 |
| set | 整数 | 一组固定合法值组成的集 |
在生产中最容易出现的就是字符串字段长度不足的问题,所以在设计的时候注意选对类型。
char 之所以是定长,比如我们定义 char(10),那就意味着传的最大长度是 10,如果不够补充空格,反正就是占用 10 个字符。
varchar 相比之下,则是在指定的范围内按需分配,如 varchar(10),最大长度 10,不足就不足,不浪费。
至于 enum,则属于特别的使用,如本字段的值是指定范围,如 enum("北京", "上海", "广州", "深圳"),这样使用能够优化索引。但用的其实并不多。
时间类型:
| 类型 | 格式 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| date | YYYY-MM-DD | 2019-08-08 |
| time | hh:mm:ss[.uuuuuu] | 10:50:29.123456 |
| datetime | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.uuuuuu] | 2019-08-08 10:50:29.123456 |
| timestamp | YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss[.uuuuuu] | 2019-08-08 10:50:29.123456 |
| year | YYYY | 2019 |
timestamp 会受到时区的影响,且范围有限制。不是很建议。
二进制类型(这类不建议存到 MySQL):
| 类 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| binary | 二进制 | 类似 char 固定长度,但存储的是二进制 |
| varbinary | 二进制 | 类型 varchar |
| tinyblob | blob | 最大长度 255 的 blob 列 |
| blob | blob | 最大长度 65535 的 blob 列 |
| mediumblob | blob | 最大长度 1600万+ 的 blob 列 |
| longblob | blob | 最大长度 42亿+ 的 blob 列 |
表属性
1. 列属性(主要关键字):
primary key:主键,非空唯一约束,一个表只能有一个,但是能由多个列组成。
not null:非空约束,属于设计规范,尽可能不要列空,可以使用默认值 0 替代空。
unique key:唯一键,值不能重复 。
unsigned:无符号,主要用于数字列,非负数。
key:索引,可以给某列建立索引来优化查询。
default:默认值,列没有值时默认填充。
auto_increment:自增,主要针对数字,顺序填充数据,默认 1 开始,可以设置起始值和偏移量。
comment:注释。
2. 表属性:
存储引擎:在 5.7 默认是 innodb,在老版本中可能是 MyISAM。
字符集:常见的 utf8,utf8mb4 等。
校对(排序)规则:如 utf8_general_ci,utf8_bin 这种。主要用于大小写是否敏感。
可以通过以下 SQL 查看系统支持:
# 查看编码 show charset; # 查看排序规则 show collation;
数据库操作(DDL)
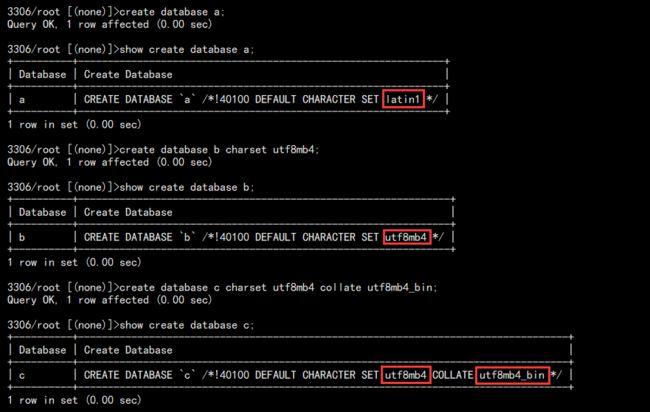
1. 创建数据库并指定查看字符集:
# 默认创建 create database a; show create database a; # 指定字符集创建 create database b charset utf8mb4; show create database b; # 指定字符集和排序规则创建 create database c charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin; show create database c;
结果如下:
可以看到,MySQL 默认不指定字符集创建数据库的时候,创建的数据库的字符集为拉丁(latin1)。
排序规则 ci 结尾的都是大小写不敏感的。bin 大小写敏感。
当然,创建数据库还可以使用:
create schema d;
这样也是能够创建数据库的。
建库规范:
a. 库名不应该包含大小写。
b. 库名不该以数字开头。
c. 建库一定要加字符集。
d. 库名要有意义。
特别注意:
禁止生产种执行 drop database xxx;
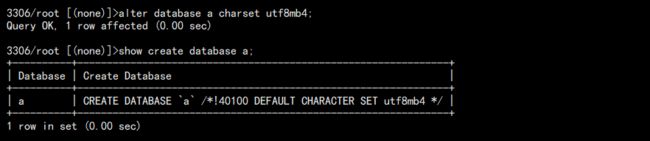
2. 修改数据库字符集:
alter database a charset utf8mb4;
查看:
但是值得注意的是,修改后的字符集必须比之前的字符集范围更大。原因是数据的兼容性。
同时,不到万不得已一般不要修改。
数据表操作(DDL)
语法格式:
create table students(
列1 属性(数据类型, 约束, 其它),
列2 属性,
...
)
1. 创建一个名为学校的测试库,创建一张名为学生的用户表:
# 创建库 create database school charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin; # 指定库 use school; # 创建表 create table students ( id int not null primary key auto_increment comment "学号", sname varchar(255) not null comment "姓名", sage tinyint unsigned not null default 0 comment "年龄", sgender enum("m", "f", "n") not null default "n" comment "性别", id_card char(18) not null unique comment "身份证", add_time timestamp not null default now() comment "入学时间" ) engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4 comment "学生表";
建表规范:
a. 表名小写,不能数字开头且具有意义。
b. 选择合适的数据类型,字符集,存储引擎。
c. 每个列都需要有注释说明且非空,如果为空选择 0 代替。
特别注意:
禁止生产种执行 drop table xxx;
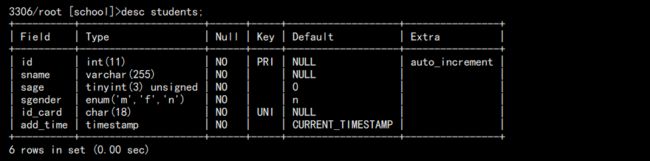
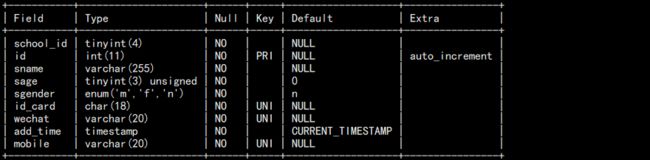
2. 查看表结构:
desc students;
结果如图:
也可以查看建表语句:
show create table students\G
3. 添加列:
a. 直接添加手机号列:
alter table students add mobile varchar(20) not null unique comment "手机号";
如图:
默认添加列加到最后面。
b. 在 id_card 后面添加微信列:
alter table students add wechat varchar(20) not null unique comment "微信" after id_card;
如图:
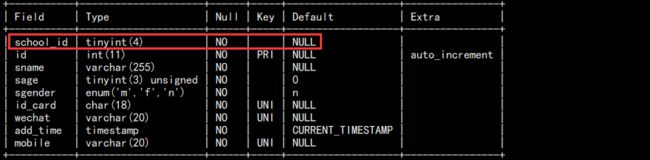
c. 在最前面加个列:
alter table students add school_id tinyint not null comment "学校编号" first;
如图:
4. 修改列:
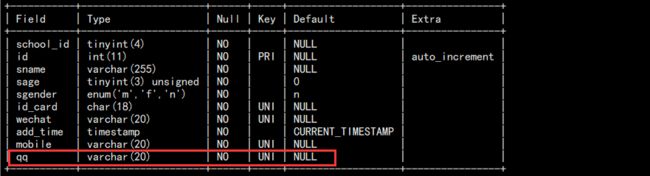
a. 添加 qq 列,然后删除它:
# 添加 alter table students add qq varchar(20) not null unique comment "QQ"; desc students; # 删除 alter table students drop qq; desc students;
添加:
删除:
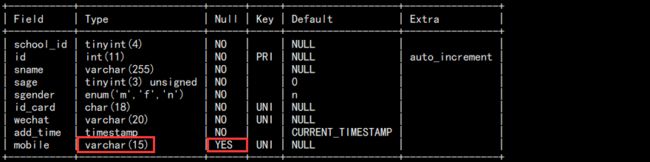
b. 修改列属性:
alter table students modify mobile varchar(15);
如图:
可以发现,虽然只是修改了 varchar,但是 null 也修改了。所以修改的时候建议多以属性都加一遍。
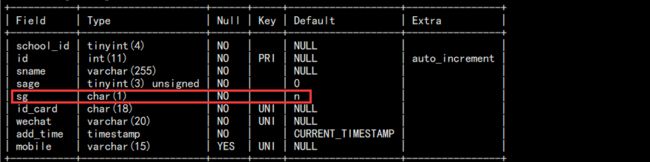
c. 修改列名和数据类型:
alter table students change sgender sg char(1) not null default 'n';
我们这里将 sgender 改为 sg,并修改类型:
在过去的版本中,我们应该避免在业务高峰期修改表结构,因为这会导致数据库锁表。
但可以使用 pt-osc 工具(Percona 的),可以在线修改,不再锁表,原理在于创建一个新表。
当然,在 MySQL 8.0 以后的版本以及自身集成了该工具。
5. 复制表结构建立一张新表:
create table t1 like students;
对于 DCL,主要就两个,一个是 grant,一个是 revoke。
数据增删改(DML)
1. 插入数据:
a. 最标准的 insert 语法:
insert into students(school_id,id,sname,sage,sg,id_card,wechat,add_time,mobile) values (11,1,'张三',18,'m','511123199311111214','13290909801',now(),'13290909801');
b. 省事写法:
由于我们每个字段都按照顺序写,所以没必须要把字段列出来。
insert into students values (11,2,'李四',19,'f','511123199311111124','13290222201',now(),'13290222201');
c. 部分插入:
因为有些字段是由默认值的,所以我们可以就使用默认值:
insert into students(school_id,sname,sage,id_card,wechat,mobile) values (11,'王五',18,'511123199311112224','13290909221','13290909221');
d. 同时插入多个:
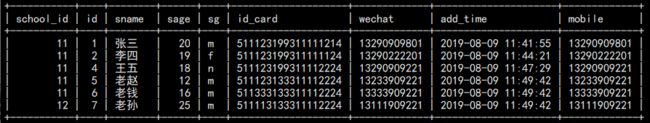
insert into students(school_id,sname,sage,id_card,wechat,mobile) values (11,'老赵',12,'511123133311112224','13233909221','13233909221'), (11,'老钱',16,'511333133311112224','13333909221','13333909221'), (12,'老孙',25,'511113133311112224','13111909221','13111909221');
e. 查看插入结果:
select * from students;
结果如图:
2. 修改数据:
a. 把张三的年龄改为 20:
update students set sage=20 where sname='张三';
b. 把所有名字老开头的性别改为 m:
update students set sg='m' where sname like '老%';
结果如图:
c. 同时修改多个值:
update students set sage=25,sg='f' where sname='张三';
结果如图:
3. 删除数据:
delete from students where sname="老孙";
不推荐使用!!!
清空表的方法:
delete from students;
delete 逐行全部删除,属于 DDL 操作,速度慢!!!
同时,我们可以从上面的 id 可以看到,由于发生了 delete 导致 id 不连续,确实的那一部分仍然占据着磁盘,这将导致可能数据量不大,但是磁盘占用很大的情况。这就是磁盘碎片。
truncate table students;
truncate 全部清空数据页,干干净净,属于 DML 操作,速度快。
都不推荐!!!
特别注意:
update / delete 一定要记得 where,否则原地爆炸。
在实际生产中,我们都是使用伪删除的方式,也就是新加数据状态字段,如可用为 1,不可用为 0,我们删除就将状态由 1 改为 0。
alter table students add status tinyint not null default 1 comment "数据状态";
删除就将改行数据 status 改为 0。
查询 DQL(Data Query Language)
1. 单独使用,查看系统参数:select @@xxx
select @@port;
select @@basedir;
select @@datadir;
select @@socket;
select @@server_id;
结果如下:
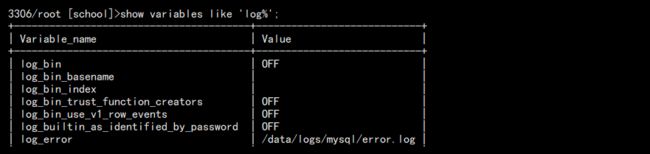
有些复杂的我们可以使用 show 来模糊查询:
show variables like 'log%';
如图:
2. 单独使用,调用函数:select 函数();
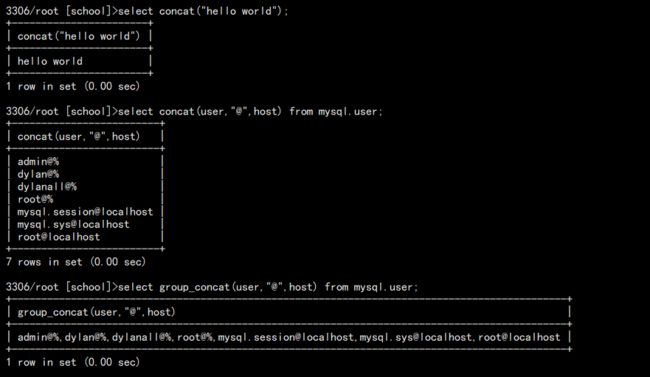
# 显示当前信息 select now(); select database(); select user(); # 打印输出 select concat("hello world"); # 定制化输出 select concat(user,"@",host) from mysql.user; # 一行输出 select group_concat(user,"@",host) from mysql.user;
结果:
更多的函数可以查看官方文档:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/func-op-summary-ref.html
3. 单表子句,FROM:
select * from students;
不建议在生产中使用,如果表数据太大会造成卡死。
查询指定列:
select sname,sage,mobile from students;
如图:
4. 单表子句,WHERE:
在使用之前,MySQL 官方提供了专门用于学习的一个数据库:world,可以前往官网下载:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-other.html
如图:
将示例的数据库导入 MySQL 中,当然也可以下载 world_x,那个是新数据,只是测试没必要:
包含三张表,城市,国家,国家语言。可以使用 desc 了解每张表的数据结构。
a. 等值查询:查询中国(CHN)的城市
select * from city where CountryCode="CHN";
结果:
也可以单独查询深圳:
select * from city where Name="shenzhen";
如图:
b. 比较查询:>,<,>=,<=,<>
查询世界人口小于 100 的城市:
select * from city where population<100;
如图:
c. 逻辑查询:and,or
查询中国人口大于 500 万的:
select * from city where countrycode="CHN" and population>=5000000;
如图:
查询中国或美国的城市:
select * from city where countrycode="CHN" or countrycode="USA";
d. 模糊查询:%
查询 bei 开头的:
select * from city where name like "bei%";
查询名字中包含 bei 的(不走索引,性能极差,不推荐):
select * from city where name like "%bei%";
如图:
e. 列表匹配:in(类似 or)
select * from city where countrycode in ("CHN","USA");
如图:
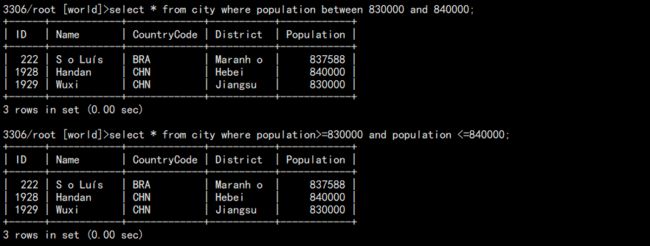
f. 查询范围:between and(类似 >= and <=)
查询人口在 830000 和 840000 之间的城市:
select * from city where population between 830000 and 840000;
换成 and 写为:
select * from city where population>=830000 and population<=840000;
结果:
5. GROUP BY + 聚合函数
常用的聚合函数有以下一些:
最大值:max()
最小值:min()
平均值:avg()
求和:sum()
统计:count()
列转行:group_concat()
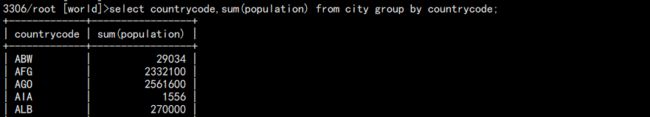
a. 统计每个国家的人口数量:
select countrycode,sum(population) from city group by countrycode;
结果:
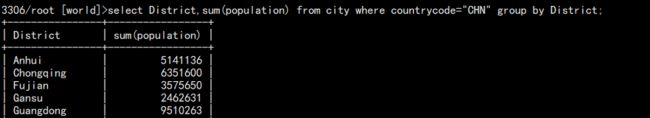
b. 统计中国各省总人口:
select District,sum(population) from city where countrycode="CHN" group by District;
结果:
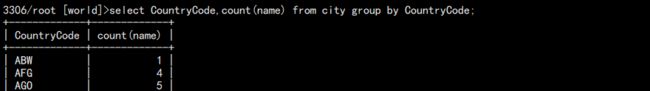
3. 统计世界上每个国家城市数量:
select CountryCode,count(name) from city group by CountryCode;
结果:
6. 单表子句:HAVING
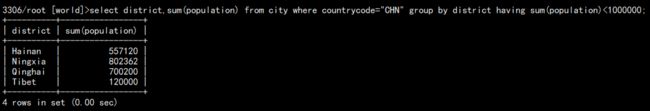
例如统计中国各省总人口数,只显示小于 100 万的。
select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode="CHN" group by district having sum(population)<1000000;
如图:
之所以使用 having,是因为 where 有顺序要求,分别是 where -- group by -- having。
在 group by 之后只能使用 having 不能再用 where 了。另外 having 后条件不走索引。
7. 排序和限制:ORDER BY + LIMIT
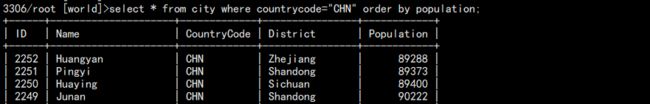
a. 查询中国的城市信息,并按照人口升序排序。
select * from city where countrycode="CHN" order by population;
如图:
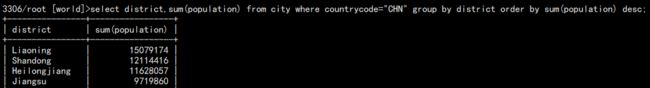
b. 统计各省总人口数并按照降序排列。
select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode="CHN" group by district order by sum(population) desc;
默认升序,降序需要 desc:
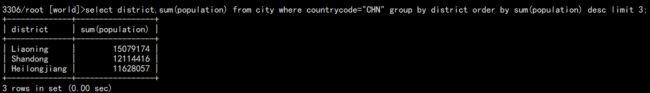
c. 统计全国各省人口大于 500 万的按照降序排列并取前三。
select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode="CHN" group by district order by sum(population) desc limit 3;
如图:
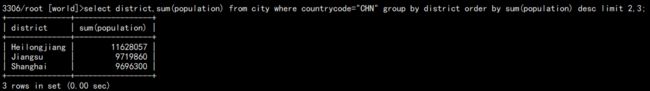
当然,limit 也可做限制,如:
select district,sum(population) from city where countrycode="CHN" group by district order by sum(population) desc limit 2,3;
limit n,m,这意味着跳过前面的 n 行,然后显示 m 行,于是结果为:
当然也可以另外的写法:limit m offset n,一个意思。
8. 去重复:DISTINCT
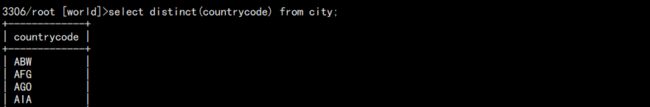
查询所有国家:
select distinct(countrycode) from city;
如果只是查询 countrycode 会有很多重复数据,可以通过 distinct 去掉重复:
9. 联合查询:union all
之前查询中国和美国使用了 and 和 in 的方法,但这并不是性能最优的方法。最好的是使用 union all:
select * from city where countrycode="CHN" union all select * from city where countrycode="USA";
值得注意的是 union 会去掉重复数据,而 union all 不会去重复。
10. 多表连接查询:join
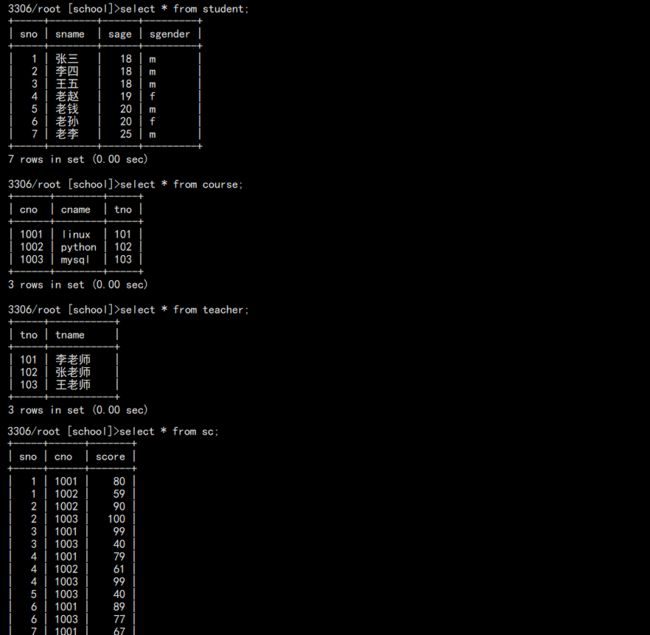
首选准备 4 张表,关系是这样的:
建表语句:
-- 删掉旧数据新建数据库 drop database school; create database school charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin; use school; -- 学生表 create table student( sno int not null primary key auto_increment comment "学号", sname varchar(20) not null comment "姓名", sage tinyint unsigned not null comment "年龄", sgender enum("m","f","n") not null default "n" comment "性别" ) engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4; -- 课程表 create table course( cno int not null primary key auto_increment comment "课程编号", cname varchar(20) not null comment "课程名称", tno int not null comment "教师编号" ) engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4; -- 学生成绩表 create table sc( sno int not null comment "学号", cno int not null comment "课程编号", score tinyint not null default 0 comment "成绩" ) engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4; -- 教师表 create table teacher( tno int not null primary key auto_increment comment "教师编号", tname varchar(20) not null comment "教师名字" ) engine=innodb charset=utf8mb4;
基础数据:
-- 学生信息 INSERT INTO student VALUES (1,'张三',18,'m'), (2,'李四',18,'m'), (3,'王五',18,'m'), (4,'老赵',19,'f'), (5,'老钱',20,'m'), (6,'老孙',20,'f'), (7,'老李',25,'m'); -- 教师信息 INSERT INTO teacher VALUES (101,'李老师'), (102,'张老师'), (103,'王老师'); -- 课程信息 INSERT INTO course VALUES (1001,'linux',101), (1002,'python',102), (1003,'mysql',103); -- 学生成绩 INSERT INTO sc VALUES (1,1001,80), (1,1002,59), (2,1002,90), (2,1003,100), (3,1001,99), (3,1003,40), (4,1001,79), (4,1002,61), (4,1003,99), (5,1003,40), (6,1001,89), (6,1003,77), (7,1001,67), (7,1003,82);
最后效果:
多表查询测试:
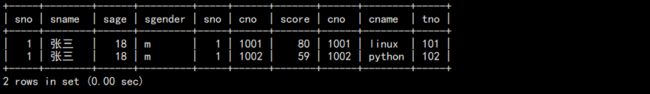
a. 统计张三学习了几门课:
select st.sname,count(sc.cno) as course_nums from student as st join sc on st.sno=sc.sno where st.sname="张三";
这里用到的知识有:
1. 通过 as 可以对字段就行取别名,便于后面书写使用。
2. 在一开始不知道这么写的时候可以选择将 select 和 from 之间的内容替换为 *,然后再根据需求修改。
结果:
b. 查询张三学习的课程名称:
同样可以先查出所有信息:
select * from student as st join sc on st.sno=sc.sno join course as co on co.cno=sc.cno where st.sname="张三";
结果:
然后我们只需要姓名列和课程名称列:
select st.sname,co.cname from student as st join sc on st.sno=sc.sno join course as co on co.cno=sc.cno where st.sname="张三";
结果:
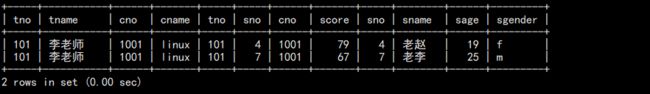
c. 查询李老师教的学生名字:
select te.tname,co.cname,st.sname from teacher as te join course as co on co.tno=te.tno join sc on sc.cno=co.cno join student as st on st.sno=sc.sno where te.tname="李老师";
结果:
d. 计算李老师所教课程的平均分:
select avg(sc.score) from teacher as te join course as co on te.tno=co.tno join sc on co.cno=sc.cno where te.tname="李老师";
结果:
e. 计算每个老师的平均分,并降序排列:
select te.tname,avg(sc.score) from teacher as te join course as co on te.tno=co.tno join sc on co.cno=sc.cno group by te.tname order by avg(sc.score) desc;
结果:
f. 查询李老师80分以下的学生:
select * from teacher as te join course as co on te.tno=co.tno join sc on sc.cno=co.cno join student as st on st.sno=sc.sno where te.tname="李老师" and sc.score<80;
结果:
g. 查询所有老师成绩不及格的:
select * from teacher as te join course as co on co.tno=te.tno join sc on sc.cno=co.cno join student as st on sc.sno=st.sno where sc.score<60;
结果:
h. 查询平均成绩大于 60 的学生:
select st.sname,avg(score) from sc join student as st on st.sno=sc.sno group by sc.sno having avg(score)>60;
结果:
这里值得注意的是,由于 group by 后面不能使用 where,所以筛选条件变成 having。
i. 显示各门成绩的最高分最低分:
select co.cname,max(sc.score) as "最高分",min(sc.score) as "最低分" from sc join course as co on co.cno=sc.cno group by sc.cno;
结果:
11. information_schema 视图库:
在说明这个之前,可以简单了解以下视图。可以这样理解,视图就是对复杂 SQL 的封装,举个例子:
select co.cname,max(sc.score) as "最高分",min(sc.score) as "最低分" from sc join course as co on co.cno=sc.cno group by sc.cno;
这是上面一条复杂的查询,如果每次用这个就写一次,这么长肯定很麻烦,这就可以将它保存为视图:
create view mytest_view as select co.cname,max(sc.score) as "最高分",min(sc.score) as "最低分" from sc join course as co on co.cno=sc.cno group by sc.cno;
可以在前面增加创建视图:create view 视图名字 as
此时就可以直接使用:
select * from mytest_view;
结果:
在 MySQL 5.7 中,有三个库用于存储视图:information_schema,performance_schema,sys
这里主要谈谈 information_schema 中的 tables 表,其中主要的字段包括:
| 字段名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| TABLE_SCHEMA | 库名 |
| TABLE_NAME | 表名 |
| ENGINE | 引擎 |
| TABLE_ROWS | 表的行数 |
| AVG_ROW_LENGTH | 表中行的平均大小(字节) |
| DATA_LENGTH | 数据占用空间大小(字节) |
| INDEX_LENGTH | 索引占用空间大小(字节) |
可以直接查询:
select TABLE_SCHEMA,TABLE_NAME,ENGINE,TABLE_ROWS,AVG_ROW_LENGTH,DATA_LENGTH,INDEX_LENGTH from tables;
示例:
a. 显示每个库都有哪些表:
select TABLE_SCHEMA,group_concat(TABLE_NAME) from information_schema.tables group by TABLE_SCHEMA;
结果类似:
| world | countrylanguage,country,city|
b. 统计所有库下表的个数:
select TABLE_SCHEMA,count(TABLE_NAME) from information_schema.tables group by TABLE_SCHEMA;
结果:
c. 统计 world 下面每张表所占的磁盘:
select TABLE_NAME,concat((DATA_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/1024, " KB") as LENGTH from information_schema.tables where TABLE_SCHEMA="world";
结果:
当然会发现小数位数太多,没啥意义,可以设置小数:保留两位
select TABLE_NAME,concat(round((DATA_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/1024, 2)," KB") as LENGTH from information_schema.tables where TABLE_SCHEMA="world";
结果:
d. 统计所有库占用大小:
select TABLE_SCHEMA,concat(round(sum(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH)/1024,2)," KB") as DB_LENGTH from information_schema.tables group by TABLE_SCHEMA;
结果:
e. 统计整个库占用的空间:
select concat(sum(DATA_LENGTH + INDEX_LENGTH)/1024," KB") as TOTAL_LENGTH from information_schema.tables;
结果:
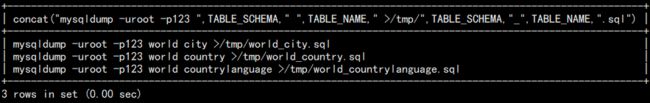
f. 假设现在有 1000 张表,需要单独生产备份语句,就需要用到 SQL 拼接:
mysqldump -uroot -p123 world city >/tmp/world_city.sql
这是备份单个表的语句,如果需要备份 1000 个,可以使用 SQL 来生成:
select concat("mysqldump -uroot -p123 ",TABLE_SCHEMA," ",TABLE_NAME," >/tmp/",TABLE_SCHEMA,"_",TABLE_NAME,".sql") from information_schema.tables where TABLE_SCHEMA="world";
结果如下:
但这只是单纯的 SQL 结果,可以将其输出到文件:前提是在 /etc/my.cnf 中指定安全目录 secure-file-priv=/tmp
select concat("mysqldump -uroot -p123 ",TABLE_SCHEMA," ",TABLE_NAME," >/tmp/",TABLE_SCHEMA,"_",TABLE_NAME,".sql") from information_schema.tables where TABLE_SCHEMA="world" into outfile '/tmp/1.sh'
12. show 命令如下表
| 命令 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| show databases; | 查看数据库 |
| show tables; | 查看表 |
| show tables from information_schema; | 查看指定库的表 |
| show create database world; | 查看建库语句 |
| show create table city; | 查看建表语句 |
| show grants for root@'%'; | 查看用户授权 |
| show charset; | 查看支持的编码 |
| show collation; | 查看数据库支持的排序规则 |
| show processlist; | 查看数据库连接情况 |
| show index from city; | 查看表索引情况 |
| show status; | 查看数据库情况 |
| show status like '%lock%'; | 模糊查询数据库状态 |
| show variables; | 查看数据库配置信息 |
| show variables like "%timeout%"; | 模糊查询配置信息 |
| show engines; | 查看存储引擎 |
| show engine innodb status\G | 查看 innodb 相关信息 |
| show binary logs; | 列举所有二进制日志 |
| show master status; | 查看数据库日志位置 |
| show binlog evnets in xxx | 查看二进制日志事件 |
| show slave status\G | 查看从库状态 |
| show relaylog events; | 查看从库 relaylog |
小结
增删查改的核心语句都在这里,内容非常多!