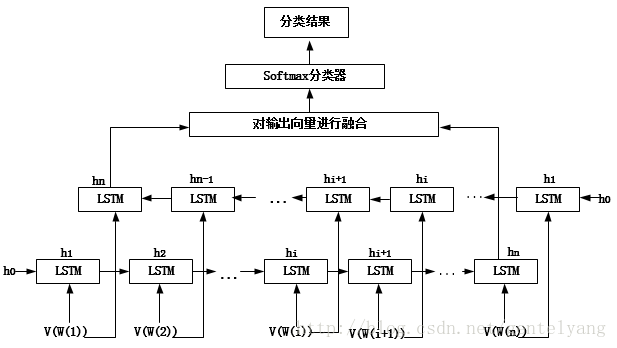
利用BiLSTM网络实现文本分类
这里数据的Preprocess过程不贴代码了,训练过程(train)也不贴了,只是记录一下BiLSTM网络实现代码:
这里隐层数为2,词向量为100维。
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.contrib import rnn class Model(object): def __init__(self, num_layers, seq_length, embedding_size, vocab_size, rnn_size, label_size): # 输入数据以及数据标签 self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, seq_length], name="input_x1") self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, label_size], name="input_y") self.dropout_keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropout_keep_prob") self.l2_loss = tf.constant(0.0) with tf.name_scope('embeddingLayer'): # w : 词表(embedding 向量),后面用来训练. w = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([vocab_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0), name='W') embedded = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(w, self.input_x) # 根据第二维展开,维度从0开始 # 删除所有大小为1的维度,删除[1]为要删除维度的参数 inputs = tf.split(embedded, seq_length, 1) inputs = [tf.squeeze(input_, [1]) for input_ in inputs] with tf.name_scope("fw"): stacked_rnn_fw = [] for _ in range(num_layers): fw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(rnn_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True) stacked_rnn_fw.append(fw_cell) lstm_fw_cell_m = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(cells=stacked_rnn_fw, state_is_tuple=True) with tf.name_scope("bw"): stacked_rnn_bw = [] for _ in range(num_layers): bw_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(rnn_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True) stacked_rnn_bw.append(bw_cell) lstm_bw_cell_m = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(cells=stacked_rnn_bw, state_is_tuple=True) with tf.name_scope("output"): outputs, _, _ = rnn.static_bidirectional_rnn(lstm_fw_cell_m, lstm_bw_cell_m, inputs, dtype=tf.float32) with tf.name_scope("result"): w = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([2 * rnn_size, label_size], -1.0, 1.0), name='W') b = tf.get_variable('b', [label_size]) self.output = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(outputs[-1], w, b) self.logits = tf.nn.softmax(self.output, dim=1) with tf.name_scope("loss"): self.losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.logits, labels=self.input_y) self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(self.losses) with tf.name_scope("accuracy"): self.accuracys = tf.equal(tf.argmax(self.logits, axis=1), tf.argmax(self.input_y, axis=1), name="equal") self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(self.accuracys, "float"), name="accuracy") # with tf.name_scope("ans"): # self.ans = tf.subtract(tf.ones_like(self.distance), self.distance, name="temp_sim") # print(self.ans) # blstm = Model(num_layers=3, # seq_length=30, # embedding_size=399, # vocab_size=120, # rnn_size=20, # label_size=6)