Android Update Engine分析(七) DownloadAction之FileWriter
Android Update Engine分析(七) DownloadAction之FileWriter
本系列到现在为止的共有六篇,分别分析分析了Makefile,Update Engine的客户端、服务端及Action机制的细节:
- Android Update Engine分析(一)Makefile
- Android Update Engine分析(二)Protobuf和AIDL文件
- Android Update Engine分析(三)客户端进程
- Android Update Engine分析(四)服务端进程
- Android Update Engine分析(五)服务端核心之Action机制
- Android Update Engine分析(六)服务端核心之Action详解
在最新的一篇里详细分析了AOSP版Update Engine使用的4个Action细节。所有的Action中,DownloadAction需要完成的事情最多,包括升级数据的下载和更新。具体实现上,DownloadAction一边下载数据一边对收到的数据进行解析并更新到相应分区。但该篇只分析了Download中如何下载数据,对下载后的数据如何解析和写入一带而过。本篇将带大家一起看看接收到的数据是如何进行解析并更新到指定分区的。
上一篇《Android Update Engine分析(六)服务端核心之Action详解》由于分析了所有的4个Action,所以整个文章显得很长。意外的是本篇针对DownloadAction中数据写入部分的分析比上一篇更长,真是所料未及啊~~想精简一些,但又担心说不清楚,最后啰啰嗦嗦一大篇,大家凑合着看吧。因此,把话说清楚或者文章写清楚但又不啰嗦真是一门学问。
为了方便阅读,制作了这个目录,想了解特定内容请点击相应的目录链接跳转:
- 1. DownloadAction何时写入接收到的数据?
- 1.1 FileWriter的初始化
- 1.2 HttpFetcher的初始化
- 1.3 DownloadAction是如何接收到数据传输通知的?
- 2. 升级文件的数据结构
- 2.1 升级文件的数据结构
- 元数据
- 具体的更新数据
- 升级包的签名
- 2.2 DeltaArchiveManifest
- 2.1 升级文件的数据结构
- 3. DeltaPerformer的Write操作
- 3.1 更新数据接收进度信息
- 3.2 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest数据
- ParsePayloadMetadata()函数
- ValidateMetadataSignature()函数
- 3.3 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查
- 3.4 从DeltaArchiveManifest中提取分区信息
- VerifySourcePartitions()函数
- 3.5 更新升级的状态信息
- 3.6 提取各分区的InstallOperation,并检查payload数据的hash
- 3.7 执行InstallOperation的更新操作
- 3.8 提取升级数据的signature
- 4. 完整的Write()操作注释
- Write()代码注释
- Write()操作总结
本文涉及的Android代码版本:android‐7.1.1_r23 (NMF27D)
1. DownloadAction何时写入接收到的数据?
1.1 FileWriter的初始化
DownloadAction类有一个FileWriter成员writer_,专门用于负责写入下载的数据。
在DownloadAction的构造函数中writer_被初始化为nullptr,然后在调用PerformAction()时对这个成员进行初始化,如下:
- DownloadAction构造函数
DownloadAction::DownloadAction(PrefsInterface* prefs,
BootControlInterface* boot_control,
HardwareInterface* hardware,
SystemState* system_state,
HttpFetcher* http_fetcher)
: prefs_(prefs),
boot_control_(boot_control),
hardware_(hardware),
system_state_(system_state),
http_fetcher_(http_fetcher),
writer_(nullptr), /* 构造时,writer_被初始化为nullptr */
code_(ErrorCode::kSuccess),
delegate_(nullptr),
bytes_received_(0),
p2p_sharing_fd_(-1),
p2p_visible_(true) {
}
PerformAction()函数
void DownloadAction::PerformAction() {
// download_action将自己设置为http_fetcher_的委托对象
http_fetcher_->set_delegate(this);
...
// 检查write_是否已经初始化,构造函数中write_被初始化为nullptr
if (writer_) {
LOG(INFO) << "Using writer for test.";
} else {
// 构造DeltaPerformer的类对象,并传递给指针delta_performer_
// 构造中,最重要的参数包括download_action的delegate_(实际上是"update_attempter_")和install_plan_
delta_performer_.reset(new DeltaPerformer(
prefs_, boot_control_, hardware_, delegate_, &install_plan_));
//
// 重要:
// 将write_指针指向delta_performer_,所以writer_实际就是delta_performer_
//
writer_ = delta_performer_.get();
}
...
// 数据获取器http_fetcher_开始工作,后续接收到数据后会通知DownloadAction进行处理
http_fetcher_->BeginTransfer(install_plan_.download_url);
}
1.2 HttpFetcher的初始化
DownloadAction类有一个HttpFetcher成员http_fetcher_,专门用于负责数据的下载。
在BuildUpdateActions()操作中会根据当前使用的数据传输协议构造用于数据下载的download_fetcher。这个download_fetcher会进一步被包装为MultiRangeHttpFetcher,并用于初始化download_action的成员http_fetcher_。因此,http_fetcher_负责数据下载。如下:
void UpdateAttempterAndroid::BuildUpdateActions(const string& url) {
...
HttpFetcher* download_fetcher = nullptr;
//
// 如果是"file:///"协议,使用FileFetcher构造download_fetcher
//
if (FileFetcher::SupportedUrl(url)) {
DLOG(INFO) << "Using FileFetcher for file URL.";
download_fetcher = new FileFetcher();
} else {
#ifdef _UE_SIDELOAD
LOG(FATAL) << "Unsupported sideload URI: " << url;
#else
//
// 除"file:///"协议外,使用LibcurlHttpFetcher构造download_fetcher
//
LibcurlHttpFetcher* libcurl_fetcher =
new LibcurlHttpFetcher(&proxy_resolver_, hardware_);
libcurl_fetcher->set_server_to_check(ServerToCheck::kDownload);
download_fetcher = libcurl_fetcher;
#endif // _UE_SIDELOAD
}
//
// 前面构造的download_fetcher会进一步被包装为MultiRangeHttpFetcher,
// 用于初始化DownloadAction类的http_fetcher_成员
//
shared_ptr download_action(new DownloadAction(
prefs_,
boot_control_,
hardware_,
nullptr, // system_state, not used.
new MultiRangeHttpFetcher(download_fetcher))); // passes ownership
...
}
1.3 DownloadAction是如何接收到数据传输通知的?
在PerformAction类PerformAction()操作的最后,http_fetcher_开始数据传输。
根据前面的分析,这里http_fetcher_自身是一个MultiRangeHttpFetcher类对象,但依赖于下一层的FileFetcher或LibcurlHttpFetcher。
在BeginTransfer()操作中,http_fetcher_会将自身设置为为FileFetcher或LibcurlHttpFetcher的委托对象, 如下:
void MultiRangeHttpFetcher::BeginTransfer(const std::string& url) {
...
LOG(INFO) << "starting first transfer";
//
// !!! 这里,http_fetcher_将自己设置为`FileFetcher`或`LibcurlHttpFetcher`的委托对象
//
base_fetcher_->set_delegate(this);
StartTransfer();
}
同时,在DownloadAction的PerformAction()一开始,download_action将自己设置为MultiRangeHttpFetcher的委托对象。
这样一来,就在DownloadAction,MultiRangeHttpFetcher和FileFetcher或LibcurlHttpFetcher之间建立起了一个委托对象的链条。
FileFetcher或LibcurlHttpFetcher在成功收取一段数据时,会通过自己的delegate_通知MultiRangeHttpFetcher类。而后者会进一步通过自己的delegate_通知DownloadAction。如下:
FileFetcher成功收取数据操作
void FileFetcher::OnReadDoneCallback(size_t bytes_read) {
ongoing_read_ = false;
if (bytes_read == 0) {
CleanUp();
//
// 通知MultiRangeHttpFetcher,传输完成啦!
//
if (delegate_)
delegate_->TransferComplete(this, true);
} else {
bytes_copied_ += bytes_read;
//
// 通知MultiRangeHttpFetcher,收到了bytes_read字节的数据
//
if (delegate_)
delegate_->ReceivedBytes(this, buffer_.data(), bytes_read);
ScheduleRead();
}
}
LibcurlHttpFetcher成功收取数据操作
size_t LibcurlHttpFetcher::LibcurlWrite(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb) {
...
bytes_downloaded_ += payload_size;
in_write_callback_ = true;
//
// 通知MultiRangeHttpFetcher,收到了bytes_read字节的数据
//
if (delegate_)
delegate_->ReceivedBytes(this, ptr, payload_size);
in_write_callback_ = false;
return payload_size;
}
MultiRangeHttpFetcher收到通知后进一步向外传递
void MultiRangeHttpFetcher::ReceivedBytes(HttpFetcher* fetcher,
const void* bytes,
size_t length) {
...
//
// 进一步向外通知download_action, 收到了next_size字节数据
//
if (delegate_) {
delegate_->ReceivedBytes(this, bytes, next_size);
}
...
}
DownloadAction对接收到的数据进行处理
最终,DownloadAction类的ReceivedBytes()函数被通知接收到了数据,并对接收到的数据进行处理:
void DownloadAction::ReceivedBytes(HttpFetcher* fetcher,
const void* bytes,
size_t length) {
...
//
// 进一步通知外层的代理对象(即update_attempter_)新接收到length字节的数据
//
bytes_received_ += length;
if (delegate_ && download_active_) {
// 这里传递给外层BytesReceived函数的参数,全都是size或length相关的数据,没有指针
delegate_->BytesReceived(
length, bytes_received_, install_plan_.payload_size);
}
//
// 重点在这里:调用write_成员的Write操作对接收到的数据进行处理并写入到相应位置
//
if (writer_ && !writer_->Write(bytes, length, &code_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Error " << code_ << " in DeltaPerformer's Write method when "
<< "processing the received payload -- Terminating processing";
...
}
...
}
在上面的ReceivedBytes()中,主要做了两件事情:
- 进一步通知外层的代理对象(这里是
update_attempter_),新收到length字节的数据。注意这里传递的参数全部都是整型数据,并没有传递缓冲区的指针,所以外层不再也不能处理缓冲区的数据。 - 调用write_成员的Write操作对接收到的数据进行处理并写入到相应位置。
PerformAction()中,writer_被初始化为DeltaPerformer的类对象,所以如何处理和写入接收到的数据就要看DeltaPerformer的Write()操作了。
2. 升级文件的数据结构
一般系统升级时,数据下载完成后,首先会对接收到的数据进行完整性检查(例如Hash校验),然后分析数据的头部得到元数据,再根据元数据对数据包进行拆分,将拆分得到的各部分数据分别更新到相应位置。
Update Engine对Android系统的更新也是如此,在数据下载后需要对升级包的数据进行解析。
因此,在进一步对Update Engine获取到的升级数据进行解析前,有必要介绍下升级文件的数据结构。
2.1 升级文件的数据结构
在update_metadata.proto文件的注释中有提到升级文件的数据结构,如下:
// Update file format: A delta update file contains all the deltas needed
// to update a system from one specific version to another specific
// version. The update format is represented by this struct pseudocode:
struct delta_update_file {
char magic[4] = "CrAU";
uint64 file_format_version;
uint64 manifest_size; // Size of protobuf DeltaArchiveManifest
// Only present if format_version > 1:
uint32 metadata_signature_size;
// The Bzip2 compressed DeltaArchiveManifest
char manifest[];
// The signature of the metadata (from the beginning of the payload up to
// this location, not including the signature itself). This is a serialized
// Signatures message.
char medatada_signature_message[metadata_signature_size];
// Data blobs for files, no specific format. The specific offset
// and length of each data blob is recorded in the DeltaArchiveManifest.
struct {
char data[];
} blobs[];
// These two are not signed:
uint64 payload_signatures_message_size;
char payload_signatures_message[];
};
在delta_update_file这个结构体中,主要包含3个部分:元数据,具体的更新数据和升级包的签名。
元数据
升级文件的开始部分是元数据,包括24字节的Header数据,压缩后的DeltaArchiveManifest以及元数据的签名,如下:
//
// 1. 24字节的Header数据,包括:
// magic, 4 bytes
// file_format_version, 8 bytes
// manifest_size, 8 bytes
// metadata_signature_size, 4 bytes (present if format_version > 1)
//
char magic[4] = "CrAU";
uint64 file_format_version;
uint64 manifest_size; // Size of protobuf DeltaArchiveManifest
// Only present if format_version > 1:
uint32 metadata_signature_size;
//
// 2. 压缩后的DeltaArchiveManifest
//
// The Bzip2 compressed DeltaArchiveManifest
char manifest[];
//
// 3. 元数据的签名(不包含自身)
//
// The signature of the metadata (from the beginning of the payload up to
// this location, not including the signature itself). This is a serialized
// Signatures message.
char medatada_signature_message[metadata_signature_size];
这里重点是manifest[]数据,即压缩后的DeltaArchiveManifest。
DeltaArchiveManifest是什么?简单理解为升级包数据的安装说明书,具体如何更新数据,就靠DeltaArchiveManifest的内容了。所以元数据解析的重点就是解析manifest[]部分的数据。
具体的更新数据
系统数据的更新会被划分为多个InstallOperation,每个InstallOperation的具体数据存放在这里的blobs中:
// Data blobs for files, no specific format. The specific offset
// and length of each data blob is recorded in the DeltaArchiveManifest.
struct {
char data[];
} blobs[];
这里的blobs[]只对应于InstallOperation的数据,至于这个数据有多长,如何操作等信息都存放在DeltaArchiveManifest中。因此重点还是DeltaArchiveManifest。
升级包的签名
升级包数据的最后是数据的签名,如下:
// These two are not signed:
uint64 payload_signatures_message_size;
char payload_signatures_message[];
2.2 DeltaArchiveManifest
上一节提到,在升级文件的数据中,最重要的一个就是manifest[]对应的部分,存储了一个压缩的DeltaArchiveManifest。
实际上update_metadata.proto文件定义的7个message就是用于组装一个DeltaArchiveManifest。
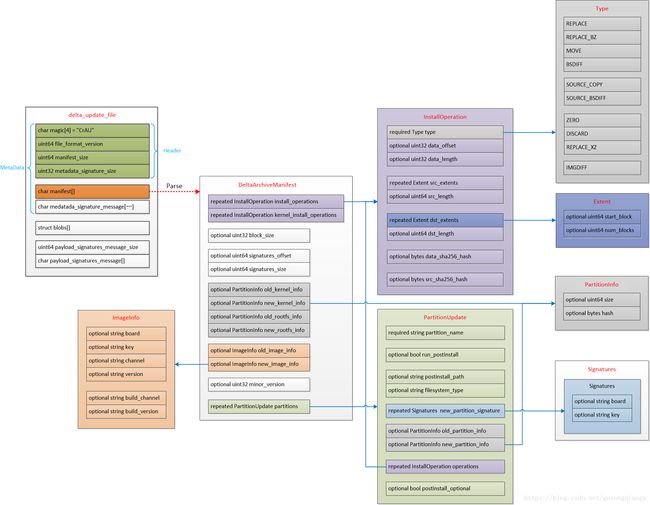
为了直观起见,我花了点时间将delta_update_file结构体和DeltaArchiveManifest以及各个组件画到了一张图上,如下:
这张图很大,点击这里查看原图。
图中外层方框与内层方框之间是包含关系,箭头表示指向具体数据结构的定义。
例如,最左边的delta_update_file外层方框中包含了若干跟内层方框,其中一个内层方框是"char manifest[]",而这个方框指向了另外一个名为"DeltaArchiveManifest"的方框,箭头上标识的是Parse,意思是前者通过解析操作,可以得到DeltaArchiveManifest结构。当然,DeltaArchiveManifest结构又包含很多子结构。
这个图是根据update_metadata.proto文件中使用ProtoBuf协议定义的数据结构绘制的,这里requried指定的成员一定存在;optional指定的成员属于可选项,有可能不存在;而repeated指示的成员我们可以看成是一个数组。
具体的各个结构成员的定义和功能这里不再详细描述,请参考update_metadata.proto文件中相应message结构的定义和注释。
这张图是我自己画的各个数据结构的一个关系框图,为什么要画这张图呢?
因为在数据结构很多的情况下,各结构间的关系会很复杂,结构成员的引用会非常繁琐,靠大脑根本不可能记住,我常常都会因为忘记某个数据结构在整个系统中的位置而迷失其中,尤其是多个数据有相近名称的成员甚至同名成员的时候,简直要崩溃啊。通过画这样一个图,相当于建立了数据结构的关系地图,瞄一眼这个图就一清二楚了。
例如,当我想了解InstallOperation的具体内容时,检查InstallOperation结构定义的方框就知道包含哪些内容了。
同时,我们看到整个系统中,有三个地方采用了InstallOperation结构,分别是DeltaArchiveManifest结构的install_operations和kernel_install_operations成员,以及PartitionUpdate结构的operations成员。
3. DeltaPerformer的Write操作
有了对升级文件数据结构的理解,这里再来看DeltaPerformer的Write()操作就简单多了。
整个Write()操作围绕DeltaArchiveManifest结构及其子结构进行。如果代码分析中忘记了DeltaArchiveManifest结构的细节,那就去看一眼关系图吧,这是我最喜欢读代码的方式之一。
Write()函数负责对所接收到的数据进行解析和写入。总共3个参数,包括两个输入参数和一个输出参数:
- 输入参数包括数据缓冲区地址和缓冲数据的大小
- 输出参数为操作执行的ErrorCode
如果缓冲区的数据写入成功,则Write()返回true;如果缓冲区的数据写入失败,则返回false,输出参数error携带相应的ErrorCode。
由于Write()操作包含数据解析、验证和写入的整个过程,代码篇幅较长,所以接下来对Write()函数分片进行注释,如果没有特别说明当前的代码属于哪个函数,那就默认是Write()函数的代码。
简单来说,Write()函数主要包含了以下几个操作:
- 更新数据接收进度信息;
- 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest数据;
- 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查;
- 从DeltaArchiveManifest中提取分区信息;
- 更新升级的状态信息
- 提取各分区的InstallOperation,并检查payload数据的hash
- 执行InstallOperation的更新操作;
- 提取升级数据的signature;
3.1 更新数据接收进度信息
Write()操作一开始,就先更新数据接收的进度信息:
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
const char* c_bytes = reinterpret_cast(bytes);
//
// 1. 更新数据接收进度信息
// logcat中抓取到的打印信息如下:
// ...
// Completed 0/? operations, 14169/282164983 bytes downloaded (0%), overall progress 0%
// Completed 23/377 operations (6%), 40302425/282164983 bytes downloaded (14%), overall progress 10%
// ...
// Completed 377/377 operations (100%), 282164983/282164983 bytes downloaded (100%), overall progress 100%
// ...
//
// Update the total byte downloaded count and the progress logs.
total_bytes_received_ += count;
UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed ");
使用传入参数count更新已经收到的字节数total_bytes_received_, 然后调用UpdateOverallProgress()计算进度信息,包括数据下载进度,更新操作operations的完成进度等。
代码中,UpdateOverallProgress()函数会调用LogProgress(),将计算的进度信息通过logcat输出,函数比较简单,这里不再展开。
3.2 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest数据
Write()操作在更新完数据接收的进度信息后,开始解析头部数据,主要就是metadata的解析,解析完就得到了DeltaArchiveManifest数据:
// 检查manifest_valid_标志是否有效
// 如果为false,表示没有解析过manifest数据,则此处进行解析
while (!manifest_valid_) {
// Read data up to the needed limit; this is either maximium payload header
// size, or the full metadata size (once it becomes known).
// 检查是否已经解析了Header数据
const bool do_read_header = !IsHeaderParsed();
// 根据是否已经解析Header决定复制的字节数
// 如果连Header都没解析过,那就先复制23字节的Header数据进行接卸
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count,
(do_read_header ? kMaxPayloadHeaderSize :
metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_));
//
// 2. 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest信息;
// 这里的数据分为两部分:
// 1). Header数据: 前24字节
// 2). MetaData数据: 包括前24字节的Header数据,Manifest数据,以及这二者数据的Signature
//
MetadataParseResult result = ParsePayloadMetadata(buffer_, error);
if (result == kMetadataParseError) // 解析错误,则返回
return false;
// 解析MetaData返回数据不够的情况下,继续等待更多数据
if (result == kMetadataParseInsufficientData) {
// If we just processed the header, make an attempt on the manifest.
// 如果刚解析完Header,继续解析MetaData需要复制更多数据
if (do_read_header && IsHeaderParsed())
continue;
return true;
}
...
}
这里主要调用了两个函数,CopyDataToBuffer()和ParsePayloadMetadata()。
CopyDataToBuffer()函数将指定的数据复制到数据缓冲区buffer_上,随后的操作都基于buffer_进行,这里略过。所以整个解析的重点在ParsePayloadMetadata()函数。
ParsePayloadMetadata()函数
升级文件开始的前24字节为Header数据。Header数据同随后的manifest[]数据一起,统称为metadata。注意metadata不包含自身的signature数据metadata_signature。
这里根据delta_update_file文件的数据结构,对metadata进行解析和签名验证。
DeltaPerformer::MetadataParseResult DeltaPerformer::ParsePayloadMetadata(
const brillo::Blob& payload, ErrorCode* error) {
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
uint64_t manifest_offset;
//
// 1. 解析Metadata前面的24字节Header数据
//
// Header数据包括:
// magic[4], 4 bytes
// file_format_version, 8 bytes
// manifest_size, 8 bytes
// metadata_signature_size, 4 bytes (present if format_version > 1)
//
if (!IsHeaderParsed()) {
// 想解析头部的24字节,结果payload中buffer大小还不足,返回InsufficientData信息
// Ensure we have data to cover the major payload version.
if (payload.size() < kDeltaManifestSizeOffset)
return kMetadataParseInsufficientData;
//
// 1.1 检查magic字段
//
// 整个校验就是比较magic字段是否为字符串"CrAU",可是为什么是这么个怪怪的字符串啊?
// Validate the magic string.
if (memcmp(payload.data(), kDeltaMagic /*"CrAU"*/, sizeof(kDeltaMagic)) != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Bad payload format -- invalid delta magic.";
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadInvalidMetadataMagicString;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
//
// 1.2 提取file_format_version字段
//
// 只有 file_format_version > 1 的情况下,metadata_signature_size字段才存在
//
// Extract the payload version from the metadata.
static_assert(sizeof(major_payload_version_) == kDeltaVersionSize,
"Major payload version size mismatch");
memcpy(&major_payload_version_,
&payload[kDeltaVersionOffset],
kDeltaVersionSize);
// switch big endian to host
major_payload_version_ = be64toh(major_payload_version_);
// 检查 major_payload_version_
// 代码中各个版本变量的定义:
// supported_major_version_ = 2
// kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion = 1
// kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion = 2
//
if (major_payload_version_ != supported_major_version_ &&
major_payload_version_ != kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Bad payload format -- unsupported payload version: "
<< major_payload_version_;
*error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
//
// 1.3 提取manifest_size字段
//
// 由于manifest[]数据位于metadata_signature_size字段之后,后者依赖于file_format_version版本,
// 所以这里先计算manifest[]数据的偏移 manifest_offset
//
// Get the manifest offset now that we have payload version.
if (!GetManifestOffset(&manifest_offset)) {
*error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
// Check again with the manifest offset.
if (payload.size() < manifest_offset)
return kMetadataParseInsufficientData;
//
// 提取 manifest_size, 存放到manifest_size_
//
// Next, parse the manifest size.
static_assert(sizeof(manifest_size_) == kDeltaManifestSizeSize,
"manifest_size size mismatch");
memcpy(&manifest_size_,
&payload[kDeltaManifestSizeOffset],
kDeltaManifestSizeSize);
manifest_size_ = be64toh(manifest_size_); // switch big endian to host
//
// 1.4 提取metadata_signature_size字段
//
if (GetMajorVersion() == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) {
// Parse the metadata signature size.
static_assert(sizeof(metadata_signature_size_) ==
kDeltaMetadataSignatureSizeSize,
"metadata_signature_size size mismatch");
uint64_t metadata_signature_size_offset;
// 获取 metadata_signature_size 字段的 offset
if (!GetMetadataSignatureSizeOffset(&metadata_signature_size_offset)) {
*error = ErrorCode::kError;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
memcpy(&metadata_signature_size_,
&payload[metadata_signature_size_offset],
kDeltaMetadataSignatureSizeSize);
metadata_signature_size_ = be32toh(metadata_signature_size_);
}
//
// 1.5 计算并检查metadata size
//
// 计算metadata_size, 检查 install_plan中的metadata_size同解析Header数据得到的值是否一致
// 实际上metadata由24字节的Header数据和随后压缩的manifest数据组成, 即:
// metadata = magic[4] + file_format_version + manifest_size + metadata_signature_size + manifest[]
//
// If the metadata size is present in install plan, check for it immediately
// even before waiting for that many number of bytes to be downloaded in the
// payload. This will prevent any attack which relies on us downloading data
// beyond the expected metadata size.
metadata_size_ = manifest_offset + manifest_size_;
// 只有当当前为Official Build的时候,hash_checks_mandatory才为真
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
// 升级数据相应的payload_properties.txt文件包含METADATA_SIZE数据,在升级时作为参数,最终传递给install_plan_
// 将其同这里解析得到的metadata_size_比较
if (install_plan_->metadata_size != metadata_size_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory metadata size in Omaha response ("
<< install_plan_->metadata_size
<< ") is missing/incorrect, actual = " << metadata_size_;
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadInvalidMetadataSize;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
}
}
//
// 验证过metadata size以后,确认是否已经接收到完整的metadata和metadata signature数据
// 如果没有,则需要等待收集齐数据后才能进一步操作;
// Now that we have validated the metadata size, we should wait for the full
// metadata and its signature (if exist) to be read in before we can parse it.
if (payload.size() < metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_)
return kMetadataParseInsufficientData;
// 再次检查metadata size
// 检查install_plan中的metadata_size数据和解析得到的metadata_size数据是否一致
//
// Log whether we validated the size or simply trusting what's in the payload
// here. This is logged here (after we received the full metadata data) so
// that we just log once (instead of logging n times) if it takes n
// DeltaPerformer::Write calls to download the full manifest.
if (install_plan_->metadata_size == metadata_size_) {
LOG(INFO) << "Manifest size in payload matches expected value from Omaha";
} else {
// For mandatory-cases, we'd have already returned a kMetadataParseError
// above. We'll be here only for non-mandatory cases. Just send a UMA stat.
LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring missing/incorrect metadata size ("
<< install_plan_->metadata_size
<< ") in Omaha response as validation is not mandatory. "
<< "Trusting metadata size in payload = " << metadata_size_;
}
//
// 2. 校验metadata数据的签名
//
// 前面的步骤已经确认当前已经收到了完整的metadata以及metadata signature
// 所以这里检查metdata的签名
//
// We have the full metadata in |payload|. Verify its integrity
// and authenticity based on the information we have in Omaha response.
*error = ValidateMetadataSignature(payload);
// 签名校验失败
if (*error != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
// 如果需要强制检查签名,则这里退出
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
// The autoupdate_CatchBadSignatures test checks for this string
// in log-files. Keep in sync.
LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory metadata signature validation failed";
return kMetadataParseError;
}
// 不需要强制检查签名的情况下,签名检查失败只显示提示信息
// For non-mandatory cases, just send a UMA stat.
LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring metadata signature validation failures";
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
//
// 3. 解析manifest[]数据,存放到manifest_成员中
//
// 先获取manifest[]数据的offset
if (!GetManifestOffset(&manifest_offset)) {
*error = ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMajorPayloadVersion;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
// 解析manifest数据并保存到manifest_中
// The payload metadata is deemed valid, it's safe to parse the protobuf.
if (!manifest_.ParseFromArray(&payload[manifest_offset], manifest_size_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to parse manifest in update file.";
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadManifestParseError;
return kMetadataParseError;
}
// 设置manifest_parsed_标识为true,这样在调用GetManifest()时直接使用已经解析好的manifest数据
manifest_parsed_ = true;
return kMetadataParseSuccess;
}
总结一下,ParsePayloadMetadata()的操作按顺序包括:
- 解析Metadata前面的24字节Header数据
- 1.1 检查magic字段
- 1.2 提取file_format_version字段
- 1.3 提取manifest_size字段
- 1.4 提取metadata_signature_size字段
- 1.5 计算并检查metadata size
- 校验metadata数据的签名
- 解析manifest[]数据,存放到manifest_成员中
因此,解析完metadata,我们就从数据包中复原了DeltaArchiveManifest结构,并存放在manifest_中。
在第2步时,会调用ValidateMetadataSignature()函数检查metadata的签名,不妨来看看这个签名的检查是如何工作的。
ValidateMetadataSignature()函数
ErrorCode DeltaPerformer::ValidateMetadataSignature(
const brillo::Blob& payload) {
//
// 1. 检查用于签名的数据长度是否满足要求
//
// metadata签名校验包括metadata数据本身和metadata signature
// 这里再次检查用于校验的数据长度上是否包含metadata和signature
if (payload.size() < metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_)
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError;
//
// 2. 从install_plan或待验证数据中提取metadata signature
//
brillo::Blob metadata_signature_blob, metadata_signature_protobuf_blob;
//
// 如果install_plan_中包含metadata_signature,那这个数据需要先经过Base64解码;
// 如果install_plan_不包含metadata_signature, 则从验证的数据中提取签名数据;
//
// 默认情况下install_plan_不包含metadata_signature,所以这里会从待验证的数据中提取签名
if (!install_plan_->metadata_signature.empty()) {
// 对install_plan_包含的metadata_signature进行Base64解码
// Convert base64-encoded signature to raw bytes.
if (!brillo::data_encoding::Base64Decode(
install_plan_->metadata_signature, &metadata_signature_blob)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to decode base64 metadata signature: "
<< install_plan_->metadata_signature;
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError;
}
} else if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) {
// 从待验证的数据中提取签名
metadata_signature_protobuf_blob.assign(payload.begin() + metadata_size_,
payload.begin() + metadata_size_ +
metadata_signature_size_);
}
// 如果install_plan_的metadata_signature或待解析数据中没有metadata_signature_protobuf
// 没有签名数据,验证自然就无法往下走了,报错吧
if (metadata_signature_blob.empty() &&
metadata_signature_protobuf_blob.empty()) {
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Missing mandatory metadata signature in both Omaha "
<< "response and payload.";
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMissingError;
}
LOG(WARNING) << "Cannot validate metadata as the signature is empty";
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
//
// 3. 生成用于签名验证的的公钥
//
// 先指定用于验证的key:
// 默认使用path_to_public_key,同时检查检查升级参数中有没有指定验证的key,如果有,则用指定的key。
//
// path_to_public_key使用public_key_path_指定的文件初始化。
// public_key_path_在delta_performer.h中定义时被设置为:kUpdatePayloadPublicKeyPath
// kUpdatePayloadPublicKeyPath在platform_constants_android.c中的定义为:"/etc/update_engine/update-payload-key.pub.pem"
//
// See if we should use the public RSA key in the Omaha response.
base::FilePath path_to_public_key(public_key_path_);
base::FilePath tmp_key;
// 调用GetPublicKeyFromResponse()检查升级参数中指定的key
if (GetPublicKeyFromResponse(&tmp_key))
path_to_public_key = tmp_key;
ScopedPathUnlinker tmp_key_remover(tmp_key.value());
// 如果升级参数中没有指定key,则销毁tmp_key_remover
if (tmp_key.empty())
tmp_key_remover.set_should_remove(false);
LOG(INFO) << "Verifying metadata hash signature using public key: "
<< path_to_public_key.value();
//
// 4. 计算metadata的hash
//
// 根据metadata计算hash
HashCalculator metadata_hasher;
metadata_hasher.Update(payload.data(), metadata_size_);
if (!metadata_hasher.Finalize()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to compute actual hash of manifest";
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureVerificationError;
}
// 对metadata的hash进行填充
brillo::Blob calculated_metadata_hash = metadata_hasher.raw_hash();
PayloadVerifier::PadRSA2048SHA256Hash(&calculated_metadata_hash);
if (calculated_metadata_hash.empty()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Computed actual hash of metadata is empty.";
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureVerificationError;
}
//
// 5. 使用第2步提取的signature验证第4步生成的hash
//
// 如果从install_plan_中解析的metadata signature不为空
// 说明可以从metadata signature提取hash
if (!metadata_signature_blob.empty()) {
brillo::Blob expected_metadata_hash;
// 从签名数据提取raw hash数据
if (!PayloadVerifier::GetRawHashFromSignature(metadata_signature_blob,
path_to_public_key.value(),
&expected_metadata_hash)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to compute expected hash from metadata signature";
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureError;
}
// 比较通过数据计算的hash和通过签名得到的hash
// 比较失败则退出
if (calculated_metadata_hash != expected_metadata_hash) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest hash verification failed. Expected hash = ";
utils::HexDumpVector(expected_metadata_hash);
LOG(ERROR) << "Calculated hash = ";
utils::HexDumpVector(calculated_metadata_hash);
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMismatch;
}
} else { // install_plan_中没有metadata signature,那就只能从待验证数据提取metadata_signature进行验证
// 检查通过计算得到的hash,和待验证数据中signature对应的hash是否一致
// 验证失败则退出
if (!PayloadVerifier::VerifySignature(metadata_signature_protobuf_blob,
path_to_public_key.value(),
calculated_metadata_hash)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest hash verification failed.";
return ErrorCode::kDownloadMetadataSignatureMismatch;
}
}
// 成功检查hash会从这里返回,否则在这之前就已经退出了
// The autoupdate_CatchBadSignatures test checks for this string in
// log-files. Keep in sync.
LOG(INFO) << "Metadata hash signature matches value in Omaha response.";
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
总结一下metadata的签名验证操作:
- 检查用于签名的数据长度是否满足要求
- 从
install_plan或待验证数据中提取metadata signature - 生成用于签名验证的的公钥
- 计算metadata的hash
- 使用第2步提取的signature验证第4步生成的hash
补充一下,这里第2步提取metadata signature的来源有两个,install_plan或待验证数据。如果install_plan中包含metadata signature,那就优先使用install_plan中的signature进行验证。其次才使用待验证数据中包含的signature。
但是,在UpdateAttempterAndroid类的ApplyPayload()中,install_plan的metadata_signature被初始化为空,所以最终是使用待验证数据本身包含的签名进行校验的。
关于私钥签名和公钥验证:
如何使用私钥对数据进行签名?
步骤如下:
- 计算原始数据的SHA256哈希;
- 对SHA256哈希的结果进行BER编码;
- 将BER编码后的哈希填充为256字节数据;
- 对填充后的数据使用私钥进行加密,加密的输出结果就是256字节的签名;
如何使用公钥如何对签名进行验证?
步骤如下:
- 使用公钥解密256字节的签名数据,得到的是哈希经过BER编码并填充为256字节的数据;
- 去掉填充数据,得到经过BER编码的哈希;
- 从BER编码数据中提取哈希;
- 计算原始数据的哈希;
- 比较第3步中提取的和第4步中计算得到的哈希;
关于如何使用RSA Key进行数据签名和校验的细节,请参考我的另外一篇文章:《OpenSSL和Python实现RSA Key数字签名和验证》
3.3 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查
Write()中,完成对metadata的解析后,其包含的数据存放到DeltaArchiveManifest的结构中,所以接下来就是对解析的结果进行检查。
其实所谓的检查,也就是看看DeltaArchiveManifest结构中指定当前是全量升级还是增量升级。
//
// 3. 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查
//
// 验证DeltaArchiveManifest的结构,确定升级类型是Full还是Delta
// 如:
// Detected a 'full' payload.
//
// Checks the integrity of the payload manifest.
if ((*error = ValidateManifest()) != ErrorCode::kSuccess)
return false;
// 设置Manifest为有效
manifest_valid_ = true;
// 已经完成了MetaData的解析,所以可以抛弃已经解析的数据
// Clear the download buffer.
DiscardBuffer(false, metadata_size_);
这里检查DeltaArchiveManifest结构的操作由ValidateManifest()函数来完成:
ErrorCode DeltaPerformer::ValidateManifest() {
// Perform assorted checks to sanity check the manifest, make sure it
// matches data from other sources, and that it is a supported version.
// 检查是否包含用于对比的 old 分区信息,因为增量升级需要new和old分区进行对比
// 1). 检查manifest数据是否存在 old_kernel_info 和 old_rootfs_info
// 2). 检查manifest的分区更新信息中是否包含 old_partition_info
bool has_old_fields =
(manifest_.has_old_kernel_info() || manifest_.has_old_rootfs_info());
for (const PartitionUpdate& partition : manifest_.partitions()) {
has_old_fields = has_old_fields || partition.has_old_partition_info();
}
// 根据manifest数据中是否包含对比的 old 分区信息来确定升级类型
// 1. 不包含old分区信息,则全量升级(Full);
// 2. 包含old分区信息,则增量升级(Delta)
// The presence of an old partition hash is the sole indicator for a delta
// update.
InstallPayloadType actual_payload_type =
has_old_fields ? InstallPayloadType::kDelta : InstallPayloadType::kFull;
// logcat日志显示升级类型信息, 如:Detected a 'full' payload.
if (install_plan_->payload_type == InstallPayloadType::kUnknown) {
LOG(INFO) << "Detected a '"
<< InstallPayloadTypeToString(actual_payload_type)
<< "' payload.";
install_plan_->payload_type = actual_payload_type;
// 检查install_plan中指示的升级类型和解析升级包得到的升级类型是否匹配
} else if (install_plan_->payload_type != actual_payload_type) {
LOG(ERROR) << "InstallPlan expected a '"
<< InstallPayloadTypeToString(install_plan_->payload_type)
<< "' payload but the downloaded manifest contains a '"
<< InstallPayloadTypeToString(actual_payload_type)
<< "' payload.";
return ErrorCode::kPayloadMismatchedType;
}
// 检查升级版本的兼容性
// 即制作数据包时指定的minor version和代码运行时需要的minor version是否匹配
// Check that the minor version is compatible.
if (actual_payload_type == InstallPayloadType::kFull) {
if (manifest_.minor_version() != kFullPayloadMinorVersion) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains minor version "
<< manifest_.minor_version()
<< ", but all full payloads should have version "
<< kFullPayloadMinorVersion << ".";
return ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMinorPayloadVersion;
}
} else {
if (manifest_.minor_version() != supported_minor_version_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains minor version "
<< manifest_.minor_version()
<< " not the supported "
<< supported_minor_version_;
return ErrorCode::kUnsupportedMinorPayloadVersion;
}
}
if (major_payload_version_ != kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
if (manifest_.has_old_rootfs_info() ||
manifest_.has_new_rootfs_info() ||
manifest_.has_old_kernel_info() ||
manifest_.has_new_kernel_info() ||
manifest_.install_operations_size() != 0 ||
manifest_.kernel_install_operations_size() != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Manifest contains deprecated field only supported in "
<< "major payload version 1, but the payload major version is "
<< major_payload_version_;
return ErrorCode::kPayloadMismatchedType;
}
}
// TODO(garnold) we should be adding more and more manifest checks, such as
// partition boundaries etc (see chromium-os:37661).
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
好吧,看完实现代码,发现这个函数主要做了一件事,即通过检查manifest中是否有old分区的信息来确定当前的升级类型:
- 如果有old分区的信息,属于增量升级(Delta)
- 如果没有old分区的信息,属于全量升级(Full)
3.4 从DeltaArchiveManifest中提取分区信息
Write()操作检查完DeltaArchiveManifest结构确定是全量升级还是增量升级后,继续提取升级分区的信息:
// 提取Manifest中的partitions信息,
// This populates |partitions_| and the |install_plan.partitions| with the
// list of partitions from the manifest.
if (!ParseManifestPartitions(error))
return false;
// partitions_的每个分区都包含一个operations数组,里面存放的是InstallOperation数据
// 所有分区的operations数组大小累加到num_total_operations_
// 所以最后num_total_operations_是所有InstallOperation的总数
//
// 这里的acc_num_operations_计算比较特别:
// 如果有三个分区,第1个分区的operations大小为10,第2个分区为15,第3个分区为8
// 则acc_num_operations_应该为{10, 25, 33},
// 这里25=10+15, 33=10+15+8,即后面的数据是前面数据的累加结果
num_total_operations_ = 0;
for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
num_total_operations_ += partition.operations_size();
acc_num_operations_.push_back(num_total_operations_);
}
这里通过ParseManifestPartitions()操作提取分区信息,然后计算所有分区的InstallOperation数量。
函数ParseManifestPartitions()干了些什么呢?
bool DeltaPerformer::ParseManifestPartitions(ErrorCode* error) {
// 我手上基于r7.1.1版本制作的payload.bin中解析得到的major_payload_version_为2:
// $ hexdump -Cv -s 0x04 -n 8 payload.bin
// 00000004 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 02 |........|
// 0000000c
//
// 由于kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion为0,所以这里的条件成立
if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion) {
// 清空原有分区信息
partitions_.clear();
// 将manifest_中的PartitionUpdate数据依次存放到partitions_成员中去
for (const PartitionUpdate& partition : manifest_.partitions()) {
partitions_.push_back(partition);
}
// 我去,提取了分区信息后,竟然把原有的信息clear了,为什么要clear啊?不懂。
manifest_.clear_partitions();
// 由于if条件已经成立,else if这一大段代码跳过
// 这里的分区提取信息比if条件下的复杂一些,但是不用去看了,哈哈,开心
} else if (major_payload_version_ == kChromeOSMajorPayloadVersion) {
LOG(INFO) << "Converting update information from old format.";
PartitionUpdate root_part;
root_part.set_partition_name(kLegacyPartitionNameRoot);
#ifdef __ANDROID__
LOG(WARNING) << "Legacy payload major version provided to an Android "
"build. Assuming no post-install. Please use major version "
"2 or newer.";
root_part.set_run_postinstall(false);
#else
root_part.set_run_postinstall(true);
#endif // __ANDROID__
if (manifest_.has_old_rootfs_info()) {
*root_part.mutable_old_partition_info() = manifest_.old_rootfs_info();
manifest_.clear_old_rootfs_info();
}
if (manifest_.has_new_rootfs_info()) {
*root_part.mutable_new_partition_info() = manifest_.new_rootfs_info();
manifest_.clear_new_rootfs_info();
}
*root_part.mutable_operations() = manifest_.install_operations();
manifest_.clear_install_operations();
partitions_.push_back(std::move(root_part));
PartitionUpdate kern_part;
kern_part.set_partition_name(kLegacyPartitionNameKernel);
kern_part.set_run_postinstall(false);
if (manifest_.has_old_kernel_info()) {
*kern_part.mutable_old_partition_info() = manifest_.old_kernel_info();
manifest_.clear_old_kernel_info();
}
if (manifest_.has_new_kernel_info()) {
*kern_part.mutable_new_partition_info() = manifest_.new_kernel_info();
manifest_.clear_new_kernel_info();
}
*kern_part.mutable_operations() = manifest_.kernel_install_operations();
manifest_.clear_kernel_install_operations();
partitions_.push_back(std::move(kern_part));
}
// 如果install_plan_的partitions有数据的话,那就验证partitions数据对应分区的source分区Hash
// 从英文注释看,这段代码后面可能会被拿掉。
// TODO(deymo): Remove this block of code once we switched to optional
// source partition verification. This list of partitions in the InstallPlan
// is initialized with the expected hashes in the payload major version 1,
// so we need to check those now if already set. See b/23182225.
if (!install_plan_->partitions.empty()) {
if (!VerifySourcePartitions()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadStateInitializationError;
return false;
}
}
// partitions_中的信息来自manifest_, 而后者通过解析升级包数据得到
// 逐个提取partitions_成员中的数据,用于构建install_plan_中的分区数据
// Fill in the InstallPlan::partitions based on the partitions from the
// payload.
install_plan_->partitions.clear();
for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
// 新建的install_part变量用于提取partitons_成员的分区信息
InstallPlan::Partition install_part;
// 提取partition_name信息
install_part.name = partition.partition_name();
// 提取run_postinstall信息
install_part.run_postinstall =
partition.has_run_postinstall() && partition.run_postinstall();
if (install_part.run_postinstall) {
// 在有run_postinstall信息存在的情况下,提取postinstall_path信息
install_part.postinstall_path =
(partition.has_postinstall_path() ? partition.postinstall_path()
: kPostinstallDefaultScript);
// 提取filesystem_type信息
install_part.filesystem_type = partition.filesystem_type();
// 提取postinstall_optional信息
install_part.postinstall_optional = partition.postinstall_optional();
}
// 所谓的old分区,在升级时对应于source分区
// 所谓的new分区,在升级时对应于target分区
// 提取old_partition_info信息,实际上就是提取了size和hash信息
if (partition.has_old_partition_info()) {
const PartitionInfo& info = partition.old_partition_info();
install_part.source_size = info.size();
install_part.source_hash.assign(info.hash().begin(), info.hash().end());
}
// 升级数据包必须有new_partition_info才行,不然那就那就真是扯淡了
// 为什么?没有为什么,升级后就是新分区,需要用这个数据检查升级后的hash和size啊
if (!partition.has_new_partition_info()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to get new partition hash info on partition "
<< install_part.name << ".";
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadNewPartitionInfoError;
return false;
}
// 提取new_partition_info信息,实际上也就是提取了size和hash信息
const PartitionInfo& info = partition.new_partition_info();
install_part.target_size = info.size();
install_part.target_hash.assign(info.hash().begin(), info.hash().end());
// 将构建的分区信息install_part添加到install_plan_的分区数组中
install_plan_->partitions.push_back(install_part);
}
// 根据partition的name,提取source和target对应的source_path和target_path
if (!install_plan_->LoadPartitionsFromSlots(boot_control_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to determine all the partition devices.";
*error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
return false;
}
LogPartitionInfo(partitions_);
return true;
}
整个ParseManifestPartitions()看起来很复杂,因为分区涉及的信息真实太多了。而解析的时候,需要逐个复制分区信息,所以代码很长,但功能很简单。
一句话,ParseManifestPartitions()就是将解析得到的DeltaArchiveManifest结构中的分区信息转移到install_plan_中。
那为什么要转移呢?
因为install_plan_是在整个更新的ActionPipe中传输的,这里更新了install_plan_中的分区信息,接下来的其它Action就可以直接使用了。例如,在FilesystemVerifyAction中,如果需要校验整个分区的hash,那只需要计算分区的hash后同install_plan_中保存的hash数据比较一下就可以了。
在整个ParseManifestPartitions()中,有个VerifySourcePartitions()调用需要特别说明下:
// TODO(deymo): Remove this block of code once we switched to optional
// source partition verification. This list of partitions in the InstallPlan
// is initialized with the expected hashes in the payload major version 1,
// so we need to check those now if already set. See b/23182225.
if (!install_plan_->partitions.empty()) {
if (!VerifySourcePartitions()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadStateInitializationError;
return false;
}
}
为什么呢?因为有很多人升级的过程中,在这一步挂掉了,好几个兄弟在微信上问过我,又例如下这两篇:
- 《Android A/B System OTA 升级以及报错处理》
- 《Android OTA差分包升级失败》
从上面这段代码看,如果install_plan_中包含了分区信息,那就调用VerifySourcePartitions()操作,操作中具体做了什么呢?看看代码怎么说的吧。
VerifySourcePartitions()函数
bool DeltaPerformer::VerifySourcePartitions() {
LOG(INFO) << "Verifying source partitions.";
CHECK(manifest_valid_);
CHECK(install_plan_);
//
// 检查分区数
//
// 比较install_plan_->partitions和partitions_中的分区数
if (install_plan_->partitions.size() != partitions_.size()) {
DLOG(ERROR) << "The list of partitions in the InstallPlan doesn't match the "
"list received in the payload. The InstallPlan has "
<< install_plan_->partitions.size()
<< " partitions while the payload has " << partitions_.size()
<< " partitions.";
return false;
}
//
// 先检查分区名,然后检查相同分区名的hash是否一致
//
for (size_t i = 0; i < partitions_.size(); ++i) {
// 逐个将install_plan_中分区的name同提取到的partitions_成员中分区的name进行比较
if (partitions_[i].partition_name() != install_plan_->partitions[i].name) {
DLOG(ERROR) << "The InstallPlan's partition " << i << " is \""
<< install_plan_->partitions[i].name
<< "\" but the payload expects it to be \""
<< partitions_[i].partition_name()
<< "\". This is an error in the DeltaPerformer setup.";
return false;
}
// 如果partitions_中没有用于对比的old分区的信息,那继续比较下一个分区
// 因为有old信息,说明该分区是增量升级(Delta)方式
if (!partitions_[i].has_old_partition_info())
continue;
// 有old信息才会到这里,先提取用于old信息
const PartitionInfo& info = partitions_[i].old_partition_info();
// 取得install_plan_中相应分区的指针
const InstallPlan::Partition& plan_part = install_plan_->partitions[i];
bool valid =
!plan_part.source_hash.empty() && // plan_part中存在source_hash信息
plan_part.source_hash.size() == info.hash().size() && // plan_part中source_hash信息的长度同待检查的hash信息长度进行比较
memcmp(plan_part.source_hash.data(), // 逐字比较二者的hash数据是否一致
info.hash().data(),
plan_part.source_hash.size()) == 0;
// 升级包中旧分区的hash同install_plan_中分区的hash不一致,提示错误信息
if (!valid) {
LogVerifyError(partitions_[i].partition_name(),
plan_part.source_path,
info.hash().size(),
StringForHashBytes(plan_part.source_hash.data(),
plan_part.source_hash.size()),
StringForHashBytes(info.hash().data(),
info.hash().size()));
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
这个函数就是检查增量升级时,升级数据中携带old_partition_info()的分区hash应该和install_plan_中对应分区的hash一致。
理论上,如果做增量升级的话,增量升级的基线版本应该是当前正在运行的版本。举个例子,对于增量升级,如果需要在system分区的block A上进行某个增量操作,应该是基于当前分区的block A 进行操作。先把当前分区的block A写到目标分区,然后再打上增量补丁就是期望的结果了。
所以如果下载得到的增量升级包指定的基线版本同实际的基线版本不一致的话,那这里的hash就会出错。
但是我有一个疑问,就是没有找到
install_plan_里用于比较的partitions信息是在哪里准备的。这个问题待解决。
3.5 更新升级的状态信息
在前面的操作中,提取了manifest信息,并将manifest中的分区信息搬到到install_plan_中,眼看着就要开始正式升级了。
别急,如果这次升级是一次断点升级,即这次恢复上次暂停的升级继续操作,那会怎样?当然是要获取上次升级的状态信息了:
// 保存 metadata_size和metadata_signature_size数据到磁盘
// 保存这些数据是因为如果升级暂停(pause)了,下次恢复(resume)时传输的数据和可能就不再包含metadata了
LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestMetadataSize,
metadata_size_))
<< "Unable to save the manifest metadata size.";
LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestSignatureSize,
metadata_signature_size_))
<< "Unable to save the manifest signature size.";
// 如果之前暂停(pause),现在恢复(resume)继续升级,获取暂停时保存的状态数据
// 上一次升级的信息可能已经丢失(例如暂停后系统重启过),所以需要通过prefs_机制重新从磁盘获取这些信息
// 如果没有取得上一次的升级信息,说明当前是全新升级
if (!PrimeUpdateState()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadStateInitializationError;
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to prime the update state.";
return false;
}
// 打开第1个分区
if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
return false;
}
// 如果开始操作的不是InstallOperation索引大于0,说明这次是恢复(resume)升级操作
if (next_operation_num_ > 0)
UpdateOverallProgress(true, "Resuming after ");
LOG(INFO) << "Starting to apply update payload operations";
PrimeUpdateState()从磁盘获取之前保存的升级状态信息:
bool DeltaPerformer::PrimeUpdateState() {
CHECK(manifest_valid_);
block_size_ = manifest_.block_size();
//
// 1. 取得即将执行的InstallOperation
//
// 读取上次升级即将执行的InstallOperation
int64_t next_operation = kUpdateStateOperationInvalid;
if (!prefs_->GetInt64(kPrefsUpdateStateNextOperation, &next_operation) ||
next_operation == kUpdateStateOperationInvalid ||
next_operation <= 0) {
// Initiating a new update, no more state needs to be initialized.
return true;
}
// 将上次升级即将执行的操作作为此次升级的第一个操作
// 例如上次升级执行了5步,即将执行第6步,那这次升级需要从第6步起开始执行
next_operation_num_ = next_operation;
//
// 2. 取得下一步操作的data offset
//
// 读取上次升级时下一步操作的data offset
// Resuming an update -- load the rest of the update state.
int64_t next_data_offset = -1;
TEST_AND_RETURN_FALSE(prefs_->GetInt64(kPrefsUpdateStateNextDataOffset,
&next_data_offset) &&
next_data_offset >= 0);
// 恢复操作需要的data offset
buffer_offset_ = next_data_offset;
//
// 3. 取得InstallOperation对应数据的hash上下文
//
// The signed hash context and the signature blob may be empty if the
// interrupted update didn't reach the signature.
string signed_hash_context;
if (prefs_->GetString(kPrefsUpdateStateSignedSHA256Context,
&signed_hash_context)) {
TEST_AND_RETURN_FALSE(
signed_hash_calculator_.SetContext(signed_hash_context));
}
string signature_blob;
if (prefs_->GetString(kPrefsUpdateStateSignatureBlob, &signature_blob)) {
signatures_message_data_.assign(signature_blob.begin(),
signature_blob.end());
}
string hash_context;
TEST_AND_RETURN_FALSE(prefs_->GetString(kPrefsUpdateStateSHA256Context,
&hash_context) &&
payload_hash_calculator_.SetContext(hash_context));
int64_t manifest_metadata_size = 0;
TEST_AND_RETURN_FALSE(prefs_->GetInt64(kPrefsManifestMetadataSize,
&manifest_metadata_size) &&
manifest_metadata_size > 0);
metadata_size_ = manifest_metadata_size;
int64_t manifest_signature_size = 0;
TEST_AND_RETURN_FALSE(
prefs_->GetInt64(kPrefsManifestSignatureSize, &manifest_signature_size) &&
manifest_signature_size >= 0);
metadata_signature_size_ = manifest_signature_size;
// Advance the download progress to reflect what doesn't need to be
// re-downloaded.
total_bytes_received_ += buffer_offset_;
// Speculatively count the resume as a failure.
int64_t resumed_update_failures;
if (prefs_->GetInt64(kPrefsResumedUpdateFailures, &resumed_update_failures)) {
resumed_update_failures++;
} else {
resumed_update_failures = 1;
}
prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsResumedUpdateFailures, resumed_update_failures);
return true;
}
这个代码较长,总之,就是恢复上次中断保存的状态。如果这次是全新升级,那函数最开始就无法获取next operation而返回。
3.6 提取各分区的InstallOperation,并检查payload数据的hash
Write()中经过前面的操作,升级的分区信息准备好了,升级状态也恢复好了,接下来就是要提取每个分区的InstallOperation开始升级操作了:
// num_total_operations_用于指示manifest中所有InstallOperation的总数
// 因此通过(next_operation_num_ < num_total_operations_)比较来确定是否执行完了所有的InstallOperation
while (next_operation_num_ < num_total_operations_) {
// Check if we should cancel the current attempt for any reason.
// In this case, *error will have already been populated with the reason
// why we're canceling.
if (download_delegate_ && download_delegate_->ShouldCancel(error))
return false;
//
// 1. 打开下一个要操作的分区
//
// 前面已经打开了第一个操作的分区,这里根据下一个要操作的InstallOperation的索引值next_operation_num_,确定需要打开哪一个分区
// 例如,前面的例子,更新包需要更新有三个分区,第1个分区的operations大小为10,第2个分区为15,第3个分区为8,因此acc_num_operations_数组为{10,25,8}
// 下一个要执行的InstallOperation的索引值next_operation_num_的值为17,那刚好位于第2个分区中,所以此时需要关闭第1个分区,打开第2个分区。
// 所以这里通过next_operation_num_的比较,确保要操作的分区已经打开
// We know there are more operations to perform because we didn't reach the
// |num_total_operations_| limit yet.
while (next_operation_num_ >= acc_num_operations_[current_partition_]) {
CloseCurrentPartition();
current_partition_++;
if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
return false;
}
}
//
// 2. 提取分区中下一个要操作的InstallOperation
//
// 通过nexus_operation_num_和acc_num_operations_数组,来查找下一个InstallOperation在某个partition更新的Operation的所以值
// 简单说来,将下一个InstallOperation操作在全部操作中的索引值转化为相应分区内的索引值。
const size_t partition_operation_num = next_operation_num_ - (
current_partition_ ? acc_num_operations_[current_partition_ - 1] : 0);
// 根据分区内InstallOperation的索引值partition_operation_num, 来从当前操作的分区中提取InstallOperation
const InstallOperation& op =
partitions_[current_partition_].operations(partition_operation_num);
//
// 3. 根据InstallOperation指示的长度将操作数据存放到缓冲区中
//
// 当前要操作的InstallOperation的数据从接收数据的缓冲区复制到DeltaPerformer内部操作的缓冲区buffer_中去
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, op.data_length());
// 检查确保已经接收到当前要操作的InstallOperationd的数据
// Check whether we received all of the next operation's data payload.
if (!CanPerformInstallOperation(op))
return true;
//
// 4. 检查InstallOperation对应操作数据的hash
//
// 在metadata signature存在的情况下,校验InstallOperation对应数据的hash
// Validate the operation only if the metadata signature is present.
// Otherwise, keep the old behavior. This serves as a knob to disable
// the validation logic in case we find some regression after rollout.
// NOTE: If hash checks are mandatory and if metadata_signature is empty,
// we would have already failed in ParsePayloadMetadata method and thus not
// even be here. So no need to handle that case again here.
if (!install_plan_->metadata_signature.empty()) {
// Note: Validate must be called only if CanPerformInstallOperation is
// called. Otherwise, we might be failing operations before even if there
// isn't sufficient data to compute the proper hash.
// 计算当前InstallOperation数据的hash,并将其同预先计算的hash进行比较
*error = ValidateOperationHash(op);
if (*error != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory operation hash check failed";
return false;
}
// For non-mandatory cases, just send a UMA stat.
LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring operation validation errors";
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
}
ValidateOperationHash()操作校验单个InstallOperation对应数据blob的Hash值。
ErrorCode DeltaPerformer::ValidateOperationHash(
const InstallOperation& operation) {
// InstallOperation没有Hash数据的情况
// 注释里面提到,在HTTP/HTTPS下可能存在没有data blob的operation, 这样的operation也就没有hash
if (!operation.data_sha256_hash().size()) {
if (!operation.data_length()) {
// Operations that do not have any data blob won't have any operation hash
// either. So, these operations are always considered validated since the
// metadata that contains all the non-data-blob portions of the operation
// has already been validated. This is true for both HTTP and HTTPS cases.
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
// No hash is present for an operation that has data blobs. This shouldn't
// happen normally for any client that has this code, because the
// corresponding update should have been produced with the operation
// hashes. So if it happens it means either we've turned operation hash
// generation off in DeltaDiffGenerator or it's a regression of some sort.
// One caveat though: The last operation is a dummy signature operation
// that doesn't have a hash at the time the manifest is created. So we
// should not complaint about that operation. This operation can be
// recognized by the fact that it's offset is mentioned in the manifest.
if (manifest_.signatures_offset() &&
manifest_.signatures_offset() == operation.data_offset()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Skipping hash verification for signature operation "
<< next_operation_num_ + 1;
} else {
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Missing mandatory operation hash for operation "
<< next_operation_num_ + 1;
return ErrorCode::kDownloadOperationHashMissingError;
}
LOG(WARNING) << "Cannot validate operation " << next_operation_num_ + 1
<< " as there's no operation hash in manifest";
}
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
//
// 检查InstallOperation数据的hash
//
// 对每一个InstallOperation来说,
// 其type, data_offset, data_length, hash等数据保存在Manifest中
// 但真正的payload数据则保存在manifest后面的"struct blobs[]"结构中。
// 所以这里取出InstallOperation在Manifest中的hash,
// 同时计算"struct blobs[]"结构中对应operation数据的hash,
// 将预存的hash同计算的hash进行比较
// 存储operation自带的data hash到expected_op_hash
brillo::Blob expected_op_hash;
expected_op_hash.assign(operation.data_sha256_hash().data(),
(operation.data_sha256_hash().data() +
operation.data_sha256_hash().size()));
// 根据当前InstallOperation对应的数据,计算Hash
HashCalculator operation_hasher;
operation_hasher.Update(buffer_.data(), operation.data_length());
if (!operation_hasher.Finalize()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to compute actual hash of operation "
<< next_operation_num_;
return ErrorCode::kDownloadOperationHashVerificationError;
}
// 将重新计算出来的hash值calculated_op_hash同operation自带的Hash数据进行比较
brillo::Blob calculated_op_hash = operation_hasher.raw_hash();
if (calculated_op_hash != expected_op_hash) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Hash verification failed for operation "
<< next_operation_num_ << ". Expected hash = ";
utils::HexDumpVector(expected_op_hash);
LOG(ERROR) << "Calculated hash over " << operation.data_length()
<< " bytes at offset: " << operation.data_offset() << " = ";
utils::HexDumpVector(calculated_op_hash);
return ErrorCode::kDownloadOperationHashMismatch;
}
return ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
一句话,ValidateOperationHash()中,重新计算InstalOperation的payload数据的hash,然后同预先计算好的hash进行比较,通过这种手段来确保数据的正确性。
3.7 执行InstallOperation的更新操作
Write()中检查完每个InstallOperation的Payload数据的hash后,就需要使用payload数据进行更新工作了:
// Makes sure we unblock exit when this operation completes.
ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker exit_unblocker =
ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker(); // Avoids a compiler unused var bug.
// 根据InstallOperation具体的操作类型,执行相应的操作
bool op_result;
switch (op.type()) {
case InstallOperation::REPLACE:
case InstallOperation::REPLACE_BZ:
case InstallOperation::REPLACE_XZ:
op_result = PerformReplaceOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::ZERO:
case InstallOperation::DISCARD:
op_result = PerformZeroOrDiscardOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::MOVE:
op_result = PerformMoveOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::BSDIFF:
op_result = PerformBsdiffOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::SOURCE_COPY:
op_result = PerformSourceCopyOperation(op, error);
break;
case InstallOperation::SOURCE_BSDIFF:
op_result = PerformSourceBsdiffOperation(op, error);
break;
default:
op_result = false;
}
// 如果当前InstallOperation执行错误,显示相应的错误信息,
if (!HandleOpResult(op_result, InstallOperationTypeName(op.type()), error))
return false;
// 递增下一个操作的InstallOperation的索引next_operation_num_
next_operation_num_++;
UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed ");
// 保存当前更新的进度和数据状态信息,以放中间挂了,下次仍然可以从当前点开始继续升级
CheckpointUpdateProgress();
这里的操作比较简单,就是跟去当前InstallOperation的type,执行相应的操作就好了。对于每个具体的操作,这里不再展开分析。
当然,我们也可以看到,在执行完每一个InstallOperation后,会调用CheckpointUpdateProgress()保存到当前操作为止的状态信息,美其名曰检查点(CheckPoint)。
所以,我们假设,当前升级过程中暂停,或者突然断电,系统仍然保存了当前最后一个InstallOperation执行后的状态信息,下次可以继续升级而不用重新开始。
3.8 提取升级数据的signature
在升级数据包的最后,还包含了payload_signatures_message的size和data。
所以Write()操作的最后还需要将payload_signatures_message信息保存到signatures_message_data_中。
//
// 检查payload_signatures_message数据存在的合理性
// 如果各种条件指示存在payload_signatures_message,但最后却没有实际数据,这就搞笑了,报错!
//
// In major version 2, we don't add dummy operation to the payload.
// If we already extracted the signature we should skip this step.
if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion &&
manifest_.has_signatures_offset() && manifest_.has_signatures_size() &&
signatures_message_data_.empty()) {
if (manifest_.signatures_offset() != buffer_offset_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Payload signatures offset points to blob offset "
<< manifest_.signatures_offset()
<< " but signatures are expected at offset "
<< buffer_offset_;
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
return false;
}
// 将signature数据复制到buffer_
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, manifest_.signatures_size());
// Needs more data to cover entire signature.
if (buffer_.size() < manifest_.signatures_size())
return true;
//
// 提取signatrue数据,并通过perf机制将其保存起来
//
if (!ExtractSignatureMessage()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Extract payload signature failed.";
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
return false;
}
DiscardBuffer(true, 0);
//
// 接收到signature数据后更新检查点(check point),这样下次就不需要再处理signature数据了
//
// Since we extracted the SignatureMessage we need to advance the
// checkpoint, otherwise we would reload the signature and try to extract
// it again.
CheckpointUpdateProgress();
}
到这里,你或许会问,这个payload_signatures_message保存下来有什么用,哪里会用到呢?
DownloadAction类在接收完数据后会受到通知并调用TransferComplete()进行处理。在函数TransferComplete()中,会进一步调用VerifyPayload()去检查下载到的数据,同时附带上install_plan_中的payload_hash信息。
此时会计算升级文件数据(即payload)的hash, 并同install_plan_传递下来的payload_hash进行比较,二者一致的情况下,再使用payload_signatures_message去校验这个hash是否真的合法。
由于文档篇幅太长,这里略过对VerifyPayload()函数的详细注释。
4. 完整的Write()操作注释
感觉上面几节对Write()的分片注释注释容易让人迷失在代码的细节里,尽管已经很长了,最后决定还是把Write()操作的注释完整的贴一次:
Write()代码注释
// Wrapper around write. Returns true if all requested bytes
// were written, or false on any error, regardless of progress
// and stores an action exit code in |error|.
bool DeltaPerformer::Write(const void* bytes, size_t count, ErrorCode *error) {
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
const char* c_bytes = reinterpret_cast(bytes);
//
// 1. 更新数据接收进度信息
// logcat中抓取到的打印信息如下:
// ...
// Completed 0/? operations, 14169/282164983 bytes downloaded (0%), overall progress 0%
// Completed 23/377 operations (6%), 40302425/282164983 bytes downloaded (14%), overall progress 10%
// ...
// Completed 377/377 operations (100%), 282164983/282164983 bytes downloaded (100%), overall progress 100%
// ...
//
// Update the total byte downloaded count and the progress logs.
total_bytes_received_ += count;
UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed ");
// 检查manifest_valid_标志是否有效
// 如果为false,表示没有解析过manifest数据,则此处进行解析
while (!manifest_valid_) {
// Read data up to the needed limit; this is either maximium payload header
// size, or the full metadata size (once it becomes known).
// 检查是否已经解析了Header数据
const bool do_read_header = !IsHeaderParsed();
// 根据是否已经解析Header决定复制的字节数
// 如果连Header都没解析过,那就先复制23字节的Header数据进行接卸
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count,
(do_read_header ? kMaxPayloadHeaderSize :
metadata_size_ + metadata_signature_size_));
//
// 2. 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest信息;
// 这里的数据分为两部分:
// 1). Header数据: 前24字节
// 2). MetaData数据: 包括前24字节的Header数据,Manifest数据,以及这二者数据的Signature
//
MetadataParseResult result = ParsePayloadMetadata(buffer_, error);
if (result == kMetadataParseError) // 解析错误,则返回
return false;
// 解析MetaData返回数据不够的情况下,继续等待更多数据
if (result == kMetadataParseInsufficientData) {
// If we just processed the header, make an attempt on the manifest.
// 如果刚解析完Header,继续解析MetaData需要复制更多数据
if (do_read_header && IsHeaderParsed())
continue;
return true;
}
//
// 3. 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查
//
// 验证DeltaArchiveManifest的结构,确定升级类型是Full还是Delta
// 如:
// Detected a 'full' payload.
//
// Checks the integrity of the payload manifest.
if ((*error = ValidateManifest()) != ErrorCode::kSuccess)
return false;
// 设置Manifest为有效
manifest_valid_ = true;
// 已经完成了MetaData的解析,所以可以抛弃已经解析的数据
// Clear the download buffer.
DiscardBuffer(false, metadata_size_);
// 提取Manifest中的partitions信息,
// This populates |partitions_| and the |install_plan.partitions| with the
// list of partitions from the manifest.
if (!ParseManifestPartitions(error))
return false;
// partitions_的每个分区都包含一个operations数组,里面存放的是InstallOperation数据
// 所有分区的operations数组大小累加到num_total_operations_
// 所以最后num_total_operations_是所有InstallOperation的总数
//
// 这里的acc_num_operations_计算比较特别:
// 如果有三个分区,第1个分区的operations大小为10,第2个分区为15,第3个分区为8
// 则acc_num_operations_应该为{10, 25, 33},
// 这里25=10+15, 33=10+15+8,即后面的数据是前面数据的累加结果
num_total_operations_ = 0;
for (const auto& partition : partitions_) {
num_total_operations_ += partition.operations_size();
acc_num_operations_.push_back(num_total_operations_);
}
// 保存 metadata_size和metadata_signature_size数据到磁盘
// 保存这些数据是因为如果升级暂停(pause)了,下次恢复(resume)时传输的数据和可能就不再包含metadata了
LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestMetadataSize,
metadata_size_))
<< "Unable to save the manifest metadata size.";
LOG_IF(WARNING, !prefs_->SetInt64(kPrefsManifestSignatureSize,
metadata_signature_size_))
<< "Unable to save the manifest signature size.";
// 如果之前暂停(pause),现在恢复(resume)继续升级,获取暂停时保存的状态数据
// 上一次升级的信息可能已经丢失(例如暂停后系统重启过),所以需要通过prefs_机制重新从磁盘获取这些信息
// 如果没有取得上一次的升级信息,说明当前是全新升级
if (!PrimeUpdateState()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadStateInitializationError;
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to prime the update state.";
return false;
}
// 打开第1个分区
if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
return false;
}
// 如果开始操作的不是InstallOperation索引大于0,说明这次是恢复(resume)升级操作
if (next_operation_num_ > 0)
UpdateOverallProgress(true, "Resuming after ");
LOG(INFO) << "Starting to apply update payload operations";
}
// num_total_operations_用于指示manifest中所有InstallOperation的总数
// 因此通过(next_operation_num_ < num_total_operations_)比较来确定是否执行完了所有的InstallOperation
while (next_operation_num_ < num_total_operations_) {
// Check if we should cancel the current attempt for any reason.
// In this case, *error will have already been populated with the reason
// why we're canceling.
if (download_delegate_ && download_delegate_->ShouldCancel(error))
return false;
//
// 1. 打开下一个要操作的分区
//
// 前面已经打开了第一个操作的分区,这里根据下一个要操作的InstallOperation的索引值next_operation_num_,确定需要打开哪一个分区
// 例如,前面的例子,更新包需要更新有三个分区,第1个分区的operations大小为10,第2个分区为15,第3个分区为8,因此acc_num_operations_数组为{10,25,8}
// 下一个要执行的InstallOperation的索引值next_operation_num_的值为17,那刚好位于第2个分区中,所以此时需要关闭第1个分区,打开第2个分区。
// 所以这里通过next_operation_num_的比较,确保要操作的分区已经打开
// We know there are more operations to perform because we didn't reach the
// |num_total_operations_| limit yet.
while (next_operation_num_ >= acc_num_operations_[current_partition_]) {
CloseCurrentPartition();
current_partition_++;
if (!OpenCurrentPartition()) {
*error = ErrorCode::kInstallDeviceOpenError;
return false;
}
}
//
// 2. 提取分区中下一个要操作的InstallOperation
//
// 通过nexus_operation_num_和acc_num_operations_数组,来查找下一个InstallOperation在某个partition更新的Operation的所以值
// 简单说来,将下一个InstallOperation操作在全部操作中的索引值转化为相应分区内的索引值。
const size_t partition_operation_num = next_operation_num_ - (
current_partition_ ? acc_num_operations_[current_partition_ - 1] : 0);
// 根据分区内InstallOperation的索引值partition_operation_num, 来从当前操作的分区中提取InstallOperation
const InstallOperation& op =
partitions_[current_partition_].operations(partition_operation_num);
//
// 3. 根据InstallOperation指示的长度将操作数据存放到缓冲区中
//
// 当前要操作的InstallOperation的数据从接收数据的缓冲区复制到DeltaPerformer内部操作的缓冲区buffer_中去
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, op.data_length());
// 检查确保已经接收到当前要操作的InstallOperationd的数据
// Check whether we received all of the next operation's data payload.
if (!CanPerformInstallOperation(op))
return true;
//
// 4. 检查InstallOperation对应操作数据的hash
//
// 在metadata signature存在的情况下,校验InstallOperation对应数据的hash
// Validate the operation only if the metadata signature is present.
// Otherwise, keep the old behavior. This serves as a knob to disable
// the validation logic in case we find some regression after rollout.
// NOTE: If hash checks are mandatory and if metadata_signature is empty,
// we would have already failed in ParsePayloadMetadata method and thus not
// even be here. So no need to handle that case again here.
if (!install_plan_->metadata_signature.empty()) {
// Note: Validate must be called only if CanPerformInstallOperation is
// called. Otherwise, we might be failing operations before even if there
// isn't sufficient data to compute the proper hash.
// 计算当前InstallOperation数据的hash,并将其同预先计算的hash进行比较
*error = ValidateOperationHash(op);
if (*error != ErrorCode::kSuccess) {
if (install_plan_->hash_checks_mandatory) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Mandatory operation hash check failed";
return false;
}
// For non-mandatory cases, just send a UMA stat.
LOG(WARNING) << "Ignoring operation validation errors";
*error = ErrorCode::kSuccess;
}
}
// Makes sure we unblock exit when this operation completes.
ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker exit_unblocker =
ScopedTerminatorExitUnblocker(); // Avoids a compiler unused var bug.
// 根据InstallOperation具体的操作类型,执行相应的操作
bool op_result;
switch (op.type()) {
case InstallOperation::REPLACE:
case InstallOperation::REPLACE_BZ:
case InstallOperation::REPLACE_XZ:
op_result = PerformReplaceOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::ZERO:
case InstallOperation::DISCARD:
op_result = PerformZeroOrDiscardOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::MOVE:
op_result = PerformMoveOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::BSDIFF:
op_result = PerformBsdiffOperation(op);
break;
case InstallOperation::SOURCE_COPY:
op_result = PerformSourceCopyOperation(op, error);
break;
case InstallOperation::SOURCE_BSDIFF:
op_result = PerformSourceBsdiffOperation(op, error);
break;
default:
op_result = false;
}
// 如果当前InstallOperation执行错误,显示相应的错误信息,
if (!HandleOpResult(op_result, InstallOperationTypeName(op.type()), error))
return false;
// 递增下一个操作的InstallOperation的索引next_operation_num_
next_operation_num_++;
UpdateOverallProgress(false, "Completed ");
// 保存当前更新的进度和数据状态信息,以放中间挂了,下次仍然可以从当前点开始继续升级
CheckpointUpdateProgress();
}
//
// 检查payload_signatures_message数据存在的合理性
// 如果各种条件指示存在payload_signatures_message,但最后却没有实际数据,这就搞笑了,报错!
//
// In major version 2, we don't add dummy operation to the payload.
// If we already extracted the signature we should skip this step.
if (major_payload_version_ == kBrilloMajorPayloadVersion &&
manifest_.has_signatures_offset() && manifest_.has_signatures_size() &&
signatures_message_data_.empty()) {
if (manifest_.signatures_offset() != buffer_offset_) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Payload signatures offset points to blob offset "
<< manifest_.signatures_offset()
<< " but signatures are expected at offset "
<< buffer_offset_;
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
return false;
}
// 将signature数据复制到buffer_
CopyDataToBuffer(&c_bytes, &count, manifest_.signatures_size());
// Needs more data to cover entire signature.
if (buffer_.size() < manifest_.signatures_size())
return true;
//
// 提取signatrue数据,并通过perf机制将其保存起来
//
if (!ExtractSignatureMessage()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Extract payload signature failed.";
*error = ErrorCode::kDownloadPayloadVerificationError;
return false;
}
DiscardBuffer(true, 0);
//
// 接收到signature数据后更新检查点(check point),这样下次就不需要再处理signature数据了
//
// Since we extracted the SignatureMessage we need to advance the
// checkpoint, otherwise we would reload the signature and try to extract
// it again.
CheckpointUpdateProgress();
}
return true;
}
Write()操作总结
- 更新数据接收进度信息;
- 解析升级包的头部数据,得到DeltaArchiveManifest数据;
- 对DeltaArchiveManifest结构进行检查;
- 从DeltaArchiveManifest中提取分区信息;
- 更新升级的状态信息
- 提取各分区的InstallOperation,并检查payload数据的hash
- 依次提取各分区的InstallOperation,提取数据,并进行相应的更新操作;
- 保存整个升级文件的signature