Java反射机制常用总结
Java反射机制详解
Java反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性;这种动态获取的信息以及动态调用对象的方法的功能称为Java语言的反射机制。
1、关于Class
1、Class是一个类,一个描述类的类(也就是描述类本身),封装了描述方法的Method,描述字段的Filed,描述构造器的Constructor等属性
2、对象照镜子后(反射)可以得到的信息:某个类的数据成员名、方法和构造器、某个类到底实现了哪些接口。
3、对于每个类而言,JRE 都为其保留一个不变的 Class 类型的对象。
一个 Class 对象包含了特定某个类的有关信息。
4、Class 对象只能由系统建立对象
5、一个类在 JVM 中只会有一个Class实例
- package com.java.reflection;
- public class Person {
- String name;
- private int age;
- public Person() {
- System.out.println("无参构造器");
- }
- public Person(String name, int age) {
- System.out.println("有参构造器");
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Person{" +
- "name='" + name + '\'' +
- ", age=" + age +
- '}';
- }
- }
2、反射机制获取类有三种方法
- /**
- * 反射机制获取类有三种方法
- */
- @Test
- public void testGetClass() throws ClassNotFoundException {
- Class clazz = null;
- //1 直接通过类名.Class的方式得到
- clazz = Person.class;
- System.out.println("通过类名: " + clazz);
- //2 通过对象的getClass()方法获取,这个使用的少(一般是传的是Object,不知道是什么类型的时候才用)
- Object obj = new Person();
- clazz = obj.getClass();
- System.out.println("通过getClass(): " + clazz);
- //3 通过全类名获取,用的比较多,但可能抛出ClassNotFoundException异常
- clazz = Class.forName("com.java.reflection.Person");
- System.out.println("通过全类名获取: " + clazz);
- }
| 通过类名: class com.java.reflection.Person 无参构造器 通过getClass(): class com.java.reflection.Person 通过全类名获取: class com.java.reflection.Person |
3、利用newInstance创建对象:调用的类必须有无参的构造器
- /**
- * Class类的newInstance()方法,创建类的一个对象。
- */
- @Test
- public void testNewInstance()
- throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
- Class clazz = Class.forName("com.java.reflection.Person");
- //使用Class类的newInstance()方法创建类的一个对象
- //实际调用的类的那个 无参数的构造器(这就是为什么写的类的时候,要写一个无参数的构造器,就是给反射用的)
- //一般的,一个类若声明了带参数的构造器,也要声明一个无参数的构造器
- Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
- System.out.println(obj);
- }
| 无参构造器 Person{name='null', age=0} |
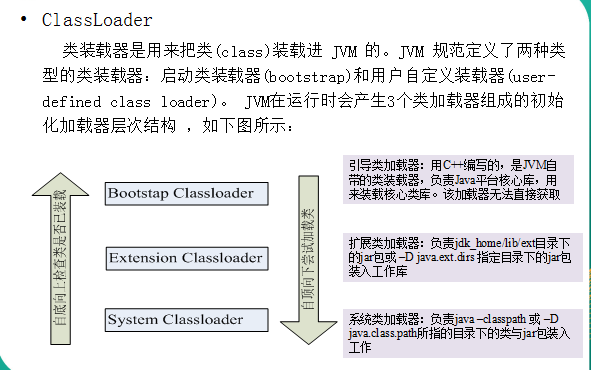
4、ClassLoader类加载器
类加载器详解:http://blog.csdn.net/ochangwen/article/details/51473120
- /**
- * ClassLoader类装载器
- */
- @Test
- public void testClassLoader1() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
- //1、获取一个系统的类加载器
- ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
- System.out.println("系统的类加载器-->" + classLoader);
- //2、获取系统类加载器的父类加载器(扩展类加载器(extensions classLoader))
- classLoader = classLoader.getParent();
- System.out.println("扩展类加载器-->" + classLoader);
- //3、获取扩展类加载器的父类加载器
- //输出为Null,无法被Java程序直接引用
- classLoader = classLoader.getParent();
- System.out.println("启动类加载器-->" + classLoader);
- //
- //4、测试当前类由哪个类加载器进行加载 ,结果就是系统的类加载器
- classLoader = Class.forName("com.java.reflection.Person").getClassLoader();
- System.out.println("当前类由哪个类加载器进行加载-->"+classLoader);
- //5、测试JDK提供的Object类由哪个类加载器负责加载的
- classLoader = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getClassLoader();
- System.out.println("JDK提供的Object类由哪个类加载器加载-->" + classLoader);
- }
| 系统的类加载器-->sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@43be2d65 扩展类加载器-->sun.misc.Launcher$ExtClassLoader@7a9664a1 启动类加载器-->null 当前类由哪个类加载器进行加载-->sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@43be2d65 JDK提供的Object类由哪个类加载器加载-->null |
4.1、getResourceAsStream方法
- @Test
- public void testGetResourceAsStream() throws ClassNotFoundException, IOException {
- // 这么写的话,文件需要放到src目录下
- // InputStream in = new FileInputStream("test.properties");
- //5、关于类加载器的一个主要方法
- //调用getResourceAsStream 获取类路径下的文件对应的输入流
- InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader()
- .getResourceAsStream("com/java/reflection/test.properties");
- System.out.println("in: " +in);
- Properties properties = new Properties();
- properties.load(in);
- String driverClass = properties.getProperty("dirver");
- String jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
- //中文可能会出现乱码,需要转换一下
- String user = new String(properties.getProperty("user").getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "UTF-8");
- String password = properties.getProperty("password");
- System.out.println("diverClass: "+driverClass);
- System.out.println("user: " + user);
- }
test.properties内容如下:
| dirver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://192.168.42.108:3306/test user=测试 password=993803 |
结果:
| in: java.io.BufferedInputStream@2aca0115 diverClass: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver; user: 测试 |
5、Method: 对应类中的方法
- public class Person {
- private String name;
- private int age;
- //新增一个私有方法
- private void privateMthod(){
- }
- public Person() {
- System.out.println("无参构造器");
- }
- public Person(String name, int age) {
- System.out.println("有参构造器");
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- /**
- *
- * @param age 类型用Integer,不用int
- */
- public void setName(String name , int age){
- System.out.println("name: " + name);
- System.out.println("age:"+ age);
- }
- public int getAge() {
- return age;
- }
- public void setAge(int age) {
- this.age = age;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() {
- return "Person{" +
- "name='" + name + '\'' +
- ", age=" + age +
- '}';
- }
- }
- @Test
- public void testMethod() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException,
- IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
- Class clazz = Class.forName("com.java.reflection.Person");
- //1、得到clazz 对应的类中有哪些方法,不能获取private方法
- Method[] methods =clazz.getMethods();
- System.out.print(" getMethods: ");
- for (Method method : methods){
- System.out.print(method.getName() + ", ");
- }
- //2、获取所有的方法(且只获取当着类声明的方法,包括private方法)
- Method[] methods2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
- System.out.print("\ngetDeclaredMethods: ");
- for (Method method : methods2){
- System.out.print(method.getName() + ", ");
- }
- //3、获取指定的方法
- Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setName",String.class);//第一个参数是方法名,后面的是方法里的参数
- System.out.println("\nmethod : " + method);
- Method method2 = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setName",String.class ,int.class);//第一个参数是方法名,后面的是方法里的参数
- System.out.println("method2: " + method2);
- //4、执行方法!
- Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
- method2.invoke(obj, "changwen", 22);
- }
| getMethods: toString, getName, setName, setName, setAge, getAge, wait, wait, wait, equals, hashCode, getClass, notify, notifyAll, getDeclaredMethods: toString, getName, setName, setName, setAge, getAge, privateMthod, method : public void com.java.reflection.Person.setName(java.lang.String) method2: public void com.java.reflection.Person.setName(java.lang.String,int) 无参构造器 name: changwen age:22 |
6、invoke方法
- public class PersonInvoke {
- public PersonInvoke() {
- }
- private String method2() {
- return "Person private String method2";
- }
- }
- public class StudentInvoke extends PersonInvoke{
- private void method1(Integer age) {
- System.out.println("Student private void method1, age=:" +age);
- }
- }
获取当前类的父类定义的私有方法
- /**
- * 获取当前类的父类中定义的私有方法
- * 直接调用getSuperclass()
- */
- @Test
- public void testGetSuperClass() throws Exception {
- String className = "com.java.reflection.StudentInvoke";
- Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
- Class superClazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
- System.out.println(superClazz);
- //输出结果:class com.java.reflection.PersonInvoke
- }
另一种写法
- /**
- * @param className 某个类的全类名
- * @param methodName 类的一个方法的方法名,该方法也可能是私有方法
- * @param args 调用该方法需要传入的参数 ...可变参数的意思
- * @return 调用方法后的返回值
- */
- public Object invoke(String className, String methodName, Object ... args) {
- Object obj = null;
- try {
- obj = Class.forName(className).newInstance();
- return invoke(obj, methodName, args);
- } catch (InstantiationException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return invoke(null, methodName, args);
- }
- /**
- * @param obj 方法执行的那个对象
- * @param methodName 类的一个方法的方法名,该方法也可能是私有方法,还可能是该方法在父类中定义的私有方法
- * @param args 调用该方法需要传入的参数 ...可变参数的意思
- * @return 调用方法后的返回值
- */
- public Object invoke(Object obj, String methodName, Object ... args) {
- //1、获取Method对象
- Class [] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length];
- for (int i=0 ; i
- parameterTypes[i] = args[i].getClass();
- }
- try {
- //2、执行Method方法
- Method method = getMethod(obj.getClass(), methodName,parameterTypes);
- //通过反射执行private方法
- method.setAccessible(true);
- //3、返回方法的返回值
- return method.invoke(obj,args);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- }
- return null;
- }
- /**
- * 获取clazz 的methodName 方法, 该方法可能是私有方法,还可能是父类中的私有方法
- */
- public Method getMethod(Class clazz, String methodName, Class ... parameterTypes) {
- //注意这个循环里的内容!!!
- for (; clazz != Object.class; clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()){
- try {
- return clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
- } catch (Exception e) { //这里要写Exception,不然会出错,应该是有部分异常没有捕获
- }
- }
- return null;
- }
测试:
- @Test
- public void testInvoke2() {
- Object obj = new StudentInvoke();
- invoke(obj, "method1", 10);
- Object result = invoke(obj, "method2");
- System.out.println(result);
- }
| private void method1,age:10 Person private String method2 |
7、Field字段
- public class Person {
- public String name;
- private Integer age;
- public Person() {
- }
- public Person(String name, Integer age) {
- this.name = name;
- this.age = age;
- }
- }
- /**
- * Field: 封装了字段的信息
- */
- @Test
- public void testField() throws
- ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
- Class clazz = Class.forName("com.java.reflection.Person");
- //1、获取字段
- //1.1 获取Field的数组,私有字段也能获取
- Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
- for (Field field: fields) {
- System.out.print(field.getName() + ", ");
- }
- //1.2 获取指定名字的Field(如果是私有的,见下面的4)
- Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
- System.out.println("\n获取指定Field名=: " + field.getName());
- Person person = new Person("ABC", 12);
- //2、获取指定对象的Field的值
- Object val = field.get(person);
- System.out.println("获取指定对象字段'name'的Field的值=: " + val);
- //3、设置指定对象的Field的值
- field.set(person, "changwen2");
- System.out.println("设置指定对象字段'name'的Field的值=: " + person.name);
- //4、若该字段是私有的,需要调用setAccessible(true)方法
- Field field2 = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
- field2.setAccessible(true);
- System.out.println("获取指定私有字段名=: " + field2.getName());
- }
| name, age, 获取指定Field名=: name 获取指定对象字段'name'的Field的值=: ABC 设置指定对象字段'name'的Field的值=: changwen2 获取指定私有字段名=: age |
- /**
- * 一个实例:
- * 反射获取一个继承Person2的Student类
- * 设置字段"age"=20(该字段可能为私有,可能在其父类中)
- */
- @Test
- public void testClassField() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
- String className = "com.java.reflection.Student";
- String fieldName = "age"; //可能为私有,可能在其父类中
- Object val = 20;
- //创建className 对应类的对象,并为其fieldName赋值为val
- Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
- Field field = null;
- for (Class clazz2 = clazz; clazz2 != Object.class; clazz2 = clazz2.getSuperclass()){
- try {
- field = clazz2.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- }
- }
- Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
- assert field != null;
- field.setAccessible(true);
- field.set(obj, val);
- Student stu = (Student) obj;
- System.out.println("age = " + stu.getAge());
- }
8、构造器(Constructor)
- /**
- * 构造器:开发用的比较少
- */
- @Test
- public void testConstructor() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException,
- IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
- String className = "com.java.reflection.Person";
- Class
clazz = (Class ) Class.forName(className); - //1.获取Constructor对象
- Constructor
[] constructors = - (Constructor
[]) Class.forName(className).getConstructors(); - for (Constructor
constructor: constructors) { - System.out.println(constructor);
- }
- Constructor
constructor = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, Integer.class); - System.out.println("指定的-->" + constructor);
- //2.调用构造器的newInstance()方法创建对象
- Object obj= constructor.newInstance("changwen", 11);
- }
| public com.java.reflection.Person() public com.java.reflection.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer) 指定的-->public com.java.reflection.Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer) |
9、注解(Annotation)
•从 JDK5.0 开始,Java 增加了对元数据(MetaData)的支持,也就是Annotation(注释)
•Annotation其实就是代码里的特殊标记,这些标记可以在编译,类加载, 运行时被读取,并执行相应的处理.通过使用Annotation,程序员可以在不改变原有逻辑的情况下,在源文件中嵌入一些补充信息.
•Annotation 可以像修饰符一样被使用,可用于修饰包,类,构造器, 方法,成员变量, 参数,局部变量的声明,这些信息被保存在Annotation的 “name=value”对中.
•Annotation能被用来为程序元素(类,方法,成员变量等)设置元数据
基本的 Annotation
•使用 Annotation时要在其前面增加@符号,并把该Annotation 当成一个修饰符使用.用于修饰它支持的程序元素
•三个基本的Annotation:
–@Override:限定重写父类方法,该注释只能用于方法
–@Deprecated:用于表示某个程序元素(类,方法等)已过时
–@SuppressWarnings:抑制编译器警告.
自定义 Annotation
•定义新的 Annotation类型使用@interface关键字
•Annotation 的成员变量在Annotation 定义中以无参数方法的形式来声明.其方法名和返回值定义了该成员的名字和类型.
•可以在定义Annotation的成员变量时为其指定初始值,指定成员变量的初始值可使用default关键字
•没有成员定义的Annotation称为标记;包含成员变量的Annotation称为元数据Annotation
- @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //运行时检验
- @Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD}) //作用在方法上
- public @interface AgeValidator {
- int min();
- int max();
- }
- /**
- * 通过反射才能获取注解
- */
- @Test
- public void testAnnotation() throws Exception {
- //这样的方式不能使用注解
- Person3 person3 = new Person3();
- person3.setAge(10);*/
- String className = "com.java.reflection.Person3";
- Class clazz = Class.forName(className);
- Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
- Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setAge",Integer.class);
- int val =40;
- //获取注解
- Annotation annotation = method.getAnnotation(AgeValidator.class);
- if (annotation != null){
- if (annotation instanceof AgeValidator){
- AgeValidator ageValidator = (AgeValidator) annotation;
- if (val< ageValidator.min() || val>ageValidator.max()){
- throw new RuntimeException("数值超出范围");
- }
- }
- }
- method.invoke(obj, val);
- System.out.println(obj);
- }
提取 Annotation信息
•JDK5.0 在 java.lang.reflect包下新增了 AnnotatedElement接口,该接口代表程序中可以接受注释的程序元素
•当一个 Annotation类型被定义为运行时Annotation后,该注释才是运行时可见,当 class文件被载入时保存在 class文件中的 Annotation才会被虚拟机读取
•程序可以调用AnnotationElement对象的如下方法来访问 Annotation信息
–获取 Annotation实例:
• getAnnotation( Class annotationClass)
• getDeclaredAnnotations()
• getParameterAnnotations()
JDK 的元Annotation
•JDK 的元Annotation 用于修饰其他Annotation 定义
•@Retention:只能用于修饰一个 Annotation定义,用于指定该 Annotation可以保留多长时间,@Rentention包含一个RetentionPolicy类型的成员变量,使用 @Rentention时必须为该 value成员变量指定值:
–RetentionPolicy.CLASS:编译器将把注释记录在 class文件中.当运行 Java程序时,JVM 不会保留注释.这是默认值
–RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:编译器将把注释记录在class文件中. 当运行 Java 程序时, JVM 会保留注释. 程序可以通过反射获取该注释
–RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:编译器直接丢弃这种策略的注释
•@Target: 用于修饰Annotation 定义,用于指定被修饰的 Annotation能用于修饰哪些程序元素.@Target 也包含一个名为 value的成员变量.
•@Documented:用于指定被该元 Annotation修饰的 Annotation类将被 javadoc工具提取成文档.
•@Inherited:被它修饰的 Annotation将具有继承性.如果某个类使用了被@Inherited 修饰的Annotation, 则其子类将自动具有该注释