Rocketmq的通信协议和方法分析
根据rocketmq的模块设计,其通信相关的代码放在源码包下的rocketmq-remoting模块。主要内容包括了编解码处理,使用了nety框架对接收发送消息的处理等。其类图见下:
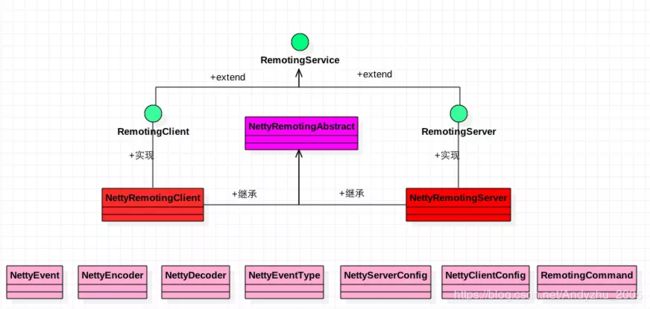
其中,以RemotingService为最上层接口,提供了三个接口:
void start();
void shutdown();
void registerRPCHook(RPCHook rpcHook);
RemotingClient和RemotingServer都继承了RemotingService接口, 并增加了自己特有的接口.NettyRemotingClient和NettyRemotingServer分别实现了RemotingClient和RemotingServer, 并且都继承了NettyRemotingAbstract类. NettyRemotingAbstract这个抽象类包含了很多公共数据处理,也包含了很多重要的数据结构, 这个稍后介绍.
其它还有NettyEvent, NettyEncoder, NettyDecoder和RemotingCommand等一系列通信过程中使用到的类.
1、协议设计和编解码
1.1 协议设计
rocketmq的协议如下

从上面可以看出,其总长度是4+4+消息头长度+消息体长度。
其中消息头的长度值,在第二个4字节中的2,、3、4个字节中。
1.2消息的编码
以rocketmq给的关于remoting的test调试入手,具体类是

以同步通信为例
@Test
public void testInvokeSync() throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException,
RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
RequestHeader requestHeader = new RequestHeader();
requestHeader.setCount(1);
requestHeader.setMessageTitle("Welcome");
RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(0, requestHeader);
RemotingCommand response = remotingClient.invokeSync("localhost:8888", request, 100000 * 3);
assertTrue(response != null);
System.out.println(response);
assertThat(response.getLanguage()).isEqualTo(LanguageCode.JAVA);
assertThat(response.getExtFields()).hasSize(2);
}
上面的例子中, requestHeader实现了CommandCustomHeader接口,即requestHeader是我们的消息头部信息。然后,以requestHeader为参,建立RemoteCommand消息。
public static RemotingCommand createRequestCommand(int code, CommandCustomHeader customHeader) {
RemotingCommand cmd = new RemotingCommand();
cmd.setCode(code);
cmd.customHeader = customHeader;
setCmdVersion(cmd);
return cmd;
}
其中,RemoteCommand是rocketmq中传输信息的消息定义体。其成员变量定义如下,其中extFields可以存储用户的键值对信息:
private int code;
private LanguageCode language = LanguageCode.JAVA;
private int version = 0;
private int opaque = requestId.getAndIncrement();
private int flag = 0;
private String remark;
private HashMap extFields;
private transient CommandCustomHeader customHeader;
private SerializeType serializeTypeCurrentRPC = serializeTypeConfigInThisServer;
private transient byte[] body;
在test之前,会先启动remotingServer 服务端和remotingClient 客户端。
@BeforeClass
public static void setup() throws InterruptedException {
remotingServer = createRemotingServer();
remotingClient = createRemotingClient();
}
上述的服务端和客户端都一netty为基础。首先看客户端的启动createRemotingClient。客户端的启动之前,会先定义一些线程池中,创建线程如何定义等,然后调用start
@Override
public void start() {
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(
nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(),
new ThreadFactory() {
private AtomicInteger threadIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "NettyClientWorkerThread_" + this.threadIndex.incrementAndGet());
}
});
Bootstrap handler = this.bootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupWorker).channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, false)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketSndBufSize())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketRcvBufSize())
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
if (nettyClientConfig.isUseTLS()) {
if (null != sslContext) {
pipeline.addFirst(defaultEventExecutorGroup, "sslHandler", sslContext.newHandler(ch.alloc()));
log.info("Prepend SSL handler");
} else {
log.warn("Connections are insecure as SSLContext is null!");
}
}
pipeline.addLast(
defaultEventExecutorGroup,
new NettyEncoder(),
new NettyDecoder(),
new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, nettyClientConfig.getClientChannelMaxIdleTimeSeconds()),
new NettyConnectManageHandler(),
new NettyClientHandler());
}
});
this.timer.scheduleAtFixedRate(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
NettyRemotingClient.this.scanResponseTable();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("scanResponseTable exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 3, 1000);
if (this.channelEventListener != null) {
this.nettyEventExecutor.start();
}
}
其中,编码工作在new NettyEncoder()中。查看其定义:
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand remotingCommand, ByteBuf out)
throws Exception {
try {
ByteBuffer header = remotingCommand.encodeHeader();
out.writeBytes(header);
byte[] body = remotingCommand.getBody();
if (body != null) {
out.writeBytes(body);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("encode exception, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), e);
if (remotingCommand != null) {
log.error(remotingCommand.toString());
}
RemotingUtil.closeChannel(ctx.channel());
}
}
可以看到,上面主要完成了消息头和消息体的写入。其中消息体本身就是byte[]数组,不需要多做关注。重点勘察remotingCommand.encodeHeader();方法。
ByteBuffer header = remotingCommand.encodeHeader();
out.writeBytes(header);
public ByteBuffer encodeHeader(final int bodyLength) {
// 1> header length size
int length = 4;
// 2> header data length
byte[] headerData;
//这里是重点,完成了消息头的编码
headerData = this.headerEncode();
length += headerData.length;
// 3> body data length
length += bodyLength;
ByteBuffer result = ByteBuffer.allocate(4 + length - bodyLength);
// length 写入length
result.putInt(length);
// header length 写入headerlenth和序列化方式
result.put(markProtocolType(headerData.length, serializeTypeCurrentRPC));
// header data 写入头数据
result.put(headerData);
result.flip();
return result;
}
可以看到,上面的方法完成了除了body之外的消息转为bytebuf的过程。其中:
1、前四个字节存放的是整个消息体的长度(但是这个长度不包括前四个字节),即length的长度值包括上面rocket协议图中2,3,4部分的长度;
2、查看 headerData = this.headerEncode();,将消息头转为byte[]数组。
private byte[] headerEncode() {
this.makeCustomHeaderToNet();
if (SerializeType.ROCKETMQ == serializeTypeCurrentRPC) {
return RocketMQSerializable.rocketMQProtocolEncode(this);
} else {
//默认采用了json序列化。这里的this指代的是RemotingCommand
return RemotingSerializable.encode(this);
}
}
/**
makeCustomHeaderToNet方法是将customHeader中定义的键值对参数写入 extFields中,比如我们在测试用例中,写入了requestHeader.setCount(1);
requestHeader.setMessageTitle("Welcome");
*/
public void makeCustomHeaderToNet() {
if (this.customHeader != null) {
Field[] fields = getClazzFields(customHeader.getClass());
if (null == this.extFields) {
this.extFields = new HashMap();
}
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
String name = field.getName();
if (!name.startsWith("this")) {
Object value = null;
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
value = field.get(this.customHeader);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to access field [{}]", name, e);
}
if (value != null) {
this.extFields.put(name, value.toString());
}
}
}
}
}
}
重点关注上面的 RemotingSerializable.encode(this);,其中,this指代的RemotingCommand,我们通过断点调试,看一下这个this主要包含了什么内容:
RemotingCommand [code=0, language=JAVA, version=0, opaque=0, flag(B)=0, remark=null, extFields={count=1, messageTitle=Welcome}, serializeTypeCurrentRPC=JSON]
可以看到,里面内容是RemotingCommand 的相关信息,其中包括了我们自己定义的count和messageTitle信息。
这是因为RemotingCommand 重新定义了RemotingCommand 的tostring方法。(如果没有重新定义tostring方法,则this表示类的实例org.apache.rocketmq.remoting.RemotingCommand @3b764bce)
public String toString() {
return "RemotingCommand [code=" + code + ", language=" + language + ", version=" + version + ", opaque=" + opaque + ", flag(B)="
+ Integer.toBinaryString(flag) + ", remark=" + remark + ", extFields=" + extFields + ", serializeTypeCurrentRPC="
+ serializeTypeCurrentRPC + "]";
}
总结rocketmq的编码: 消息体需要用户自己转为byte[]数组,进行传输。而消息头,是rocketmq来完成序列化和转为byte[] 数组操作。这样的设计,应该是考虑到RemotingCommand的很多设置是默认的,但又是必须的,由系统来完成消息头的序列化操作。
1.3 消息的解码
消息的解码定义于NettyDecoder中,
@Override
public Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
ByteBuf frame = null;
try {
frame = (ByteBuf) super.decode(ctx, in);
if (null == frame) {
return null;
}
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = frame.nioBuffer();
return RemotingCommand.decode(byteBuffer);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("decode exception, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), e);
RemotingUtil.closeChannel(ctx.channel());
} finally {
if (null != frame) {
frame.release();
}
}
return null;
}
其中,解码操作位于 RemotingCommand.decode(byteBuffer);
public static RemotingCommand decode(final ByteBuffer byteBuffer) {
//获取消息长度,不包括消息长度本身
int length = byteBuffer.limit();
//获取消息头的长度
int oriHeaderLen = byteBuffer.getInt();
//执行 length & 0xFFFFFF,将int的后24位取出
int headerLength = getHeaderLength(oriHeaderLen);
byte[] headerData = new byte[headerLength];
byteBuffer.get(headerData);
//将消息头解码
RemotingCommand cmd = headerDecode(headerData, getProtocolType(oriHeaderLen));
int bodyLength = length - 4 - headerLength;
byte[] bodyData = null;
if (bodyLength > 0) {
bodyData = new byte[bodyLength];
byteBuffer.get(bodyData);
}
cmd.body = bodyData;
return cmd;
}
private static RemotingCommand headerDecode(byte[] headerData, SerializeType type) {
switch (type) {
//默认采用json方式将字符串转为RemotingCommand类
case JSON:
RemotingCommand resultJson = RemotingSerializable.decode(headerData, RemotingCommand.class);
resultJson.setSerializeTypeCurrentRPC(type);
return resultJson;
case ROCKETMQ:
RemotingCommand resultRMQ = RocketMQSerializable.rocketMQProtocolDecode(headerData);
resultRMQ.setSerializeTypeCurrentRPC(type);
return resultRMQ;
default:
break;
}
return null;
}
2 .rocketmq的通信流程
2.1同步发送
2.1.1 客户端流程
@Test
public void testInvokeSync() throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException,
RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
RequestHeader requestHeader = new RequestHeader();
requestHeader.setCount(1);
requestHeader.setMessageTitle("Welcome");
RemotingCommand request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(0, requestHeader);
RemotingCommand response = remotingClient.invokeSync("localhost:8888", request, 100000 * 3);
assertTrue(response != null);
System.out.println(response);
assertThat(response.getLanguage()).isEqualTo(LanguageCode.JAVA);
assertThat(response.getExtFields()).hasSize(2);
}
真正的发送和接收数据在下面这一行:其中,为了调试方便,把时间增加到10s。即如果10s内收不到返回的数据,就报错
RemotingCommand response = remotingClient.invokeSync(“localhost:8888”, request, 10000 * 1);
而invokeSync方法的定义如下:
@Override
public RemotingCommand invokeSync(String addr, final RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
//调用之前的操作
try {
if (this.rpcHook != null) {
this.rpcHook.doBeforeRequest(addr, request);
}
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeSync call timeout");
}
//真正的调用在于这里
RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
//结果返回后,如果有相关操作,则执行
if (this.rpcHook != null) {
this.rpcHook.doAfterResponse(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), request, response);
}
return response;
} catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
log.warn("invokeSync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw e;
} catch (RemotingTimeoutException e) {
if (nettyClientConfig.isClientCloseSocketIfTimeout()) {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
log.warn("invokeSync: close socket because of timeout, {}ms, {}", timeoutMillis, addr);
}
log.warn("invokeSync: wait response timeout exception, the channel[{}]", addr);
throw e;
}
} else {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
}
}
再看invokeSyncImpl的定义
public RemotingCommand invokeSyncImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request,
final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
//这里的opaque是我们每次新建一个RemotingCommand时,就会自动+1.可以理解为RemotingCommand的id
final int opaque = request.getOpaque();
try {
//responseFuture用于异步获取处理的结果
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = new ResponseFuture(channel, opaque, timeoutMillis, null, null);
this.responseTable.put(opaque, responseFuture);
final SocketAddress addr = channel.remoteAddress();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if (f.isSuccess()) {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(true);
return;
} else {
responseFuture.setSendRequestOK(false);
}
responseTable.remove(opaque);
responseFuture.setCause(f.cause());
responseFuture.putResponse(null);
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + addr + "> failed.");
}
});
//异步等待timeoutMillis时间后,从responseFuture获取返回结果,如果没有结果的话就是null
RemotingCommand responseCommand = responseFuture.waitResponse(timeoutMillis);
if (null == responseCommand) {
if (responseFuture.isSendRequestOK()) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), timeoutMillis,
responseFuture.getCause());
} else {
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseSocketAddressAddr(addr), responseFuture.getCause());
}
}
return responseCommand;
} finally {
this.responseTable.remove(opaque);
}
}
可以看到,我们是从ResponseFuture中取的结果,那么ResponseFuture的结果又从哪来的呢?
private final int opaque;
private final Channel processChannel;
private final long timeoutMillis;
private final InvokeCallback invokeCallback;
private final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
private final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
private final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once;
private final AtomicBoolean executeCallbackOnlyOnce = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private volatile RemotingCommand responseCommand;
private volatile boolean sendRequestOK = true;
private volatile Throwable cause;
ResponseFuture类中有一些用于控制多线程的工具类,比如CountDownLatch ,Semaphore等。
先跳出来,去看看我们收到消息后是如何处理的:
client的处理类是
class NettyClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand msg) throws Exception {
processMessageReceived(ctx, msg);
}
}
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
//从收到的数据中找到opaque,
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
//从responseTable中找到此标识号的ResponseFuture
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
//把结果存入responseFuture
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
//处理完了,移除
responseTable.remove(opaque);
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
//好像和 responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);是一样的
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
//异步时候有用
responseFuture.release();
}
} else {
log.warn("receive response, but not matched any request, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()));
log.warn(cmd.toString());
}
}
上面方法中,客户端收到数据后,会将结果存入responseFuture中,而在我们前面的分析中可以看到,客户端发送完消息后,会在一定的时间之后,从responseFuture去取这个结果。
2.1.1 服务端流程
在单元测试中,服务端的建立方法如下:
public static RemotingServer createRemotingServer() throws InterruptedException {
NettyServerConfig config = new NettyServerConfig();
RemotingServer remotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(config);
//registerProcessor是后面的处理方法与0进行绑定。即请求中如果cmd的code是0的话,就调用后面这个方法
remotingServer.registerProcessor(0, new NettyRequestProcessor() {
@Override
public RemotingCommand processRequest(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request) {
request.setRemark("Hixxxxx " + ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
return request;
}
@Override
public boolean rejectRequest() {
return false;
}
}, Executors.newCachedThreadPool());
remotingServer.start();
return remotingServer;
}
其中registerProcessor
@Override
public void registerProcessor(int requestCode, NettyRequestProcessor processor, ExecutorService executor) {
//运行processor的线程池
ExecutorService executorThis = executor;
if (null == executor) {
executorThis = this.publicExecutor;
}
Pair pair = new Pair(processor, executorThis);
//把requestCode与处理方法做成键值对,存入processorTable中
this.processorTable.put(requestCode, pair);
}
与客户端类似,服务端收到数据后,也会进行处理,流程不再说,其处理方法如下
public void processRequestCommand(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, final RemotingCommand cmd) {
//根据cmd.getCode()找到对应的处理方法
final Pair matched = this.processorTable.get(cmd.getCode());
//如果没有,就用默认的
final Pair pair = null == matched ? this.defaultRequestProcessor : matched;
//得到消息的id号
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
if (pair != null) {
Runnable run = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
RPCHook rpcHook = NettyRemotingAbstract.this.getRPCHook();
if (rpcHook != null) {
rpcHook.doBeforeRequest(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), cmd);
}
//执行消息处理方法,得到返回值
final RemotingCommand response = pair.getObject1().processRequest(ctx, cmd);
if (rpcHook != null) {
rpcHook.doAfterResponse(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()), cmd, response);
}
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
if (response != null) {
//设置返回消息的id
response.setOpaque(opaque);
//设置返回消息的类型
response.markResponseType();
try {
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("process request over, but response failed", e);
log.error(cmd.toString());
log.error(response.toString());
}
} else {
//如果是isOnewayRPC,单向消息,就不用处理了
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("process request exception", e);
log.error(cmd.toString());
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_ERROR,
RemotingHelper.exceptionSimpleDesc(e));
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
}
};
if (pair.getObject1().rejectRequest()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_BUSY,
"[REJECTREQUEST]system busy, start flow control for a while");
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
return;
}
try {
//生成一个runnable,绑定channel
final RequestTask requestTask = new RequestTask(run, ctx.channel(), cmd);
//pair.getObject2()得到的是一个线程池,线程池执行requestTask,就是我们上面定义的runnable
pair.getObject2().submit(requestTask);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
if ((System.currentTimeMillis() % 10000) == 0) {
log.warn(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel())
+ ", too many requests and system thread pool busy, RejectedExecutionException "
+ pair.getObject2().toString()
+ " request code: " + cmd.getCode());
}
if (!cmd.isOnewayRPC()) {
final RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.SYSTEM_BUSY,
"[OVERLOAD]system busy, start flow control for a while");
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
} else {
String error = " request type " + cmd.getCode() + " not supported";
final RemotingCommand response =
RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(RemotingSysResponseCode.REQUEST_CODE_NOT_SUPPORTED, error);
response.setOpaque(opaque);
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
log.error(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()) + error);
}
}
2.2 单向(oneway)
public void invokeOnewayImpl(final Channel channel, final RemotingCommand request, final long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingTooMuchRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException, RemotingSendRequestException {
//表明是单向发送
request.markOnewayRPC();
//semaphoreOneway用于控制发送顺序,
//semaphoreOneway的默认许可是65535,每次发送前获取一次许可(许可-1),发送完成之后许可+1
boolean acquired = this.semaphoreOneway.tryAcquire(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (acquired) {
final SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce once = new SemaphoreReleaseOnlyOnce(this.semaphoreOneway);
try {
channel.writeAndFlush(request).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
once.release();
if (!f.isSuccess()) {
log.warn("send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
once.release();
log.warn("write send a request command to channel <" + channel.remoteAddress() + "> failed.");
throw new RemotingSendRequestException(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), e);
}
} else {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("invokeOnewayImpl invoke too fast");
} else {
String info = String.format(
"invokeOnewayImpl tryAcquire semaphore timeout, %dms, waiting thread nums: %d semaphoreAsyncValue: %d",
timeoutMillis,
this.semaphoreOneway.getQueueLength(),
this.semaphoreOneway.availablePermits()
);
log.warn(info);
throw new RemotingTimeoutException(info);
}
}
}
2.3 异步调用
异步调用与同步调用流程大体类似,
public void processResponseCommand(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand cmd) {
//从收到的数据中找到opaque,
final int opaque = cmd.getOpaque();
//从responseTable中找到此标识号的ResponseFuture
final ResponseFuture responseFuture = responseTable.get(opaque);
if (responseFuture != null) {
//把结果存入responseFuture
responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);
//处理完了,移除
responseTable.remove(opaque);
//***********在这里执行异步调用,结果返回*****************
if (responseFuture.getInvokeCallback() != null) {
executeInvokeCallback(responseFuture);
} else {
//好像和 responseFuture.setResponseCommand(cmd);是一样的
responseFuture.putResponse(cmd);
//异步时候有用
responseFuture.release();
}
} else {
log.warn("receive response, but not matched any request, " + RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(ctx.channel()));
log.warn(cmd.toString());
}
}
/**
* Execute callback in callback executor. If callback executor is null, run directly in current thread
*/
private void executeInvokeCallback(final ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
boolean runInThisThread = false;
ExecutorService executor = this.getCallbackExecutor();
if (executor != null) {
try {
executor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, and callback throw", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
runInThisThread = true;
log.warn("execute callback in executor exception, maybe executor busy", e);
}
} else {
runInThisThread = true;
}
if (runInThisThread) {
try {
responseFuture.executeInvokeCallback();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn("executeInvokeCallback Exception", e);
} finally {
responseFuture.release();
}
}
}
public void executeInvokeCallback() {
if (invokeCallback != null) {
if (this.executeCallbackOnlyOnce.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
invokeCallback.operationComplete(this);
}
}
}
上面的operationComplete就是我们在单元测试类中,定义的
remotingClient.invokeAsync("localhost:8888", request, 1000 * 3, new InvokeCallback() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ResponseFuture responseFuture) {
latch.countDown();
System.out.println("latch.countDown()运行");
assertTrue(responseFuture != null);
assertThat(responseFuture.getResponseCommand().getLanguage()).isEqualTo(LanguageCode.JAVA);
assertThat(responseFuture.getResponseCommand().getExtFields()).hasSize(2);
}
});