写在前面
局部特征相关算法在过去二十年期间风靡一时,其中代表的有SIFT、SURF算法等(广泛应用于目标检测、识别、匹配定位中),这两种算法是用金字塔策略构建高斯尺度空间(SURF算法采用框滤波来近似高斯函数)。不论SIFT还是SURF算法在构造尺度空间时候存在一个重要的缺点:高斯模糊不保留对象边界信息并且在所有尺度上平滑到相同程度的细节与噪声,影响定位的准确性和独特性。
针对高斯核函数构建尺度空间的缺陷,有学者提出了非线性滤波构建尺度空间:双边滤波、非线性扩散滤波方式。非线性滤波策略构建尺度空间主要能够局部自适应进行滤除小细节同时保留目标的边界使其尺度空间保留更多的特征信息。例如:BFSIFT采取双边滤波与双向匹配方式改善SIFT算法在SAR图像上匹配性能低下的问题(主要由于SAR图像斑点噪声严重),但是付出更高的计算复杂度。AKAZE作者之前提出的KAZE算法采取非线性扩散滤波相比于SIFT与SURF算法提高了可重复性和独特性。但是KAZE算法缺点在于计算密集,通过AOS数值逼近的策略来求解非线性扩散方程,虽然AOS求解稳定并且可并行化,但是需要求解大型线性方程组,在移动端实时性要求难以满足。
特征点的提取与特征匹配的概述
特征点提取,输入一幅图片,提取出能代表这幅图片特征的一些点
这些点根据不同提特征的算法,具有一些性质
特征提取通常分为两步:
- 检测特征点 keypoints
- 计算描述子 descriptors
特征匹配: 通过计算的描述子,运用一定的度量方式,对描述子进行匹配,输出匹配成功的特征点对 maches
ORB 特征
BRISK 特征
Binary Robust Invariant Scalable Keypoints
2011年ICCV上提出来的一种特征提取算法,BRISK算法中构造了图像金字塔进行多尺度表达,因此具有较好的旋转不变性、尺度不变性,较好的鲁棒性等。
在图像配准应用中,速度比较:SIFT
AKAZE 特征
KAZE是EECV 2012年新提出来的特征点检测和描述算法,AKAZE是在KAZE基础上进行改进的. (Accelerated-KAZE)
作者目的在于如何将局部特征算法应用到移动设备(由于移动设备资源有限同时实时性要求较高),主要正对KAZE算法改进一下两点
- 1 利用非线性扩散滤波的优势获取低计算要求的特征,因此作者引入快速显示扩散数学框架FED来快速求解偏微分方程**。采用FED来建立尺度空间要比当下其它的非线性模式建立尺度空间都要快,同时比AOS更加准确。
- 2 引入一个高效的改进局部差分二进制描述符(M-LDB),较原始LDB增加了旋转与尺度不变的鲁棒性,结合FED构建的尺度空间梯度信息增加了独特性。
与SIFT、SURF算法相比,AKAZE算法更快同时与ORB、BRISK算法相比,可重复性与鲁棒性提升很大。
OpenCV3实现代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //time
// #include
// #include "extra.h" // use this if in OpenCV2
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
// FAST特征提取
void FAST_feature(const Mat& img, std::vector& keypoints);
//orb特征提取与匹配
void ORB_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1,
std::vector& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
//BRISK 特征提取与匹配
void BRISK_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1,
std::vector& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
//BRISK 特征提取与匹配
void AKAZE_feature_matches (
const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1,
std::vector& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches );
int main ( int argc, char** argv )
{
if ( argc != 3 )
{
cout<<"usage: inpute img1 img2"< fast_keypoints;
FAST_feature(img_1, fast_keypoints);
cout<<"use FAST_feature_matches found "< orb_keypoints_1, orb_keypoints_2;
vector orb_matches;
ORB_feature_matches ( img_1, img_2, orb_keypoints_1, orb_keypoints_2, orb_matches );
cout<<"use ORB_feature_matches found"< brisk_keypoint_1, brisk_keypoint_2;
vector brisk_matches;
BRISK_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, brisk_keypoint_1, brisk_keypoint_2, brisk_matches);
cout << "use BRISK_feature_matches found " << brisk_keypoint_1.size() << "keypoints" << endl;
Mat brisk_feature_image, brisk_matches_image;
drawKeypoints(img_1, brisk_keypoint_1, brisk_feature_image, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("BRISK feature image", brisk_feature_image);
drawMatches(img_1, brisk_keypoint_1, img_2 ,brisk_keypoint_2, brisk_matches, brisk_matches_image);
imshow("BRISK matches image", brisk_matches_image);
cout << "\r\n" << endl;
// AKAZE-FEATURE
vector akaze_keypoint_1, akaze_keypoint_2;
vector akaze_matches;
AKAZE_feature_matches(img_1, img_2, akaze_keypoint_1, akaze_keypoint_2, akaze_matches);
cout << "use akaze_feature_matches found " << akaze_keypoint_1.size() << "keypoints" << endl;
Mat akaze_feature_image, akaze_matches_image;
drawKeypoints(img_1, akaze_keypoint_1, akaze_feature_image, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT);
imshow("akaze feature image", akaze_feature_image);
drawMatches(img_1, akaze_keypoint_1, img_2 ,akaze_keypoint_2, akaze_matches, akaze_matches_image);
imshow("akaze matches image", akaze_matches_image);
cvWaitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void FAST_feature(const Mat& img, std::vector& keypoints)
{
const int threshold = 50;
const bool nonmaxSuppression = true;
const int type = FastFeatureDetector::TYPE_7_12;
Ptr fast_feature = FastFeatureDetector::create(threshold, nonmaxSuppression, type);
// Ptr fast_feature = FastFeatureDetector::create();
fast_feature->detect(img, keypoints);
}
void ORB_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1,
std::vector& keypoints_2,
std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
//-- 初始化
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
// used in OpenCV3
Ptr detector = ORB::create(500);
Ptr descriptor = ORB::create();
// use this if you are in OpenCV2
// Ptr detector = FeatureDetector::create ( "ORB" );
// Ptr descriptor = DescriptorExtractor::create ( "ORB" );
Ptr matcher = DescriptorMatcher::create ( "BruteForce-Hamming" );
//-- 第一步:检测 Oriented FAST 角点位置
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t1 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
detector->detect ( img_1,keypoints_1 );
detector->detect ( img_2,keypoints_2 );
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t2 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used1 = chrono::duration_cast>( t2-t1 );
cout << "ORB Feature detector time: " << time_used1.count() << "seconds" <compute ( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
descriptor->compute ( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t4 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used2 = chrono::duration_cast>( t4-t3 );
cout << "ORB Descriptor Extractor time: " << time_used2.count() << "seconds" < match;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t5 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
//BFMatcher matcher ( NORM_HAMMING );
matcher->match ( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match );
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t6 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used3 = chrono::duration_cast>( t6-t5 );
cout << "ORB Descriptor match time: " << time_used3.count() << "seconds" < max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
//当描述子之间的距离大于两倍的最小距离时,即认为匹配有误.但有时候最小距离会非常小,设置一个经验值30作为下限.
for ( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if ( match[i].distance <= max ( 2*min_dist, 30.0 ) )
{
matches.push_back ( match[i] );
}
}
printf ( "ORB-- All matches : %d \n", (int)match.size() );
printf ( "ORB-- filter match : %d \n", (int)matches.size() );
}
//BRISK 特征提取与匹配
void BRISK_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1, std::vector& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
// BRISK 初始化 关键点和描述子
Ptr brisk_feature = BRISK::create(40);
Ptr descriptor = BRISK::create();
Ptr matche = DescriptorMatcher::create( "BruteForce-Hamming" );
//提取关键点 计算描述子
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t7 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
brisk_feature->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
brisk_feature->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t8 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used4 = chrono::duration_cast>( t8-t7 );
cout << "BRISK Feature detector time: " << time_used4.count() << "seconds" <compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t4 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used2 = chrono::duration_cast>( t4-t3 );
cout << "BRISK Descriptor Extractor time: " << time_used2.count() << "seconds" < match;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t5 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
matche->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t6 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used3 = chrono::duration_cast>( t6-t5 );
cout << "BRISK Descriptor match time: " << time_used3.count() << "seconds" < max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "BRESK-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "BRESK-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
for(int j=0; j< descriptors_1.rows; j++)
{
if(match[j].distance < max (2*min_dist, 30.0))
matches.push_back(match[j]);
}
printf ( "BRESK-- All matches : %d \n", (int)match.size() );
printf ( "BRESK-- filter match : %d \n", (int)matches.size() );
}
//AKAZE 特征提取与匹配
void AKAZE_feature_matches ( const Mat& img_1, const Mat& img_2,
std::vector& keypoints_1, std::vector& keypoints_2, std::vector< DMatch >& matches )
{
// AKAZE 初始化 关键点和描述子
Ptr akaze_feature = AKAZE::create();
Ptr descriptor = AKAZE::create();
Ptr matche = DescriptorMatcher::create( "BruteForce-Hamming" );
//提取关键点 计算描述子
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t7 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
akaze_feature->detect(img_1, keypoints_1);
akaze_feature->detect(img_2, keypoints_2);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t8 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used4 = chrono::duration_cast>( t8-t7 );
cout << "AKAZE Feature detector time: " << time_used4.count() << "seconds" <compute(img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1);
descriptor->compute(img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t4 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used2 = chrono::duration_cast>( t4-t3 );
cout << "AKAZE Descriptor Extractor time: " << time_used2.count() << "seconds" < match;
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t5 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
matche->match(descriptors_1, descriptors_2, match);
chrono::steady_clock::time_point t6 = chrono::steady_clock::now();
chrono::duration time_used3 = chrono::duration_cast>( t6-t5 );
cout << "AKAZE Descriptor match time: " << time_used3.count() << "seconds" < max_dist) max_dist = dist;
}
printf ( "AKAZE-- Max dist : %f \n", max_dist );
printf ( "AKAZE-- Min dist : %f \n", min_dist );
for(int j=0; j< descriptors_1.rows; j++)
{
if(match[j].distance < max (2*min_dist, 30.0))
matches.push_back(match[j]);
}
printf ( "AKAZE-- All matches : %d \n", (int)match.size() );
printf ( "AKAZE-- filter match : %d \n", (int)matches.size() );
}
cmake_minimum_required( VERSION 2.8 )
project( vo1 )
set( CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release" )
set( CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-std=c++11 -O3" )
find_package( OpenCV 3.1 REQUIRED )
include_directories(
${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
add_executable( feature_extraction feature_extraction.cpp )
target_link_libraries( feature_extraction ${OpenCV_LIBS} )
对比实验
ORB Feature detector time: 0.344205seconds
ORB Descriptor Extractor time: 0.0210536seconds
ORB Descriptor match time: 0.00212562seconds
– Max dist : 95.000000
– Min dist : 7.000000
ORB-- All matches : 500
ORB-- filter match : 81
use ORB_feature_matches found500keypoints
================================================
BRISK Feature detector time: 0.0580227seconds
BRISK Descriptor Extractor time: 0.0406389seconds
BRISK Descriptor match time: 0.00707552seconds
BRESK-- Max dist : 183.000000
BRESK-- Min dist : 16.000000
BRESK-- All matches : 1117
BRESK-- filter match : 44
use BRISK_feature_matches found 1117keypoints
================================================
AKAZE Feature detector time: 0.121612seconds
AKAZE Descriptor Extractor time: 0.092555seconds
AKAZE Descriptor match time: 0.00412018seconds
AKAZE-- Max dist : 174.000000
AKAZE-- Min dist : 9.000000
AKAZE-- All matches : 773
AKAZE-- filter match : 73
use akaze_feature_matches found 773keypoints
-
ORB 特征提取
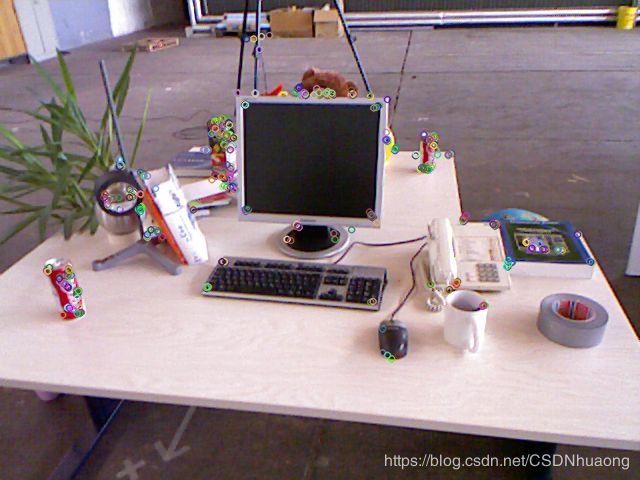

-
BRISK特征提取
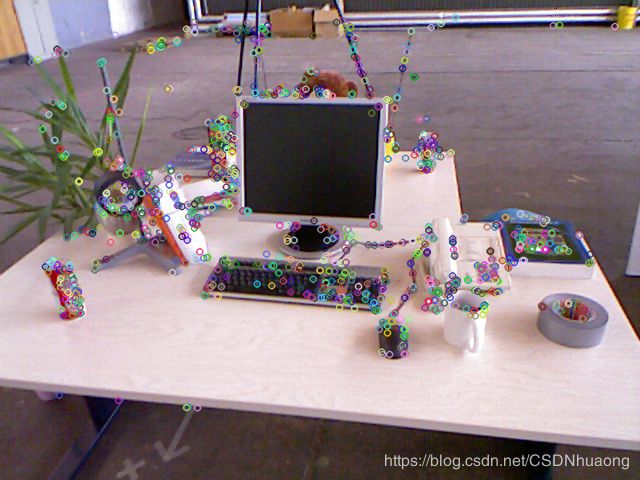

-
AKAZE特征提取
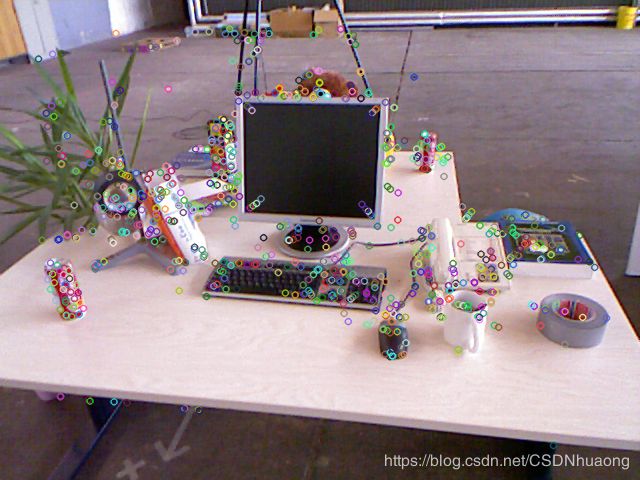

-
ORB 特征匹配
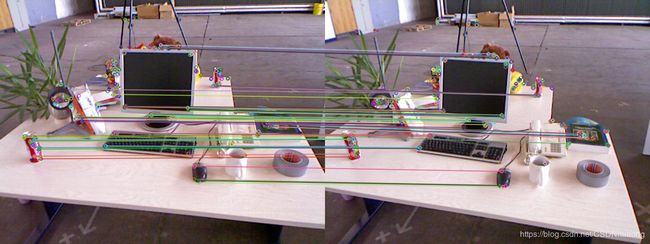
-
BRISK 特征匹配
-
AKAZE 特征匹配
参考文档
AKAZE算法分析



