-Flask开发轻博客(七):分页
作者:chen_h
微信号 & QQ:862251340
微信公众号:coderpai
目录
Flask开发轻博客(一):欢迎来到 Flask 的世界
Flask开发轻博客(二):Flask 模板
Flask开发轻博客(三):Flask 的 Web 表单
Flask开发轻博客(四):数据库
Flask开发轻博客(五):用户登录
Flask开发轻博客(六):用户首页和发布博客
Flask开发轻博客(七):分页
分页简介
应用程序看起来比任何时候都要好,但是还是有个问题。我们把所有关注者的 blog 展示在首页上。如果数量超过上千的话会发生些什么?或者上百万?你可以想象得到,处理如此大数据量的列表对象将会及其低效的。
相反,如果我们分组或者分页显示大量的 blog 呢?效率和效果会不会好一些了?
Flask-SQLAlchemy 天生就支持分页。比如如果我们想要得到用户的前三篇文章,我们可以这样做:
pagination = user.posts.paginate(1, PER_PAGE, False).itemspaginate 方法能够被任何查询调用。它接受三个参数:
- 页数,从 1 开始,
- 每一页的项目数,这里也就是说每一页显示的 blog 数,
- 错误标志。如果是 True,当请求的范围页超出范围的话,一个 404 错误将会自动地返回到客户端的网页浏览器。如果是 False,返回一个空列表而不是错误。
从 paginate 返回的值是一个 Pagination 对象。这个对象的 items 成员包含了请求页面项目(本文是指 blog )的列表。在 Pagination 对象中还有其它有帮助的东西,我们将在后面能看到。
现在让我们想想如何在我们的blog首页视图函数中实现分页。我们首先在配置文件中添加一些决定每页显示的 blog 数的配置项(新建文件app/utils.py)
PER_PAGE = 3在最后的应用程序中我们当然会使用每页显示的 blog 数大于 3,但是测试的时候用小的数量更加方便。
接着,让我们看看不同页的 URLs 是什么样的。我们知道 Flask 路由可以携带参数,因此我们在 URL 后添加一个后缀表示所需的页面
http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/1 <-- page #1 (default)
http://127.0.0.1:5000/user/1/page/1 <-- page #1这种格式的 URLs 能够轻易地通过在我们的视图函数中附加一个 route 来实现(文件 app/views.py)
from utils import PER_PAGE
@app.route('/user/', defaults={'page': 1}, methods=["POST", "GET"])
@app.route('/user//page/', methods=["POST", "GET"])
@login_required
def users(user_id, page):
form = AboutMeForm()
user = User.query.filter(User.id == user_id).first()
if user.id != current_user.id:
flash("sorry, you can only view your profile!", "error")
return redirect("/index")
if not user:
flash("The user is not exist.")
redirect("/index")
blogs = user.posts.paginate(page, PER_PAGE, False).items
return render_template("user.html",
form=form,
user=user,
blogs=blogs)
我们新的路由需要页面数作为参数,并且声明为一个整型。同样我们也需要在users函数中添加 page 参数,并且我们需要给它一个默认值。
现在我们已经有可用的页面数,我们能够很容易地把它与配置中的PER_PAGE一起传入posts查询。
现在试试输入不同的 URLs,看看分页的效果。但是,需要确保可用的 blog 数要超过三个,这样你就能够看到不止一页了!
页面导航
我们现在需要添加链接允许用户访问下一页以及/或者前一页,幸好这是很容易做的,Flask-SQLAlchemy 为我们做了大部分工作。
我们现在开始在视图函数中做一些小改变。在我们目前的版本中我们按如下方式使用paginate方法
blogs = user.posts.paginate(page, PER_PAGE, False).items通过上面这样做,我们可以获得返回自 paginate 的 Pagination 对象的 items 成员。但是这个对象还有很多其它有用的东西在里面,因此我们还是使用整个对象(文件 app/views.py)
pagination = Post.query.filter_by(
user_id = current_user.id
).order_by(
db.desc(Post.timestamp)
).paginate(page, PER_PAGE, False)为了适应这种改变,我们必须修改模板(文件 app/templates/user.html)
{% for blog in pagination.items %}
<p style="color:#ff6600;">{{ blog.body }}p>
<p style="color:#4c4c4c;">{{ blog.timestamp.strftime("%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S") }}p>
<hr />
{% endfor %}这个改变使得模版能够使用完全的 Paginate 对象。我们使用的这个对象的成员有:
- has_next:如果在目前页后至少还有一页的话,返回 True
- has_prev:如果在目前页之前至少还有一页的话,返回 True
- next_num:下一页的页面数
- prev_num:前一页的页面数
有了这些元素后,我们产生了这些(文件 app/templates/user.html)
{% if pagination %}
{% for blog in pagination.items %}
<p style="color:#ff6600;">{{ blog.body }}p>
<p style="color:#4c4c4c;">{{ blog.timestamp.strftime("%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S") }}p>
<hr />
{% endfor %}
{% if pagination.has_prev %} {# 分页的前端展示 #}
<a href="{{ url_for('users', user_id=current_user.id, page=pagination.prev_num) }}"><< preva>
{% else %}
<< None
{% endif %} |
{% if pagination.has_next %}
<a href="{{ url_for('users', user_id=current_user.id, page=pagination.next_num) }}">next >>a>
{% else %}
None >>
{% endif %}
{% else %}
<p style="color:blue;">the guy is so lazy.....p>
{% endif %}因此,我们有了两个链接。第一个就是名为 “prev”,这个链接使得我们能够访问上一页。第二个就是 “next”,它指向下一页。
当我们浏览第一页的时候,我们不希望看到有上一页的链接,因为这时候是不存在前一页。这是很容易被监测的,因为 posts.has_prev 会是 False。我们简单地处理这种情况,当用户浏览首页的时候,上一页会显示出来,但是不会有任何的链接。同样,下一页也是这样的处理方式。
用户信息页
首页上的分页已经完成了。然而,我们在用户信息页上显示了 blog。
改变是跟修改首页一样的。这是我们需要做的列表:
- 添加一个额外的路由获取页面数的参数
- 添加一个默认值为 1 的 page 参数到视图函数
- 用合适的数据库查询与分页代替伪造的 blog
- 更新模板使用分页对象
下面就是更新后的视图函数(文件 app/views.py)
@app.route('/user/', defaults={'page': 1}, methods=["POST", "GET"])
@app.route('/user//page/', methods=["POST", "GET"])
@login_required
def users(user_id, page):
form = AboutMeForm()
user = User.query.filter(User.id == user_id).first()
if user.id != current_user.id:
flash("sorry, you can only view your profile!", "error")
return redirect("/index")
if not user:
flash("The user is not exist.")
redirect("/index")
blogs = user.posts.paginate(page, PER_PAGE, False).items
pagination = Post.query.filter_by(
user_id = current_user.id).order_by(
db.desc(Post.timestamp)
).paginate(page, PER_PAGE, False)
return render_template("user.html",
form=form,
user=user,
blogs=blogs,
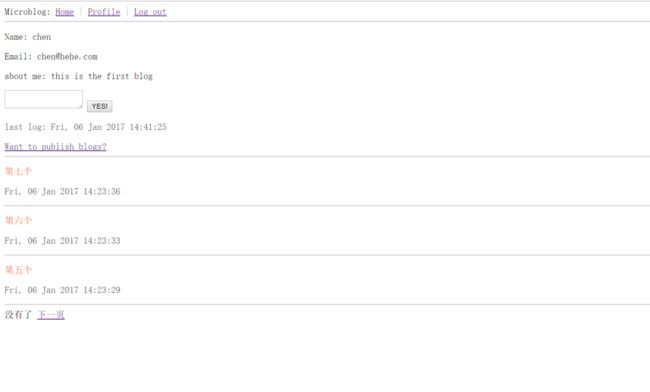
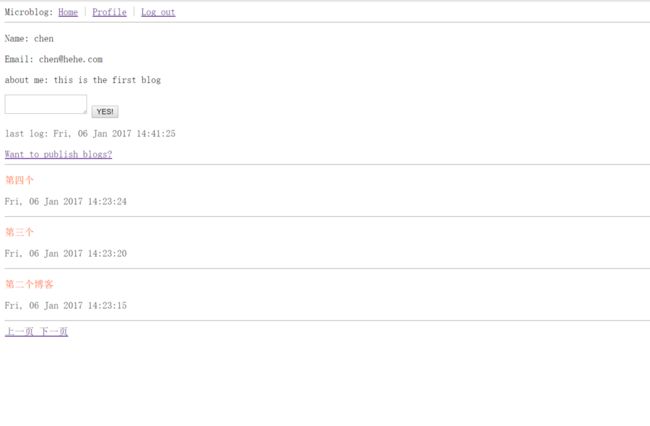
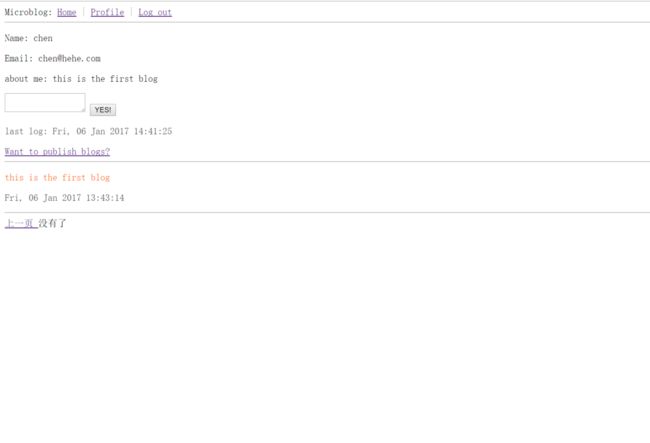
pagination=pagination)最终效果图
如果你正确运行上面的程序那么能得到以下的最终效果图。