keras CNN卷积核可视化,热度图
卷积核可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.models import load_model
# 将浮点图像转换成有效图像
def deprocess_image(x):
# 对张量进行规范化
x -= x.mean()
x /= (x.std() + 1e-5)
x *= 0.1
x += 0.5
x = np.clip(x, 0, 1)
# 转化到RGB数组
x *= 255
x = np.clip(x, 0, 255).astype('uint8')
return x
# 可视化滤波器
def kernelvisual(model, layer_target=1, num_iterate=100):
# 图像尺寸和通道
img_height, img_width, num_channels = K.int_shape(model.input)[1:4]
num_out = K.int_shape(model.layers[layer_target].output)[-1]
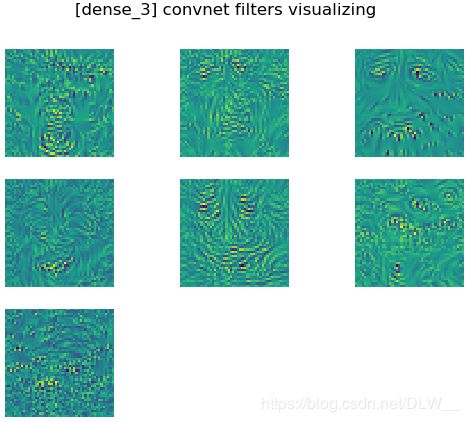
plt.suptitle('[%s] convnet filters visualizing' % model.layers[layer_target].name)
print('第%d层有%d个通道' % (layer_target, num_out))
for i_kernal in range(num_out):
input_img = model.input
# 构建一个损耗函数,使所考虑的层的第n个滤波器的激活最大化,-1层softmax层
if layer_target == -1:
loss = K.mean(model.output[:, i_kernal])
else:
loss = K.mean(model.layers[layer_target].output[:, :, :, i_kernal]) # m*28*28*128
# 计算图像对损失函数的梯度
grads = K.gradients(loss, input_img)[0]
# 效用函数通过其L2范数标准化张量
grads /= (K.sqrt(K.mean(K.square(grads))) + 1e-5)
# 此函数返回给定输入图像的损耗和梯度
iterate = K.function([input_img], [loss, grads])
# 从带有一些随机噪声的灰色图像开始
np.random.seed(0)
# 随机图像
# input_img_data = np.random.randint(0, 255, (1, img_height, img_width, num_channels)) # 随机
# input_img_data = np.zeros((1, img_height, img_width, num_channels)) # 零值
input_img_data = np.random.random((1, img_height, img_width, num_channels)) * 20 + 128. # 随机灰度
input_img_data = np.array(input_img_data, dtype=float)
failed = False
# 运行梯度上升
print('####################################', i_kernal + 1)
loss_value_pre = 0
# 运行梯度上升num_iterate步
for i in range(num_iterate):
loss_value, grads_value = iterate([input_img_data])
if i % int(num_iterate/5) == 0:
print('Iteration %d/%d, loss: %f' % (i, num_iterate, loss_value))
print('Mean grad: %f' % np.mean(grads_value))
if all(np.abs(grads_val) < 0.000001 for grads_val in grads_value.flatten()):
failed = True
print('Failed')
break
if loss_value_pre != 0 and loss_value_pre > loss_value:
break
if loss_value_pre == 0:
loss_value_pre = loss_value
# if loss_value > 0.99:
# break
input_img_data += grads_value * 1 # e-3
img_re = deprocess_image(input_img_data[0])
if num_channels == 1:
img_re = np.reshape(img_re, (img_height, img_width))
else:
img_re = np.reshape(img_re, (img_height, img_width, num_channels))
plt.subplot(np.ceil(np.sqrt(num_out)), np.ceil(np.sqrt(num_out)), i_kernal + 1)
plt.imshow(img_re) # , cmap='gray'
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
运行
model = load_model('train3.h5')
kernelvisual(model,-1) # 对最终输出可视化
kernelvisual(model,6) # 对第二个卷积层可视化
热度图
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from keras import backend as K
from keras.preprocessing import image
def heatmap(model, data_img, layer_idx, img_show=None, pred_idx=None):
# 图像处理
if data_img.shape.__len__() != 4:
# 由于用作输入的img需要预处理,用作显示的img需要原图,因此分开两个输入
if img_show is None:
img_show = data_img
# 缩放
input_shape = K.int_shape(model.input)[1:3] # (28,28)
data_img = image.img_to_array(image.array_to_img(data_img).resize(input_shape))
# 添加一个维度->(1, 224, 224, 3)
data_img = np.expand_dims(data_img, axis=0)
if pred_idx is None:
# 预测
preds = model.predict(data_img)
# 获取最高预测项的index
pred_idx = np.argmax(preds[0])
# 目标输出估值
target_output = model.output[:, pred_idx]
# 目标层的输出代表各通道关注的位置
last_conv_layer_output = model.layers[layer_idx].output
# 求最终输出对目标层输出的导数(优化目标层输出),代表目标层输出对结果的影响
grads = K.gradients(target_output, last_conv_layer_output)[0]
# 将每个通道的导数取平均,值越高代表该通道影响越大
pooled_grads = K.mean(grads, axis=(0, 1, 2))
iterate = K.function([model.input], [pooled_grads, last_conv_layer_output[0]])
pooled_grads_value, conv_layer_output_value = iterate([data_img])
# 将各通道关注的位置和各通道的影响乘起来
for i in range(conv_layer_output_value.shape[-1]):
conv_layer_output_value[:, :, i] *= pooled_grads_value[i]
# 对各通道取平均得图片位置对结果的影响
heatmap = np.mean(conv_layer_output_value, axis=-1)
# 规范化
heatmap = np.maximum(heatmap, 0)
heatmap /= np.max(heatmap)
# plt.matshow(heatmap)
# plt.show()
# 叠加图片
# 缩放成同等大小
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap, (img_show.shape[1], img_show.shape[0]))
heatmap = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)
# 将热图应用于原始图像.由于opencv热度图为BGR,需要转RGB
superimposed_img = img_show + cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap, cv2.COLORMAP_JET)[:,:,::-1] * 0.4
# 截取转uint8
superimposed_img = np.minimum(superimposed_img, 255).astype('uint8')
return superimposed_img, heatmap
# 显示图片
# plt.imshow(superimposed_img)
# plt.show()
# 保存为文件
# superimposed_img = img + cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap, cv2.COLORMAP_JET) * 0.4
# cv2.imwrite('ele.png', superimposed_img)
# 生成所有卷积层的热度图
def heatmaps(model, data_img, img_show=None):
if img_show is None:
img_show = np.array(data_img)
# Resize
input_shape = K.int_shape(model.input)[1:3] # (28,28,1)
data_img = image.img_to_array(image.array_to_img(data_img).resize(input_shape))
# 添加一个维度->(1, 224, 224, 3)
data_img = np.expand_dims(data_img, axis=0)
# 预测
preds = model.predict(data_img)
# 获取最高预测项的index
pred_idx = np.argmax(preds[0])
print("预测为:%d(%f)" % (pred_idx, preds[0][pred_idx]))
indexs = []
for i in range(model.layers.__len__()):
if 'conv' in model.layers[i].name:
indexs.append(i)
print('模型共有%d个卷积层' % indexs.__len__())
plt.suptitle('heatmaps for each conv')
for i in range(indexs.__len__()):
ret = heatmap(model, data_img, indexs[i], img_show=img_show, pred_idx=pred_idx)
plt.subplot(np.ceil(np.sqrt(indexs.__len__()*2)), np.ceil(np.sqrt(indexs.__len__()*2)), i*2 + 1)\
.set_title(model.layers[indexs[i]].name)
plt.imshow(ret[0])
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(np.ceil(np.sqrt(indexs.__len__()*2)), np.ceil(np.sqrt(indexs.__len__()*2)), i*2 + 2)\
.set_title(model.layers[indexs[i]].name)
plt.imshow(ret[1])
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
运行
from keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
from keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
model = VGG16(weights='imagenet')
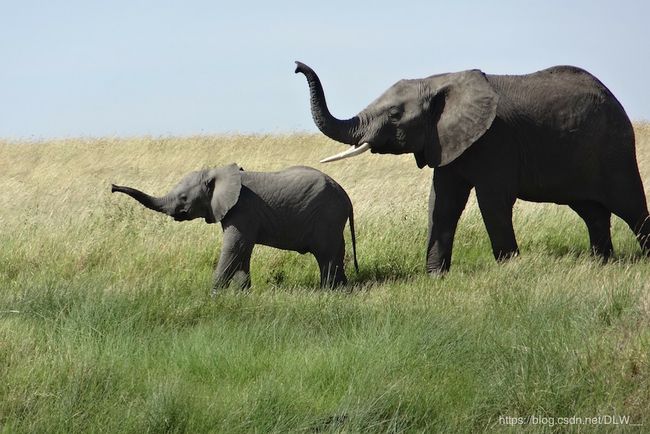
data_img = image.img_to_array(image.load_img('elephant.png'))
# VGG16预处理:RGB转BGR,并对每一个颜色通道去均值中心化
data_img = preprocess_input(data_img)
img_show = image.img_to_array(image.load_img('elephant.png'))
heatmaps(model, data_img, img_show)
结语
踩坑踩得我脚疼