Tensorflow深度学习之十:Tensorflow实现经典卷积神经网络AlexNet
本篇文章参考《Tensorflow实战Google深度学习框架》一书
之前接触了简单卷积神经网络,以后我们将利用Tensorflow提供的函数实现几个经典的卷积神经网络。
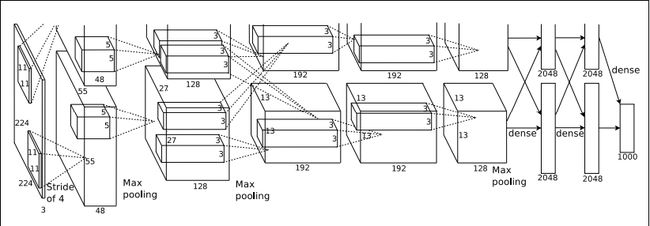
这里我们简单介绍一下AlexNet网络。
因为AlexNet训练时使用了两块GPU,因此这个结构图中不少组件都被拆成了两部分。现在我们GPU的显存可以放下全部模型数据,因此只考虑一块GPU的情况即可。
以下是利用Tensorflow代码实现AlexNet网络。
因为使用AlexNet训练一个训练集时间很长,这里我们只计算使用AlexNet向前和向后传播的时间。
from datetime import datetime
import tensorflow as tf
import math
import time
# 定义全局变量
# 训练批次的大小
batch_size = 32
# 训练批次的数目
num_batches = 100
# 输出当前操作的名称以及当前矩阵的尺寸
def print_activations(t):
print(t.op.name, " ", t.get_shape().as_list())
# 建立神经网络
def inference(image):
# 定义存储权重和偏置量的list
parameters = []
# 定义卷积层1,卷积核大小,偏置量等各项参数参考下面的程序代码,下同
with tf.name_scope("conv1") as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1, name="weights"))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(image, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding="SAME")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[64]), trainable=True, name="biases")
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
# 输出当前操作的信息,下同
print_activations(conv1)
# 将卷积核和偏置量加入到list中,下同
parameters += [kernel, biases]
pass
# LRN层
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9, beta=0.75, name="lrn1")
# 最大池化层
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1,3,3,1], strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="VALID", name="pool1")
# 输出最大池化层之后的信息
print_activations(pool1)
# 定义卷积层2
with tf.name_scope("conv2") as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5,5,64,192], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1, name="weights"))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[192]), trainable=True, name="biases")
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv2)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
pass
# LRN层
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name="lrn2")
# 最大池化层
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="VALID", name="pool2")
# 输出最大池化层之后的信息
print_activations(pool2)
# 定义卷积层3
with tf.name_scope("conv3") as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,192,384], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1, name="weights"))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[384]), trainable=True, name="biases")
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv3)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
pass
# 定义卷积层4
with tf.name_scope("conv4") as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,384,256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1, name="weights"))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[256]), trainable=True, name="biases")
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv4)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
pass
# 定义卷积层5
with tf.name_scope("conv5") as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3,3,256,256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1, name="weights"))
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[256]), trainable=True, name="biases")
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv5)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
pass
# 最大池化层
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1,3,3,1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding="VALID", name="pool5")
print_activations(pool5)
# 返回pool5,以及上面过程中所使用的所有卷积核和偏置量
return pool5, parameters
# 真正进行网络训练的,该函数评估AlexNet网络每轮的计算时间。
# session:Tensorflow的Session
# target:需要评测的算子
# info_string:测试的名称
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
# 定义预热轮数,它的作用是给程序热身,头几轮迭代有显存加载,cache命中等问题因此可以跳过,我们只考量10轮迭代之后的计算时间
num_steps_burn_in = 10
# 定义计算方差所需要使用的变量
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
# 记录开始时间
start_time = time.time()
# 训练
_ = session.run(target)
# 获取当前时间并减去开始时间,获取时间间隔
duration = time.time() - start_time
# 若是10轮迭代之后
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
# 每10轮迭代过程,输出一次结果
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' %(datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
# 计算均值
mn = total_duration / num_batches
# 计算偏差值
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' %(datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
def run_benchmark():
# 定义Tensorflow的默认Graph
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# 图片尺寸
image_size = 224
# 随机生成图片数据
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, image_size, image_size, 3], dtype = tf.float32, stddev = 1e-1))
# 点用函数建立网络
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
# 初始化所有的变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 建立Tensorflow的会话
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
# 正向传播网络数据
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, "Forward")
# 反向传播网络数据
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, "Forward-backward")
# 主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_benchmark()
pass运行结果如下:(关于运行时间的结果或有不同)
conv1 [32, 56, 56, 64]
pool1 [32, 27, 27, 64]
conv2 [32, 27, 27, 192]
pool2 [32, 13, 13, 192]
conv3 [32, 13, 13, 384]
conv4 [32, 13, 13, 256]
conv5 [32, 13, 13, 256]
pool5 [32, 6, 6, 256]
2017-07-29 10:23:32.195511: step 0, duration = 0.550
2017-07-29 10:23:37.698478: step 10, duration = 0.513
2017-07-29 10:23:43.202648: step 20, duration = 0.548
2017-07-29 10:23:48.734093: step 30, duration = 0.554
2017-07-29 10:23:54.180184: step 40, duration = 0.532
2017-07-29 10:23:59.744480: step 50, duration = 0.562
2017-07-29 10:24:05.343111: step 60, duration = 0.548
2017-07-29 10:24:10.830153: step 70, duration = 0.542
2017-07-29 10:24:16.422857: step 80, duration = 0.550
2017-07-29 10:24:21.971986: step 90, duration = 0.555
2017-07-29 10:24:26.811914: Forward across 100 steps, 0.552 +/- 0.013 sec / batch
2017-07-29 10:24:47.147143: step 0, duration = 1.849
2017-07-29 10:25:06.128335: step 10, duration = 1.920
2017-07-29 10:25:24.853938: step 20, duration = 1.937
2017-07-29 10:25:43.794501: step 30, duration = 1.795
2017-07-29 10:26:03.162755: step 40, duration = 1.942
2017-07-29 10:26:21.879098: step 50, duration = 1.846
2017-07-29 10:26:40.544190: step 60, duration = 1.913
2017-07-29 10:26:59.369070: step 70, duration = 1.838
2017-07-29 10:27:18.046394: step 80, duration = 1.806
2017-07-29 10:27:36.698052: step 90, duration = 1.862
2017-07-29 10:27:53.684294: Forward-backward across 100 steps, 1.884 +/- 0.071 sec / batch可以发现,先后传播所花费的时间大约是向前传播所花费时间的3倍多。