Kaggle神经网络实战:CNN实现手写数字辨识
简要介绍
- 本文是基于Kaggle入门项目Digit Recognizer的处理方案,在MINST数据集上训练可以识别手写数字的模型。项目链接
- 代码来自项目Kernels,使用tensorflow实现CNN网络,完整图文及代码请参照Kernel原文
代码实现
库的导入和常量定义
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cm as cm
import tensorflow as tf
LEARNING_RATE = 1e-4 #学习率
TRAINING_ITERATIONS = 2500 #训练次数
DROPOUT = 0.5 #dropout防止过拟合
BATCH_SIZE = 50 #每个训练批次大小
VALIDATION_SIZE = 2000
IMAGE_TO_DISPLAY = 10 #显示第10张图像数据预处理
通过CSV文件导入数据,数据格式为42000X785的矩阵,每行表示一条记录,一共42000张图片,每张图片采用28X28像素表示,第一列为延伸
data = pd.read_csv('../input/train.csv')图片处理
读入的数据以DataFrame格式保存,其中第一列为标签(stretched array),对其去掉第一列并去索引
images = data.iloc[:,1:].values
images = images.astype(np.float) #转换为浮点型
images = np.multiply(images,1.0/255.0) #压缩灰度值初始化图片相关属性变量
image_size = images.shape[1] #图片大小
image_width = image_height = np.ceil(np.sqrt(image_size)).astype(np.uint8)
#图片宽度和高度定义图像可视化函数
def display(img):
#(784) => (28X28)
one_image = img.reshape(image_width,image_height)
#不显示坐标轴
plt.axis('off')
#arg2:默认黑白图像
plt.imshow(one_image,cmap=cm.binary)
#函数测试
display(images[IMAGE_TO_DISPLAY])获得了4200X784的图像数组
标签处理
这里对原代码做了修改
取data的第一列即标签,展平,统计标签种类数
labels_flat = data.iloc[:,0].values
labels_count = np.unique(labels_flat).shape[0]
#np.unique(array)保留参数数组中不同的值,返回两个值
#1:不同的值组成的数组 2:这些值首次出现位置组成的数组编写函数,将标签转用独热码(one-hot)表示
# 0 => [1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
# 1 => [0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
# ...
# 9 => [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1]
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes):
#arg1:标签数组 arg2:去重标签数组
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
#统计标签数量
index_offset = np.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
#确定大小
labels_one_hot = np.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
#初始化0矩阵(42000X10)
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
#完成赋值
return labels_one_hot
labels = dense_to_one_hot(labels_flat, labels_count)
labels = labels.astype(np.uint8)获得了42000X10的标签数组
划分训练集与测试集
对图像和标签采用最简单的方法划分训练集与测试集
前2000份为测试集,后40000份为训练集
validation_images = images[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
validation_labels = labels[:VALIDATION_SIZE]
train_images = images[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
train_labels = labels[VALIDATION_SIZE:]
网络架构
激励函数使用ReLU,因为其易于训练,初始化为极小的正数避免神经元死亡的现象发生。
变量定义
权重和偏置变量
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)
#初始权重为随机正态分布
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)卷积层
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
#采用边缘补0的方法做卷积,步长为1池化层
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
#2X2划分大小,步长为2网络的输入和输出
x = tf.placeholder('float',shape=[None,imagesize])
#784维向量
y = tf.placeholder('float',shape=[None,labels_count])
#10维向量具体实现
网络采用2组卷积-池化层
第一组卷积层使用32个5X5的filter提取特征,池化层采用2X2的分割
28X28X1 => 28X28X32 =>14X14X32
#第一组卷积-池化层
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
#[width,height,channels,features]
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,image_width , image_height,1]
# (40000,784) => (40000,28,28,1)
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
#print (h_conv1.get_shape()) # => (40000, 28, 28, 32)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
#print (h_pool1.get_shape()) # => (40000, 14, 14, 32)
第二组卷积层使用64个5X5的filter提取特征,池化层采用2X2的分割
14X14X32 => 14X14X64 =>7X7X64
# second convolutional layer
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
#print (h_conv2.get_shape()) # => (40000, 14,14, 64)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
#print (h_pool2.get_shape()) # => (40000, 7, 7, 64)全连接层部分
对第二级池化层的输出做展平操作,与隐层神经元连接
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
#1024个隐层神经元
# (40000, 7, 7, 64) => (40000, 3136)
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
#print (h_fc1.get_shape()) # => (40000, 1024)dropout防止过拟合
# dropout
keep_prob = tf.placeholder('float')
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)隐层神经元连接输出层神经元,这里的激活函数使用softmax函数,输出网络判定最合适的分类
# 输出层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, labels_count])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([labels_count])
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)训练与测试
- 损失函数采用交叉熵(cross-entropy)
- 梯度下降优化法选用ADAM
# 损失函数
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y))
# 优化函数
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LEARNING_RATE).minimize(cross_entropy)
# 准确度评估函数
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, 'float'))
predict = tf.argmax(y,1)设置训练参数
epochs_completed = 0
index_in_epoch = 0
num_examples = train_images.shape[0]
# 按小批次(batch)处理数据
def next_batch(batch_size):
global train_images
global train_labels
global index_in_epoch
global epochs_completed
start = index_in_epoch
index_in_epoch += batch_size
# when all trainig data have been already used, it is reorder randomly
if index_in_epoch > num_examples:
# finished epoch
epochs_completed += 1
# shuffle the data
perm = np.arange(num_examples)
np.random.shuffle(perm)
train_images = train_images[perm]
train_labels = train_labels[perm]
# start next epoch
start = 0
index_in_epoch = batch_size
assert batch_size <= num_examples
end = index_in_epoch
return train_images[start:end], train_labels[start:end]
# start TensorFlow session
init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
sess.run(init)
# visualisation variables
train_accuracies = []
validation_accuracies = []
x_range = []
display_step=1在训练过程中追踪准确率
for i in range(TRAINING_ITERATIONS):
#get new batch
batch_xs, batch_ys = next_batch(BATCH_SIZE)
# check progress on every 1st,2nd,...,10th,20th,...,100th... step
if i%display_step == 0 or (i+1) == TRAINING_ITERATIONS:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x:batch_xs,
y_: batch_ys,
keep_prob: 1.0})
if(VALIDATION_SIZE):
validation_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={ x: validation_images[0:BATCH_SIZE],
y_: validation_labels[0:BATCH_SIZE],
keep_prob: 1.0})
print('training_accuracy / validation_accuracy => %.2f / %.2f for step %d'%(train_accuracy, validation_accuracy, i))
validation_accuracies.append(validation_accuracy)
else:
print('training_accuracy => %.4f for step %d'%(train_accuracy, i))
train_accuracies.append(train_accuracy)
x_range.append(i)
# increase display_step
if i%(display_step*10) == 0 and i:
display_step *= 10
# train on batch
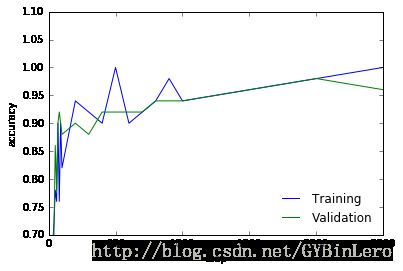
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys, keep_prob: DROPOUT})在测试集上计算误差,同时对两个准确度做可视化
# check final accuracy on validation set
if(VALIDATION_SIZE):
validation_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: validation_images,
y_: validation_labels,
keep_prob: 1.0})
print('validation_accuracy => %.4f'%validation_accuracy)
plt.plot(x_range, train_accuracies,'-b', label='Training')
plt.plot(x_range, validation_accuracies,'-g', label='Validation')
plt.legend(loc='lower right', frameon=False)
plt.ylim(ymax = 1.1, ymin = 0.7)
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.xlabel('step')
plt.show()