Data Crawling, Cleaning, and Visualization
作者: kevin
Crawling
关于使用scrapy进行爬虫的一些关键点:
- 我们需要知道有哪些爬取目标fields,并提前在items.py 里加入定义,例如下面这样
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class HospitalItem(scrapy.Item):
# Hospital Name
name = scrapy.Field()
# 成立时间 year established
establish_date = scrapy.Field()
# 医院等级 hospital level
level = scrapy.Field()
# 医疗机构类别
hosp_type = scrapy.Field()
# 经营性质
serv_property = scrapy.Field()在settings.py 中的设置基本都无需更改,除了
ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = True然后在项目中的spider directory 里新建一个爬虫py 文件,并创建专门的spider class,其中有这些需要注意的点:
推荐加入类似以下的headers来伪装爬虫,然后在call Request 的时候带上 header的选项就行
headers = { 'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/53.0.2785.143 Safari/537.36', }爬虫最主要的工作是要拿到所有需要爬取的信息的xpath,
对于没有这方面知识的人来说最简单的办法就是通过Chrome的inspect工具来获取,假设我们需要爬取商品的价格信息,例如下图操作:
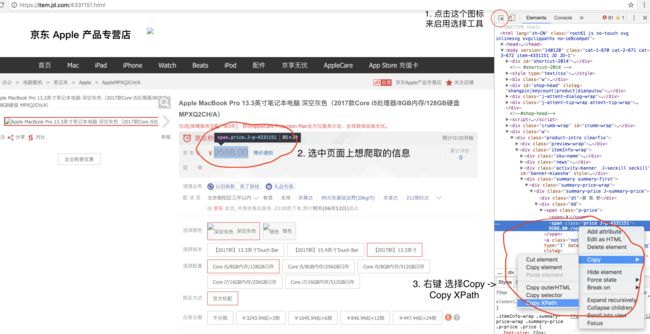
在此复制到价格的xpath信息后,在代码中用以下方式extract:def parse_dir_contents(self, response): item = HospitalItem() item['name'] = response.xpath( '/html/body/div[5]/div[3]/div[1]/ul/li[1]/text()').extract() item['establish_date'] = response.xpath( '/html/body/div[5]/div[3]/div[1]/ul/li[2]/text()').extract() ...如果需要对爬取到的文字信息通过regular expression 进行处理(例如去除newline char),可以通过以下类似的方式:
item['qq_acc'] = response.xpath( '//table[@class="link"]/tr[2]/td[2]/text()').re(r'\r\n\s*(.*)\r\n')如果需要爬取多层级信息,例如top level 是 目录,然后需要进入目录中每一个目标页面获取详细信息,这时候我们需要先爬取到目录页面中所有的目标网址,然后再iterate 每一个网址,并通过callback的方式call 专门爬取详细信息的function来实现,具体实例如下:
def parse(self, response): hospitals = response.xpath( '//div[@class="seek_int_left"]/h3/a/@href').extract() #爬取目录中所有项目的各自网址 for hospital in hospitals: # iterate 每一个网址 url = str(hospital) yield Request(url, callback=self.parse_dir_contents) #用callback的方式 call 具体爬取第二层页面的function urlhead = "http://yyk.qqyy.com/search_dplmhks0i" urltail = ".html" if self.i < 3018: #iterate 每一页目录 real = urlhead + str(self.i) + urltail self.i = self.i + 1 yield Request(real, headers=self.headers)
Cleaning and Modify
使用pandas做数据清洗的一些小笔记:
- 清洗简单的重复数据可以直接用 drop_duplicates
去除数据中例如tab,newline,等一些字符,可以使用replace进行替换,如下:
df = df.replace('\n','', regex=True)如果需要导出的数据都被双引号包裹,可以先把所有column的type 换成string,然后在导出的时候加上quoting的参数:
df.to_csv('test.csv',quoting=csv.QUOTE_NONNUMERIC)- 同时建议在用to_csv导出时,把index 设为 False,导出的数据就不会带上pandas自己index的column
- 字符模糊匹配,我用的是github上的fuzzywuzzy,它提供了几种不同模式的匹配,个人使用下来的感觉是它对中文字符的支持不够好,因为它单纯用的是Levenshtein Distance的algorithm来计算(github上的mingpipe是另外一个专门对中文进行匹配的,如果需要进行中文的模糊匹配,可以使用以上的工具)。
下面简单说说fuzzywuzzy的使用方式:
- 首先进行安装
pip3 install fuzzywuzzy[speedup]
然后import
# fuzz 比较两个string之间的 from fuzzywuzzy import fuzz # process是用来比较一个string和其他多个string之间的 from fuzzywuzzy import process- 下面是它提供的4种不同的匹配方式(output分数越高表示越相近,100表示一样):
- fuzz.ratio 比较整个string,以及单词的顺序
fuzz.ratio("this is a test", "this is a fun") #output 74
- fuzz.partial_ratio 只test string 的 subsections
fuzz.partial_ratio("this is a test", "test a is this") #output 57
- fuzz.token_sort_ratio 会忽略单词的顺序
fuzz.token_sort_ratio("this is a test", "is this a test") #output 100
- fuzz.token_set_ratio 会忽略重复的单词
fuzz.token_set_ratio("this is a test", "this is is a test") #output 100
- fuzz.ratio 比较整个string,以及单词的顺序
当我们进行一对多比较时,就要用到process.extract,例如:
choices = ['fuzzy fuzzy was a bear', 'is this a test', 'THIS IS A TEST'] process.extract("this is a test", choices, scorer=fuzz.ratio)对应的output会是:
[('THIS IS A TEST!!', 100), ('is this a test', 86), ('fuzzy fuzzy was a bear', 33)]对pandas df 中的数据我们可以通过类似以下方式来模糊匹配,假设我们要找出df中可能重复的地址:
lookups_addr = df[df.addr.notnull()].addr res = [(lookup_a,) + item for lookup_a in lookups_addr for item in process.extract(lookup_a, lookups_addr,limit=2)] df1 = pd.DataFrame(res, columns=["lookup", "matched", "score", "name"]) df1[(df1.score <100) & (df1.score >90)]- 首先进行安装
Visualization
Used Echarts for visualization, which is an open source JavaScript library by Baidu
Lots of good templates to choose from http://echarts.baidu.com/examples/
- Loading Data:
- 2 options:
- save large data as json file, and use JQuery to asynchronously get the data, and then load the data in ‘setOption’ (you need to write parser for this)
- Provide directly in code as var:good and easy for small sets of data
- loading animation:
- If data loading time is really long, we can provide a loading animation to notify users that the data is loading
- save large data as json file, and use JQuery to asynchronously get the data, and then load the data in ‘setOption’ (you need to write parser for this)
- 2 options:
myChart.showLoading();
$.get('data.json').done(function(data){
myChart.hideLoading();
myChart.setOption(...);
});- Adding Map
- If we want to exhibit data on the map, we need to include ‘geo’ or ‘bmap’ in the ‘setOption’, then setting relevant options
geo: {
map: 'china',
label: {
emphasis: {
show: false
}
},
roam: false,
itemStyle: {
normal: {
areaColor: '#404448',
borderColor: '#111'
},
emphasis: {
areaColor: '#2a333d'
}
},
silent: true, // do not responde to mouse click on map
}- Data Settings:
- We set data options in ‘series’, for visualizing data on map, usaully we choose ‘scatter’ or ‘effectScatter’ type to display data on map
series : [
{
name: 'Top 50',
type: 'effectScatter', // here we choose ''effectScatter
coordinateSystem: 'geo', // either 'geo' or 'bmap' depends on what you've specified above in setOptions
data: convertData(top50), // point data
symbolSize: function (val) {
return Math.sqrt(val[2]) / 10; // we can change symbol size based on its value
// if the range is too large, we can take
// their squareroot or even cubic root to reduce range
},
showEffectOn: 'render',
rippleEffect: {
brushType: 'stroke'
},
hoverAnimation: true,
label: {
normal: {
formatter: '{b}',
position: 'right',
show: false
}
},
itemStyle: {
normal: {
color: '#891d14',
shadowBlur: 5,
shadowColor: '#333'
}
},
zlevel: 1
},
]