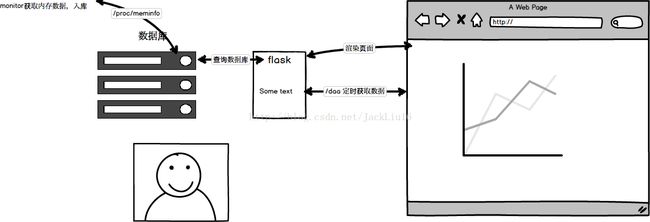
python 实时监控内存系统
一、监控文件monitor.py
import time
import MySQLdb as mysql
db = mysql.connect(user="reboot",passwd="reboot123",db="memory",host="localhost")
db.autocommit(True)
cur = db.cursor()
def getMem():
with open('/proc/meminfo') as f:
total = int(f.readline().split()[1])
free = int(f.readline().split()[1])
buffers = int(f.readline().split()[1])
cache = int(f.readline().split()[1])
mem_use = total-free-buffers-cache
t = int(time.time())
sql = 'insert into memory (memory,time) value (%s,%s)'%(mem_use/1024,t)
cur.execute(sql)
print mem_use/1024
#print 'ok'
while True:
time.sleep(1)
getMem()
二、flask
from flask import Flask,render_template,request
import MySQLdb as mysql
con = mysql.connect(user='reboot',passwd='reboot123',host='localhost',db='memory')
con.autocommit(True)
cur = con.cursor()
app = Flask(__name__)
import json
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
tmp_time = 0
@app.route('/data')
def data():
global tmp_time
if tmp_time>0:
sql = 'select * from memory where time>%s' % (tmp_time/1000)
else:
sql = 'select * from memory'
cur.execute(sql)
arr = []
for i in cur.fetchall():
arr.append([i[1]*1000,i[0]])
if len(arr)>0:
tmp_time = arr[-1][0]
return json.dumps(arr)
if __name__=='__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0',port=9092,debug=True)
三、前端
51reboot
hello world
chart:{
events:{
load:function(){
var series = this.series[0]
setInterval(function(){
$.getJSON('/data',function(res){
$.each(res,function(i,v){
series.addPoint(v)
})
})
},3000)
}
}
},series是一个数组
each() 方法为每个匹配元素规定要运行的函数。
提示:返回 false 可用于及早停止循环。
遍历处理data,可以是数组、DOM、json等,取决于直接给定或者ajax返回的类型
function (index, value)中index是当前元素的位置,value是值。
举几个例子:
// each处理一维数组
var arr1 = [ "aaa", "bbb", "ccc" ];
$.each(arr1, function(i,val){
alert(i);
alert(val);
});
// 处理json数据,例如ajax的返回值
var obj = { one:1, two:2, three:3};
$.each(obj, function(key, val) {
alert(key);
alert(val);
});
function ff(){
// 处理json数据,例如ajax的返回值
var obj = { one:[1,32,42], two:[3,323,32], three:[3,234,2342]};
$.each(obj, function(key, val) {
alert(key);
alert(val);
alert(val[2]);
});
setInterval() 方法可按照指定的周期(以毫秒计)来调用函数或计算表达式。
setInterval() 方法会不停地调用函数,直到 clearInterval() 被调用或窗口被关闭。由 setInterval() 返回的 ID 值可用作 clearInterval() 方法的参数。
提示: 1000 毫秒= 1 秒。
提示: 如果你只想执行一次可以使用 setTimeout() 方法。
每三秒(3000 毫秒)弹出 "Hello" :
setInterval
(
function
(
)
{
alert
(
"
Hello
"
)
;
}
,
3000
)
;
addPoint(添加一个数据点)
参数:
options:数据值(①可以是具体的一个Y轴数值,那么X轴坐标系统会随即分配一个;②可以设置一个数组,有着X和Y的数值,如:[xValue,yVlaue] 这样的形式;③可以设置一个Object(对象),详见 setData API;
radraw:是否设置(true/false)默认为true;
shift:默认为为false;
animation:是否动画(默认为true);
代码示例:
1.
//完整参数
2.
chart.series[0].addPoint(Math.random() * 100, true, true,true);
3.
//缺失参数
4.
chart.series[0].addPoint(Math.random() * 100);
# coding=utf-8
f = open('www_access_20140823.log')
res = {}
for l in f:
arr = l.split(' ')
# 获取ip url 和status
ip = arr[0]
url = arr[6]
status = arr[8]
# ip url 和status当key,每次统计+1
res[(ip,url,status)] = res.get((ip,url,status),0)+1
# 生成一个临时的list
res_list = [(k[0],k[1],k[2],v) for k,v in res.items()]
# 按照统计数量排序,打印前10
for k in sorted(res_list,key=lambda x:x[3],reverse=True)[:10]:
print k