kernel(十一)I2C
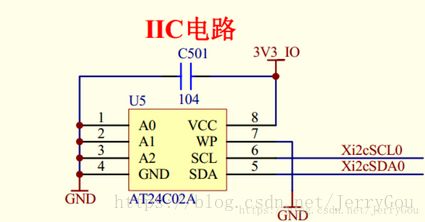
S5PV210 自带 3 个 I2C 模块, TQ210 使用的是 I2C0,挂接的是 AT24C02。
三星提供了 I2C 的总线驱动: drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c
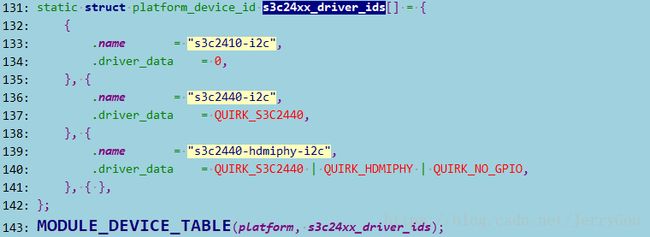
支持多种处理器,包括 s5pv210(和 s3c2440 兼容),同理,三星公用的 I2C 平台设备定义在arch/arm/plat-samsung/devs.c
默认为 s3c2410-i2c,在 arch/arm/mach-s5pv210/common.c 中的 s5pv210_map_io 函数中对其 name 属性进行了设置
操作 I2C 设备有两种方式:
一种使用内核提供的通用的驱动: drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c
一种使用具体的 I2C 设备的驱动: drivers/misc/eeprom/at24.c,它支持多个 eeprom 芯片
不管哪种方式,都需要注册 I2C 总线驱动: drivers/i2c/busses/i2c-s3c2410.c
在 mach-smdkv210.c 中已经添加到 smdkv210_devices 设备中了
配置内核支持 I2C 总线驱动
| Device Drivers ---> {*} I2C support ---> I2C Hardware Bus support ---> <*> S3C2410 I2C Driver |
方式一(i2c-dev.c)
要使用 drivers/i2c/i2c-dev.c 需要配置内核
| Device Drivers ---> <*> I2C support ---> <*> I2C device interface |
编译内核,运行测试
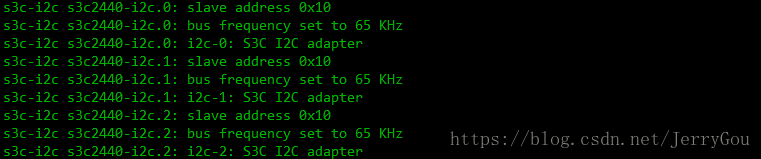
生成了 3 个 I2C 设备节点。
读写操作参考文档: Documentation/i2c/dev-interface
下载开源软件 i2c-tools,用它来操作这些字符设备。
http://linux.softpedia.com/get/System/Hardware/I2C-Tools-31650.shtml
只需要 i2c-tools 源码里面的一个头文件 include/linux/i2c-dev.h
编写测试程序 i2c_test.c
TQ210 开发板的 at24c02 接在 s5pv210 的 i2c0 上
| [root@$Louis210: /]# ./i2c_test /dev/i2c-0 0x50 w 0 1 [root@$Louis210: /]# ./i2c_test /dev/i2c-0 0x50 r 0 data:0x1 |
向 at24c02 的 0 地址写入 1 从 at24c02 的 0 地址读出 1 |
i2c_test.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "i2c-dev.h"
/* i2c_usr_test r addr
* i2c_usr_test w addr val
*/
void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("%s r addr\n", file);
printf("%s w addr val\n", file);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
unsigned char addr, data;
int dev_addr;
if ((argc != 5) && (argc != 6))
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
dev_addr = strtoul(argv[2], NULL, 0);
if (ioctl(fd, I2C_SLAVE, dev_addr) < 0)
{
perror("ioctl");
return -1;
}
addr = strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 0);
if (strcmp(argv[3], "r") == 0)
{
data = i2c_smbus_read_word_data(fd, addr);
printf("data:%#x\n", data);
}
else if ((strcmp(argv[3], "w") == 0) && (argc == 6))
{
data = strtoul(argv[5], NULL, 0);
i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(fd, addr, data);
}
else
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
i2c-dev.h
/*
i2c-dev.h - i2c-bus driver, char device interface
Copyright (C) 1995-97 Simon G. Vogl
Copyright (C) 1998-99 Frodo Looijaard
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
(at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston,
MA 02110-1301 USA.
*/
/* $Id: i2c-dev.h 5894 2010-12-12 13:22:29Z khali $ */
#ifndef LIB_I2CDEV_H
#define LIB_I2CDEV_H
#include
#include
/* -- i2c.h -- */
/*
* I2C Message - used for pure i2c transaction, also from /dev interface
*/
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* slave address */
unsigned short flags;
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x10 /* we have a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x01
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800
short len; /* msg length */
char *buf; /* pointer to msg data */
};
/* To determine what functionality is present */
#define I2C_FUNC_I2C 0x00000001
#define I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR 0x00000002
#define I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING 0x00000004 /* I2C_M_{REV_DIR_ADDR,NOSTART,..} */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PEC 0x00000008
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BLOCK_PROC_CALL 0x00008000 /* SMBus 2.0 */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_QUICK 0x00010000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE 0x00020000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE 0x00040000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA 0x00080000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE_DATA 0x00100000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA 0x00200000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_WORD_DATA 0x00400000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PROC_CALL 0x00800000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BLOCK_DATA 0x01000000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BLOCK_DATA 0x02000000
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK 0x04000000 /* I2C-like block xfer */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK 0x08000000 /* w/ 1-byte reg. addr. */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BYTE_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BYTE_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WORD_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_WORD_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_WORD_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_BLOCK_DATA | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_BLOCK_DATA)
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK (I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_READ_I2C_BLOCK | \
I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_WRITE_I2C_BLOCK)
/* Old name, for compatibility */
#define I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_HWPEC_CALC I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_PEC
/*
* Data for SMBus Messages
*/
#define I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX 32 /* As specified in SMBus standard */
#define I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_MAX 32 /* Not specified but we use same structure */
union i2c_smbus_data {
__u8 byte;
__u16 word;
__u8 block[I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_MAX + 2]; /* block[0] is used for length */
/* and one more for PEC */
};
/* smbus_access read or write markers */
#define I2C_SMBUS_READ 1
#define I2C_SMBUS_WRITE 0
/* SMBus transaction types (size parameter in the above functions)
Note: these no longer correspond to the (arbitrary) PIIX4 internal codes! */
#define I2C_SMBUS_QUICK 0
#define I2C_SMBUS_BYTE 1
#define I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA 2
#define I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA 3
#define I2C_SMBUS_PROC_CALL 4
#define I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA 5
#define I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_BROKEN 6
#define I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_PROC_CALL 7 /* SMBus 2.0 */
#define I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_DATA 8
/* ----- commands for the ioctl like i2c_command call:
* note that additional calls are defined in the algorithm and hw
* dependent layers - these can be listed here, or see the
* corresponding header files.
*/
/* -> bit-adapter specific ioctls */
#define I2C_RETRIES 0x0701 /* number of times a device address */
/* should be polled when not */
/* acknowledging */
#define I2C_TIMEOUT 0x0702 /* set timeout - call with int */
/* this is for i2c-dev.c */
#define I2C_SLAVE 0x0703 /* Change slave address */
/* Attn.: Slave address is 7 or 10 bits */
#define I2C_SLAVE_FORCE 0x0706 /* Change slave address */
/* Attn.: Slave address is 7 or 10 bits */
/* This changes the address, even if it */
/* is already taken! */
#define I2C_TENBIT 0x0704 /* 0 for 7 bit addrs, != 0 for 10 bit */
#define I2C_FUNCS 0x0705 /* Get the adapter functionality */
#define I2C_RDWR 0x0707 /* Combined R/W transfer (one stop only)*/
#define I2C_PEC 0x0708 /* != 0 for SMBus PEC */
#define I2C_SMBUS 0x0720 /* SMBus-level access */
/* -- i2c.h -- */
/* Note: 10-bit addresses are NOT supported! */
/* This is the structure as used in the I2C_SMBUS ioctl call */
struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data {
char read_write;
__u8 command;
int size;
union i2c_smbus_data *data;
};
/* This is the structure as used in the I2C_RDWR ioctl call */
struct i2c_rdwr_ioctl_data {
struct i2c_msg *msgs; /* pointers to i2c_msgs */
int nmsgs; /* number of i2c_msgs */
};
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_access(int file, char read_write, __u8 command,
int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data)
{
struct i2c_smbus_ioctl_data args;
args.read_write = read_write;
args.command = command;
args.size = size;
args.data = data;
return ioctl(file,I2C_SMBUS,&args);
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_quick(int file, __u8 value)
{
return i2c_smbus_access(file,value,0,I2C_SMBUS_QUICK,NULL);
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_read_byte(int file)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_READ,0,I2C_SMBUS_BYTE,&data))
return -1;
else
return 0x0FF & data.byte;
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_byte(int file, __u8 value)
{
return i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,value,
I2C_SMBUS_BYTE,NULL);
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_read_byte_data(int file, __u8 command)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_READ,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA,&data))
return -1;
else
return 0x0FF & data.byte;
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_byte_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 value)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
data.byte = value;
return i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BYTE_DATA, &data);
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_read_word_data(int file, __u8 command)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_READ,command,
I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA,&data))
return -1;
else
return 0x0FFFF & data.word;
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_word_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u16 value)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
data.word = value;
return i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_WORD_DATA, &data);
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_process_call(int file, __u8 command, __u16 value)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
data.word = value;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_PROC_CALL,&data))
return -1;
else
return 0x0FFFF & data.word;
}
/* Returns the number of read bytes */
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_read_block_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 *values)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
int i;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_READ,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA,&data))
return -1;
else {
for (i = 1; i <= data.block[0]; i++)
values[i-1] = data.block[i];
return data.block[0];
}
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_block_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 length, const __u8 *values)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
int i;
if (length > 32)
length = 32;
for (i = 1; i <= length; i++)
data.block[i] = values[i-1];
data.block[0] = length;
return i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_DATA, &data);
}
/* Returns the number of read bytes */
/* Until kernel 2.6.22, the length is hardcoded to 32 bytes. If you
ask for less than 32 bytes, your code will only work with kernels
2.6.23 and later. */
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_read_i2c_block_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 length, __u8 *values)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
int i;
if (length > 32)
length = 32;
data.block[0] = length;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_READ,command,
length == 32 ? I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_BROKEN :
I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_DATA,&data))
return -1;
else {
for (i = 1; i <= data.block[0]; i++)
values[i-1] = data.block[i];
return data.block[0];
}
}
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_write_i2c_block_data(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 length,
const __u8 *values)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
int i;
if (length > 32)
length = 32;
for (i = 1; i <= length; i++)
data.block[i] = values[i-1];
data.block[0] = length;
return i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_I2C_BLOCK_BROKEN, &data);
}
/* Returns the number of read bytes */
static inline __s32 i2c_smbus_block_process_call(int file, __u8 command,
__u8 length, __u8 *values)
{
union i2c_smbus_data data;
int i;
if (length > 32)
length = 32;
for (i = 1; i <= length; i++)
data.block[i] = values[i-1];
data.block[0] = length;
if (i2c_smbus_access(file,I2C_SMBUS_WRITE,command,
I2C_SMBUS_BLOCK_PROC_CALL,&data))
return -1;
else {
for (i = 1; i <= data.block[0]; i++)
values[i-1] = data.block[i];
return data.block[0];
}
}
#endif /* LIB_I2CDEV_H */
方式二(at24.c)
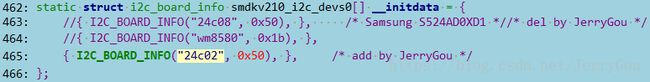
这种方式需要在 mach-smdkv210.c 中配置 at24c02 的平台数据
在 smdkv210_machine_init 中通过 i2c_register_board_info 将其注册到内核。
配置内核
| Device Drivers ---> Misc devices ---> EEPROM support ---> <*> I2C EEPROMs / RAMs / ROMs from most vendors |
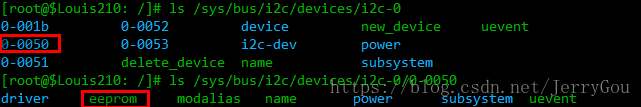
查看EEPROM内数据:hexdump -C eeprom
cat也具有同样的功能。可以通过echo修改内容:
通过读写这个 eeprom 属性文件,就能达到存取 at24c02
编程步骤:
1、首先使用 open 打开这个 eeprom
2、使用 lseek 定位文件位置,即定位 at24c02 的地址
3、使用 read 读或者使用 write 写
编写测试程序: at24_ctl.c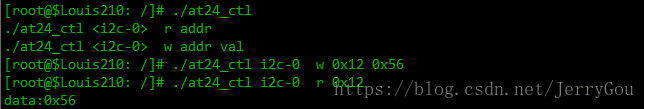
注意:在配置了第二种方式,使用 at24.c 后,不能使用第 1 种方式操作了![]()
at24_ctl.c
#include
#include
#include
#include
/* i2c_usr_test r addr
* i2c_usr_test w addr val
*/
void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("%s r addr\n", file);
printf("%s w addr val\n", file);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
unsigned char addr, data;
int dev_addr;
char bin_file_name[128];
if ((argc != 4) && (argc != 5))
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return -1;
}
sprintf(bin_file_name, "/sys/bus/i2c/devices/%s/0-0050/eeprom", argv[1]);
fd = open(bin_file_name, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
{
perror("open");
return -1;
}
addr = strtoul(argv[3], NULL, 0);
lseek(fd, addr, SEEK_SET);
if (strcmp(argv[2], "r") == 0)
{
read(fd, &data, 1);
printf("data:%#x\n", data);
}
else if ((strcmp(argv[2], "w") == 0) && (argc == 5))
{
data = strtoul(argv[4], NULL, 0);
write(fd, &data, 1);
}
else
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
close(fd);
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}