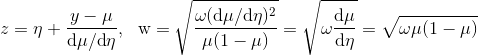R源代码研究——逻辑回归logistic regression
概述
R中逻辑回归用过很多次了,最近突然想对其源代码探究一二,以便更好理解该算法。此文章记录了R中逻辑回归的源代码的研究理解,如果有任何问题或错误欢迎各位读者提出。
建议:此篇文章主要以介绍代码实现为重点,会穿插理论知识。建议读者可以先大致了解逻辑回归理论再读此文。
R中实现逻辑回归可以通过调用glm函数实现,R中对该函数的使用方法及描述如下:
glm(formula, family = gaussian, data, weights, subset,
na.action, start = NULL, etastart, mustart, offset,
control = list(...), model = TRUE, method = "glm.fit",
x = FALSE, y = TRUE, contrasts = NULL, ...)glm is used to fit generalized linear models, specified by giving a symbolic description of the linear predictor and a description of the error distribution.
可见glm函数实际是用于广义线性模型的拟合,通过指定参数可以实现逻辑回归(实际逻辑回归属于广义线性回归的一种),简单介绍一下广义线性回归:
![]()
其中g(y)称为链接函数link function。其中逻辑回归的link function为
样例
以下是一个实现逻辑回归的代码样例,family = binomial(link = "logit) 即为指定link function的语句。先不考虑其他参数,通过这个简单的例子来研究其实现原理。
fit <- glm(label ~., family = binomial(link="logit"), data= train.yx,
control = list(maxit = 5000, epsilon = 0.00000001))family |
character: the family name. |
link |
character: the link name. |
linkfun |
function: the link. |
linkinv |
function: the inverse of the link function. |
variance |
function: the variance as a function of the mean. |
dev.resids |
function giving the deviance residuals as a function of |
aic |
function giving the AIC value if appropriate (but |
mu.eta |
function: derivative |
initialize |
expression. This needs to set up whatever data objects are needed for the family as well as |
validmu |
logical function. Returns |
valideta |
logical function. Returns |
simulate |
(optional) function |
debug该行代码进入glm函数,函数中赋值、传参等操作代码不讨论,主要讨论与实现相关的核心功能代码。下面这句代码意为调用“method”这个函数,后面为函数参数。R中这样介绍method参数:the method to be used in fitting the model. The default method "glm.fit" uses iteratively reweighted least squares (IWLS)。由于我们没有指定method,那么此时method即为glm.fit。注意这句话后半句说该method用iteratively reweighted least squares (IWLS)方法,也叫IRLS。这里是R中glm实现逻辑回归与一般对逻辑回归介绍不同的地方。一般书籍或文章介绍的逻辑回归求解时的cost function是对数似然函数,而glm.fit则是用IWLS方法,译为“迭代加权最小二乘法”。它与线性回归的求解方法采用的最小二乘法原理类似。
fit <- eval(call(if (is.function(method)) "method" else method,
x = X, y = Y, weights = weights, start = start, etastart = etastart,
mustart = mustart, offset = offset, family = family,
control = control, intercept = attr(mt, "intercept") > 0L))glm.fit(x, y, weights = rep(1, nobs),
start = NULL, etastart = NULL, mustart = NULL,
offset = rep(0, nobs), family = gaussian(),
control = list(), intercept = TRUE)1)参数初始化
conv <- FALSE #是否达到收敛的标志
nobs <- NROW(y) # number of objects,观测数目即样本数量
nvars <- ncol(x) # number of variables, 变量个数
weights <- rep.int(1, nobs)
offset <- rep.int(0, nobs)2)相关函数初始化
variance <- family$variance # function (mu) mu * (1 - mu)
linkinv <- family$linkinv #the inverse of the link function.
dev.resids <- family$dev.resids
aic <- family$aic
mu.eta <- family$mu.eta
if (is.null(mustart)) {
eval(family$initialize)
}初始化函数时,实际部分函数是通过调用C代码实现。如在R控制台输入family$linkinv,输出信息如下:
function (eta)
.Call(C_logit_linkinv, eta)
调用了名为C_logit_linkinv的函数,从CRAN上下载R的源代码可以在代码目录“R-3.5.2/src/library/stats/src/family.c”找到名为family.c的C代码文件,该C文件里面包含了family的部分函数定义。
初始化参数:mustart
# family$initialize: expression, not function
if (NCOL(y) == 1) {
if (is.factor(y))
y <- y != levels(y)[1L]
n <- rep.int(1, nobs)
y[weights == 0] <- 0
if (any(y < 0 | y > 1))
stop("y values must be 0 <= y <= 1")
mustart <- (weights * y + 0.5)/(weights + 1) # 求y与0.5的加权平均,二者的权重分别为weights、1
m <- weights * y
if (any(abs(m - round(m)) > 0.001))
warning("non-integer #successes in a binomial glm!") #暂时不知道此处是何意,望知道者告知
}
else if (NCOL(y) == 2) { # 先不管此种情况
if (any(abs(y - round(y)) > 0.001))
warning("non-integer counts in a binomial glm!")
n <- y[, 1] + y[, 2]
y <- ifelse(n == 0, 0, y[, 1]/n)
weights <- weights * n
mustart <- (n * y + 0.5)/(n + 1)
}
else stop("for the 'binomial' family, y must be a vector of 0 and 1's\nor a 2 column matrix where col 1 is no. successes and col 2 is no. failures")
})初始化参数:coefold(模型系数beta的某次迭代前的值)、eta (beta*x)
coefold <- NULL
eta <- family$linkfun(mustart)
mu <- linkinv(eta)
devold <- sum(dev.resids(y, mu, weights))
boundary <- conv <- FALSEfor (iter in 1L:control$maxit) {
good <- weights > 0
varmu <- variance(mu)[good]
if (anyNA(varmu))
stop("NAs in V(mu)")
if (any(varmu == 0))
stop("0s in V(mu)")
mu.eta.val <- mu.eta(eta)
if (any(is.na(mu.eta.val[good])))
stop("NAs in d(mu)/d(eta)")
good <- (weights > 0) & (mu.eta.val != 0)
if (all(!good)) {
conv <- FALSE
warning(gettextf("no observations informative at iteration %d",
iter), domain = NA)
break
}
z <- (eta - offset)[good] + (y - mu)[good]/mu.eta.val[good]
w <- sqrt((weights[good] * mu.eta.val[good]^2)/variance(mu)[good])
fit <- .Call(C_Cdqrls, x[good, , drop = FALSE] *
w, z * w, min(1e-07, control$epsilon/1000),
check = FALSE)
if (any(!is.finite(fit$coefficients))) {
conv <- FALSE
warning(gettextf("non-finite coefficients at iteration %d",
iter), domain = NA)
break
}
if (nobs < fit$rank)
stop(sprintf(ngettext(nobs, "X matrix has rank %d, but only %d observation",
"X matrix has rank %d, but only %d observations"),
fit$rank, nobs), domain = NA)
start[fit$pivot] <- fit$coefficients
eta <- drop(x %*% start)
mu <- linkinv(eta <- eta + offset)
dev <- sum(dev.resids(y, mu, weights))
if (control$trace)
cat("Deviance = ", dev, " Iterations - ", iter,
"\n", sep = "")
boundary <- FALSE
if (!is.finite(dev)) {
if (is.null(coefold))
stop("no valid set of coefficients has been found: please supply starting values",
call. = FALSE)
warning("step size truncated due to divergence",
call. = FALSE)
ii <- 1
while (!is.finite(dev)) {
if (ii > control$maxit)
stop("inner loop 1; cannot correct step size",
call. = FALSE)
ii <- ii + 1
start <- (start + coefold)/2
eta <- drop(x %*% start)
mu <- linkinv(eta <- eta + offset)
dev <- sum(dev.resids(y, mu, weights))
}
boundary <- TRUE
if (control$trace)
cat("Step halved: new deviance = ", dev, "\n",
sep = "")
}
if (!(valideta(eta) && validmu(mu))) {
if (is.null(coefold))
stop("no valid set of coefficients has been found: please supply starting values",
call. = FALSE)
warning("step size truncated: out of bounds",
call. = FALSE)
ii <- 1
while (!(valideta(eta) && validmu(mu))) {
if (ii > control$maxit)
stop("inner loop 2; cannot correct step size",
call. = FALSE)
ii <- ii + 1
start <- (start + coefold)/2
eta <- drop(x %*% start)
mu <- linkinv(eta <- eta + offset)
}
boundary <- TRUE
dev <- sum(dev.resids(y, mu, weights))
if (control$trace)
cat("Step halved: new deviance = ", dev, "\n",
sep = "")
}
if (abs(dev - devold)/(0.1 + abs(dev)) < control$epsilon) {
conv <- TRUE
coef <- start
break
}
else {
devold <- dev
coef <- coefold <- start
}
}核心代码如下,调用lm.c文件中的C_Cdqrls函数
z <- (eta - offset)[good] + (y - mu)[good]/mu.eta.val[good]
w <- sqrt((weights[good] * mu.eta.val[good]^2)/variance(mu)[good])
fit <- .Call(C_Cdqrls, x[good, , drop = FALSE] *
w, z * w, min(1e-07, control$epsilon/1000),
check = FALSE)
函数 SEXP Cdqrls(SEXP x, SEXP y, SEXP tol, SEXP chk)用于求解
![]() ,其中:
,其中:
z是利用牛顿法求方程f(eta)=y-linkinv(eta)=0的解的迭代公式:
即转化为一般的线性回归问题![]() ,求解系数
,求解系数![]() ,调用Cdqrls(采用IRLS方法)求解该问题。
,调用Cdqrls(采用IRLS方法)求解该问题。
Cdqrls函数又调用Fortran文件dqrls.f,该文件再调用两个f文件:dqrdc2.f、dqrsl.f。其中:
| f文件 | 说明 | 备注 |
| dqrdc2.f | uses householder transformations to compute the qr factorization of an n by p matrix x. | qr分解 |
| dqrsl.f | applies the output of dqrdc to compute coordinate transformations, projections, and least squares solutions. formed from columnns jpvt(1), ... ,jpvt(k) of the original n x p matrix x that was input to dqrdc (if no pivoting was done, xk consists of the first k columns of x in their original order). dqrdc produces a factored orthogonal matrix q and an upper triangular matrix r such that xk = q * (r) |
ouput b contains the solution of the least squares problem minimize norm2(y- xk*b) |
dqrdc2 uses householder transformations to compute the qr factorization of an n by p matrix x.
qrsl applies the output of dqrdc to compute coordinate transformations, projections, and least squares solutions.
for k .le. min(n,p), let xk be the matrix
xk = (x(jpvt(1)),x(jpvt(2)), ... ,x(jpvt(k)))
formed from columnns jpvt(1), ... ,jpvt(k) of the original n x p matrix x that was input to dqrdc (if no pivoting was done, xk consists of the first k columns of x in their original order). dqrdc produces a factored orthogonal matrix q and an upper triangular matrix r such that
xk = q * (r)
(0)
this information is contained in coded form in the arrays x and qraux.
| 英文解释 | 备注 | |
| qr | contains the output array from dqrdc2.namely the qr decomposition of x stored in compact form. | 分解的结果 |
| coefficients | contains the solution vectors with rows permuted in the same way as the columns of x. components corresponding to columns not used are set to zero. | 其次迭代得到的系数,即式中的b |
| residuals | contains the residual vectors y-x*b. | 残差矩阵,y-x*b |
| effects | qty contains the vectors q y. note that the initial p elements of this vector are permuted in the same way as the columns of x. | |
| rank | contains the number of columns of x judged to be linearly independent, i.e., "the rank" | |
| pivot | has its contents permuted as described above | |
| qraux | qraux contains further information required to recover the orthogonal part of the decomposition. | |
| tol | tolerance | |
| pivoted | jpvt(j) contains the index of the column of the original matrix that has been interchanged into the j-th column. Consequently, jpvt[] codes a permutation of 1:p; it is called 'pivot' in R | |
(to be continued)