数据结构与算法 学习笔记(7):二叉树和树
数据结构与算法 学习笔记(7):二叉树和树
本次文章主要记录了最近在LeetCode上刷的有关与二叉树和树的题目,主要涉及深度优先、广度优先、递归与非递归,并给出了算法和算法分析,如有错漏或更好的解法,欢迎到文末github中提交RP。
注:题号与LeetCode对应
题目1:100. Same Tree
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
"""
方法1: 深度优先 递归实现
方法2: 深度优先 栈实现
方法3: 广度优先 队列实现
注意:广度优先 没有合适的递归实现,非要递归也没有意义。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isSameTree(self, p, q):
"""
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
# # method 1: recursion DFS
# if not p and not q:
# return True
# if p and q:
# if p.val == q.val and self.isSameTree(p.left, q.left) and self.isSameTree(p.right, q.right):
# return True
# else:
# return False
# # method 2: DFS with stack
# stack = [(p, q)]
# while stack:
# n1, n2 = stack.pop()
# if n1 and n2 and n1.val == n2.val:
# stack.append((n1.right, n2.right))
# stack.append((n1.left, n2.left))
# elif not n1 and not n2:
# continue
# else:
# return False
# return True
# method 3: BFS with queue
queue = [(p, q)]
while queue:
n1, n2 = queue.pop(0)
if n1 and n2 and n1.val == n2.val:
queue.append((n1.left, n2.left))
queue.append((n1.right, n2.right))
elif not n1 and not n2:
continue
else:
return False
return True
题目2:101. Symmetric Tree
Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
"""
方法1:采用递归的思想
0.特殊情况:树为空,按题意返回True
1.不为空,则判断其左右子树是否镜像
2.递归判断镜像与否
完成!
时间复杂度:O(n),要遍历所有结点。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isSymmetric(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
# method 1 recursion
if root is None: #空树与否
return True
else:
return self.isMirror(root.left, root.right)
def isMirror(self, left, right):
if left is None and right is None: #左右子树存在与否
return True
if left is None or right is None:
return False
if left.val == right.val: # 存在且相等 递归判断左子树和右子树是否镜像
outPair = self.isMirror(left.left, right.right)
inPiar = self.isMirror(left.right, right.left)
return outPair and inPiar
else:
return False
题目3:104. Maximum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.

"""
method 1: 递归
0. 判空,返回树深为0
1. 非空,返回 1 + 子树深度(取左右子树中深度最深的那个数字)
2. 求子树深度:
判空,返回子树深度为 0,总深度为 1+0 =1
非空,返回 1 + 该子树的子树的深度(取左右子树相比较深的)
3. 依此递归实现
method 2: 栈 非递归
method 3: 队列 非递归
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def maxDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
# method 1: recursion
# if not root:
# return 0
# return 1 + max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))
# # method 2 : stack
# if not root:
# return 0
# tstack, h = [root], 0
# while tstack:
# nextlevel = []
# while tstack:
# top = tstack.pop()
# if top.left:
# nextlevel.append(top.left)
# if top.right:
# nextlevel.append(top.right)
# tstack = nextlevel
# h += 1
# return h
# method 3 : queue
if not root:
return 0
queue, h = [root], 0
while queue:
nextlevel = []
while queue:
top = queue.pop(0)
if top.left:
nextlevel.append(top.left)
if top.right:
nextlevel.append(top.right)
queue = nextlevel
h += 1
return h
题目4:107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II
Given a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
"""
目标: 要输出得到每一层构成的list的list。
难点: 广度优先遍历,在遍历每一层的过程中要保存当前层的所有结点的值构成的list,然后和其他层的list构成嵌套的list
0.要返回的list用res表示,data表示每层的list
1.判空
2.queue在广度优先遍历中保存遍历的数据,ncount用来记录每一层的结点的个数
3.ncount初始化为当前层结点个数(queue的长度),每次遍历了一个结点,ncount减1,直至减为0,
然后重新初始化ncount
4.把data加入到res中,待返回。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def levelOrderBottom(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res,data=[],[]
if not root:
return res
queue=[]
queue.append(root)
nCount=1#记录每层节点数
while queue:
node=queue.pop(0)
data+=[node.val]#保存每层节点的值构成的list
nCount-=1
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
if nCount==0:
res=[data]+res #由每层list构成的大list
data=[]
nCount=len(queue)
return res
题目5:108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
"""
目标:根据升序数组,构造二叉搜索树
特点:二叉搜素树,每个结点的左子结点小于它,右子结点大于它
思想:
1.找点已排序好的数组的中间结点,做根结点,其左边的数均小于它,右边的数均大于它
2.左边的序列同样抽出中间结点,作为根结点的左子结点;右边序列抽出中间结点,作为根结点的右子结点
3.左子结点和右子结点 按上述过程,继续递归。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def sortedArrayToBST(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
# # method 1
# if not nums:
# return None
# middle = len(nums)//2
# root = TreeNode(nums[middle])
# root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[:middle])
# root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(nums[middle+1:])
# return root
# method 2 :
#Time: O(n)
# Space: O(n) in the case of skewed binary tree.
def convert(left, right):
if left > right:
return None
mid = (left + right) // 2
node = TreeNode(nums[mid])
node.left = convert(left, mid - 1)
node.right = convert(mid + 1, right)
return node
return convert(0, len(nums) - 1)
题目6:110. Balanced Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.

"""
分析:需要用到深度优先搜素,递归实现
1.根结点若为空,返回True
2.不空,计算左子树深度,计算右子树深度,相差大于1,返回 -1(再返回False)
3.计算子树的深度时,用递归实现,一旦发现某层左右子树深度相差1以上,dfs时则上面的每层都返回-1,isBalanced最终会返回False.
4.若dfs返回的是-1,返回False;否则,返回True
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
def dfs(root):
if root is None:
return 0
left_depth = dfs(root.left)
right_depth = dfs(root.right)
# left_depth == -1,说明在更深一层中,左右的深度差已经大于1了,深度置-1,表示非平衡
if left_depth == -1 or right_depth == -1 or abs(left_depth - right_depth) > 1:
return -1
return 1 + max(left_depth, right_depth) # 返回当前树的深度
return dfs(root) != -1 # 成立说明平衡
题目7:111. Minimum Depth of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.

"""
思路:和计算树的最大深度一样,采用深度优先搜素
分析:不同的是,由于是计算最小深度,我们dfs返回的是左右子树深度中更小的那个,再+1
注意:特殊情况,按题意,当一个结点没有左(右)子树,那么它的子树的最小深度应为右(左)子树深度,并非是0。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def minDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if root == None:
return 0
def dfs(tn): #深度优先计算深度
if tn is None:
return 0
left_dp = dfs(tn.left)
right_dp = dfs(tn.right)
if tn.left==None or tn.right==None:#这句是判断特殊情况的,当没有左或右分支
return max(left_dp,right_dp) + 1
return 1 + min(left_dp,right_dp) #这句是正常的判断最小深度
return dfs(root)
题目8:112. Path Sum
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.

"""
思想:DFS 搜索,增stack中不仅要加入结点,还要加入搜素到当前结点时的路径和。
注:BFS 和DFS就把栈换成队列,从队列头部弹出即可。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
#method 1
if not root:
return False
stack = [(root, root.val)]
while stack:
curr, val = stack.pop()
if not curr.left and not curr.right:
if val == sum:
return True
if curr.right:
stack.append((curr.right, val+curr.right.val))
if curr.left:
stack.append((curr.left, val+curr.left.val))
return False
# #method 2
# if not root:
# return False
# queue = [(root, root.val)]
# while queue:
# curr, val = queue.pop(0)
# if not curr.left and not curr.right:
# if val == sum:
# return True
# if curr.right:
# queue.append((curr.right, val+curr.right.val))
# if curr.left:
# queue.append((curr.left, val+curr.left.val))
# return False
题目9:226. Invert Binary Tree
"""
分析:将左右子树反转
方法:首先根结点判空;不空时,交换当前结点左右子树,左右子树同样递归实现交换。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def invertTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root:
return None
temp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = temp
self.invertTree(root.left)
self.invertTree(root.right)
return root
题目10:235. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Search Tree
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
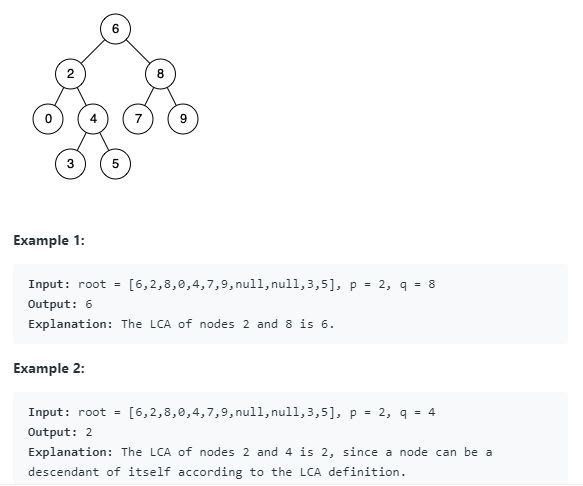
"""
目标:找p和q的最近公共祖先
分析:
0.设置根结点为当前结点
1.如果p和q都大于当前的结点,说明p和q在当前结点右子树中,设置当前结点为当前结点的右子结点
2.如果p和q都小于当前的结点,说明p和q在当前结点左子树中,设置当前结点为当前结点的左子结点
3.如果不满足上述两个条件之一,那么当前结点就是p和q的祖先
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not root:
return False
if p.val > root.val and q.val > root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
if p.val < root.val and q.val < root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)
else:
return root
题目11:257. Binary Tree Paths
Given a binary tree, return all root-to-leaf paths.

"""
分析:此题与“路径和”的题类似,只不过一个是保存和,一个是保存路径。
方案:
0.采用深度优先的非递归方式。
1.用栈保存遍历的结点和当前结点的访问路径,用data保存每个路径,用res返回所有路径的列表。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[str]
"""
if not root:
return []
stack = [(root,str(root.val))]
data = ""
res = []
while stack:
node,data = stack.pop()
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left, data + '->' + str(node.left.val)))
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right, data +"->" + str(node.right.val)))
if not node.left and not node.right:
res.append(data)
return res
题目12:404. Sum of Left Leaves
Find the sum of all left leaves in a given binary tree.
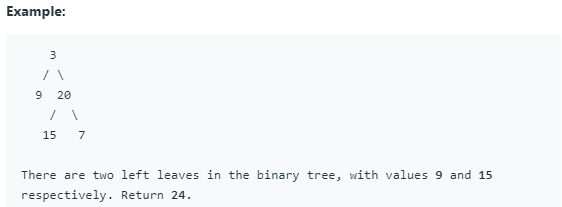
"""
方法1:递归,主要是if 语句的描述
方法2:非递归,深度优先,用栈 用sums保存每一个左叶结点的值,lst保存这些值到列表,最后返回lst中值的和
方法3:若广度优先,用队列。
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def sumOfLeftLeaves(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
# # method 1: recursion
# if not root:
# return 0
# if root.left and not root.left.left and not root.left.right:
# return root.left.val + self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
# return self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left) + self.sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right)
# # method 2: noncursion stack
# if not root:
# return 0
# stack = [(root,0)]
# lst = []
# while stack:
# node , sums = stack.pop()
# if node.left and not node.left.left and not node.left.right:
# stack.append((node.left,sums+node.left.val))
# if node.right:
# stack.append((node.right,sums))
# if node.left:
# stack.append((node.left,sums))
# lst.append(sums)
# return sum(lst)
# method 3: noncursion queue
if not root:
return 0
queue = [(root,0)]
lst = []
while queue:
node , sums = queue.pop(0)
if node.left and not node.left.left and not node.left.right:
queue.append((node.left,sums+node.left.val))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right,sums))
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left,sums))
lst.append(sums)
return sum(lst)
题目13:429. N-ary Tree Level Order Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes’ values. (ie, from left to right, level by level).

"""
此题不是二叉树,所以在BFS的基础上,还要加一个for循环
"""
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def levelOrder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
# method 1: queue
if not root:return []
res = []
stack = [root]
while stack:
temp = []
next_stack = []
for node in stack:
temp.append(node.val)
for child in node.children:
next_stack.append(child)
stack = next_stack
res.append(temp)
return res
题目14:543. Diameter of Binary Tree
Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.

"""
这个问题可递归分解为求左右子树路径长度和(但是要和子树的路径和去比较哪个大,见注释)
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
self.ans = 0
def depth(p):
if not p:
return 0
left, right = depth(p.left), depth(p.right)
#self.ans = left+right
self.ans = max(self.ans, left+right)
# 之所以有max,而不是上一句,是因为可能线路不经过根结点,但是比经过根结点的还长,可以运行上一句,看出错的结果示例。
return 1 + max(left, right)
depth(root)
return self.ans
题目15:559. Maximum Depth of N-ary Tree
Given a n-ary tree, find its maximum depth.
The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.

"""
思路:用一个队列存储各层的值,遍历完一层,result +1,需要用一个临时的temp来保存children作为下一层
"""
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def maxDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: int
"""
if not root:
return 0
queue = [root]
result = 0
while queue:
result += 1
temp = []
for node in queue:
temp += node.children
queue = temp
return result
题目16:563. Binary Tree Tilt
Given a binary tree, return the tilt of the whole tree.
The tilt of a tree node is defined as the absolute difference between the sum of all left subtree node values and the sum of all right subtree node values. Null node has tilt 0.
The tilt of the whole tree is defined as the sum of all nodes’ tilt.

"""
思路:
定义sum递归函数计算,以当前结点为根的树的结点值的和,然后ans 记录 左右子树结点值的和的差
ans不断地增加(从最深处往上),这样就记录了每个结点的左右分支的和的差,返回这个ans即可
"""
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def findTilt(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
self.ans = 0
def _sum(node):
if not node: return 0
left, right = _sum(node.left), _sum(node.right)
self.ans += abs(left - right)
return node.val + left + right
_sum(root)
return self.ans
题目17:589. N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes’ values.

"""
思路:和二叉树一样,前序遍历,把遍历的结果存在一个列表里,只不过不是二分,而是多分,用循环。
注意:由于递归,列表的操作用“+”号,不是append(append对数字操作,+对列表操作)
"""
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def preorder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root: return []
t=[root.val]
for child in root.children:
t= t + self.preorder(child) #列表加列表,不是append
return t
题目18:590. N-ary Tree Postorder Traversal
Given an n-ary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes’ values.

"""
这里采用递归的思想:
给根节点,先访问该结点的孩子结点,一直递归,直到树叶结点,res 列表增加叶子结点的值;
然后返回上一层,res继续增加该层的值,依此类推,最后把根结点加入到列表中,完成算法。
"""
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, val, children):
self.val = val
self.children = children
"""
class Solution(object):
def postorder(self, root):
"""
:type root: Node
:rtype: List[int]
"""
res = []
if root == None: return res
def recursion(root, res):
for child in root.children:
recursion(child, res)
res.append(root.val)
recursion(root, res)
return res
本次记录就到这为止~
说明
本文章所有代码及文档均以上传至github中,感谢您的rp and star.
github链接:https://github.com/LSayhi
CSDN链接:https://blog.csdn.net/LSayhi




