python人脸识别模块 face_recognition
Project description
Face Recognition
Recognize and manipulate faces from Python or from the command line with
the world’s simplest face recognition library.
Built using dlib’s state-of-the-art face recognition
built with deep learning. The model has an accuracy of 99.38% on the
Labeled Faces in the Wild benchmark.
This also provides a simple face_recognition command line tool that lets
you do face recognition on a folder of images from the command line!
Features
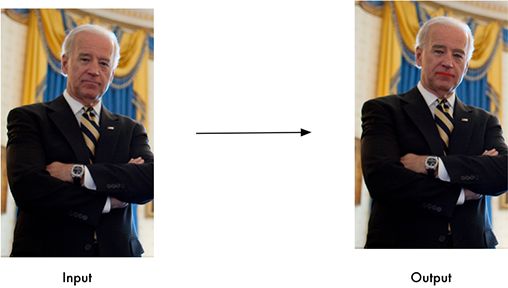
Find faces in pictures
Find all the faces that appear in a picture:
import face_recognition
image = face_recognition.load_image_file("your_file.jpg")
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(image)
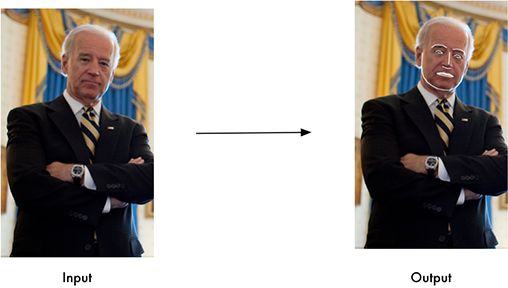
Find and manipulate facial features in pictures
Get the locations and outlines of each person’s eyes, nose, mouth and chin.
import face_recognition
image = face_recognition.load_image_file("your_file.jpg")
face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(image)
Finding facial features is super useful for lots of important stuff. But you can also use for really stupid stuff
like applying digital make-up (think ‘Meitu’):
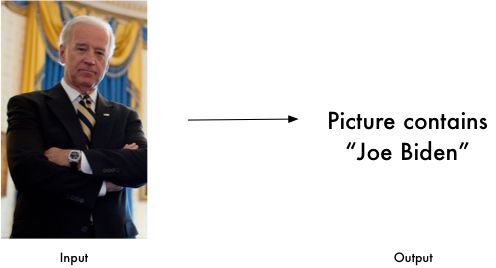
Identify faces in pictures
Recognize who appears in each photo.
import face_recognition
known_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("biden.jpg")
unknown_image = face_recognition.load_image_file("unknown.jpg")
biden_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(known_image)[0]
unknown_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(unknown_image)[0]
results = face_recognition.compare_faces([biden_encoding], unknown_encoding)
You can even use this library with other Python libraries to do real-time face recognition:
See this example for the code.
Installation
Requirements
- Python 3.3+ or Python 2.7
- macOS or Linux (Windows not officially supported, but might work)
Installing on Mac or Linux
First, make sure you have dlib already installed with Python bindings:
- How to install dlib from source on macOS or Ubuntu
Then, install this module from pypi using pip3 (or pip2 for Python 2):
pip3 install face_recognition
If you are having trouble with installation, you can also try out a
pre-configured VM.
Installing on Raspberry Pi 2+
- Raspberry Pi 2+ installation instructions
Installing on Windows
While Windows isn’t officially supported, helpful users have posted instructions on how to install this library:
- @masoudr’s Windows 10 installation guide (dlib + face_recognition)
Installing a pre-configured Virtual Machine image
- Download the pre-configured VM image (for VMware Player or VirtualBox).
Usage
Command-Line Interface
When you install face_recognition, you get a simple command-line program
called face_recognition that you can use to recognize faces in a
photograph or folder full for photographs.
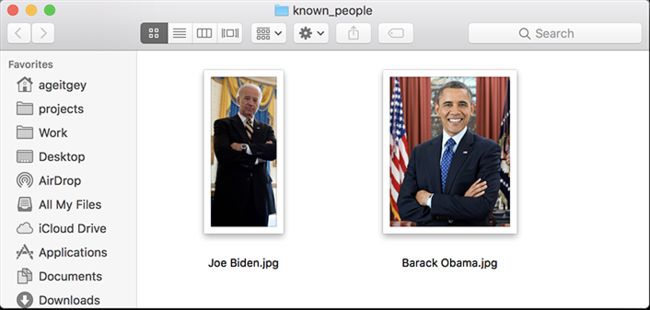
First, you need to provide a folder with one picture of each person you
already know. There should be one image file for each person with the
files named according to who is in the picture:
Next, you need a second folder with the files you want to identify:
Then in you simply run the command face_recognition, passing in
the folder of known people and the folder (or single image) with unknown
people and it tells you who is in each image:
$ face_recognition ./pictures_of_people_i_know/ ./unknown_pictures/ /unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,Barack Obama /face_recognition_test/unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,unknown_person
There’s one line in the output for each face. The data is comma-separated
with the filename and the name of the person found.
An unknown_person is a face in the image that didn’t match anyone in
your folder of known people.
ADJUSTING TOLERANCE / SENSITIVITY
If you are getting multiple matches for the same person, it might be that
the people in your photos look very similar and a lower tolerance value
is needed to make face comparisons more strict.
You can do that with the --tolerance parameter. The default tolerance
value is 0.6 and lower numbers make face comparisons more strict:
$ face_recognition --tolerance 0.54 ./pictures_of_people_i_know/ ./unknown_pictures/ /unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,Barack Obama /face_recognition_test/unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,unknown_person
If you want to see the face distance calculated for each match in order
to adjust the tolerance setting, you can use --show-distance true:
$ face_recognition --show-distance true ./pictures_of_people_i_know/ ./unknown_pictures/ /unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,Barack Obama,0.378542298956785 /face_recognition_test/unknown_pictures/unknown.jpg,unknown_person,None
MORE EXAMPLES
If you simply want to know the names of the people in each photograph but don’t
care about file names, you could do this:
$ face_recognition ./pictures_of_people_i_know/ ./unknown_pictures/ | cut -d ',' -f2 Barack Obama unknown_person
SPEEDING UP FACE RECOGNITION
Face recognition can be done in parallel if you have a computer with
multiple CPU cores. For example if your system has 4 CPU cores, you can
process about 4 times as many images in the same amount of time by using
all your CPU cores in parallel.
If you are using Python 3.4 or newer, pass in a --cpus
$ face_recognition --cpus 4 ./pictures_of_people_i_know/ ./unknown_pictures/
You can also pass in --cpus -1 to use all CPU cores in your system.
Python Module
You can import the face_recognition module and then easily manipulate
faces with just a couple of lines of code. It’s super easy!
API Docs: https://face-recognition.readthedocs.io.
AUTOMATICALLY FIND ALL THE FACES IN AN IMAGE
import face_recognition
image = face_recognition.load_image_file("my_picture.jpg")
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(image)
# face_locations is now an array listing the co-ordinates of each face!
See this example
to try it out.
You can also opt-in to a somewhat more accurate deep-learning-based face detection model.
Note: GPU acceleration (via nvidia’s CUDA library) is required for good
performance with this model. You’ll also want to enable CUDA support
when compliling dlib.
import face_recognition
image = face_recognition.load_image_file("my_picture.jpg")
face_locations = face_recognition.face_locations(image, model="cnn")
# face_locations is now an array listing the co-ordinates of each face!
See this example
to try it out.
If you have a lot of images and a GPU, you can also
find faces in batches.
AUTOMATICALLY LOCATE THE FACIAL FEATURES OF A PERSON IN AN IMAGE
import face_recognition
image = face_recognition.load_image_file("my_picture.jpg")
face_landmarks_list = face_recognition.face_landmarks(image)
# face_landmarks_list is now an array with the locations of each facial feature in each face.
# face_landmarks_list[0]['left_eye'] would be the location and outline of the first person's left eye.
See this example
to try it out.
RECOGNIZE FACES IN IMAGES AND IDENTIFY WHO THEY ARE
import face_recognition
picture_of_me = face_recognition.load_image_file("me.jpg")
my_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(picture_of_me)[0]
# my_face_encoding now contains a universal 'encoding' of my facial features that can be compared to any other picture of a face!
unknown_picture = face_recognition.load_image_file("unknown.jpg")
unknown_face_encoding = face_recognition.face_encodings(unknown_picture)[0]
# Now we can see the two face encodings are of the same person with `compare_faces`!
results = face_recognition.compare_faces([my_face_encoding], unknown_face_encoding)
if results[0] == True:
print("It's a picture of me!")
else:
print("It's not a picture of me!")
See this example
to try it out.
Python Code Examples
All the examples are available here.
Face Detection
- Find faces in a photograph
- Find faces in a photograph (using deep learning)
- Find faces in batches of images w/ GPU (using deep learning)
Facial Features
- Identify specific facial features in a photograph
- Apply (horribly ugly) digital make-up
Facial Recognition
-
Find and recognize unknown faces in a photograph based on photographs of known people
-
Compare faces by numeric face distance instead of only True/False matches
-
Recognize faces in live video using your webcam - Simple / Slower Version (Requires OpenCV to be installed)
-
Recognize faces in live video using your webcam - Faster Version (Requires OpenCV to be installed)
-
Recognize faces in a video file and write out new video file (Requires OpenCV to be installed)
-
Recognize faces on a Raspberry Pi w/ camera
-
Run a web service to recognize faces via HTTP (Requires Flask to be installed)
-
Recognize faces with a K-nearest neighbors classifier
How Face Recognition Works
If you want to learn how face location and recognition work instead of
depending on a black box library, read my article.
Caveats
- The face recognition model is trained on adults and does not work very well on children. It tends to mix up children quite easy using the default comparison threshold of 0.6.
Deployment to Cloud Hosts (Heroku, AWS, etc)
Since face_recognition depends on dlib which is written in C++, it can be tricky to deploy an app
using it to a cloud hosting provider like Heroku or AWS.
To make things easier, there’s an example Dockerfile in this repo that shows how to run an app built with
face_recognition in a Docker container. With that, you should be able to deploy
to any service that supports Docker images.
Common Issues
Issue: Illegal instruction (core dumped) when using face_recognition or running examples.
Solution: dlib is compiled with SSE4 or AVX support, but your CPU is too old and doesn’t support that.
You’ll need to recompile dlib after making the code change outlined here.
Issue: RuntimeError: Unsupported image type, must be 8bit gray or RGB image. when running the webcam examples.
Solution: Your webcam probably isn’t set up correctly with OpenCV. Look here for more.
Issue: MemoryError when running pip2 install face_recognition
Solution: The face_recognition_models file is too big for your available pip cache memory. Instead,
try pip2 --no-cache-dir install face_recognition to avoid the issue.
Issue: AttributeError: 'module' object has no attribute 'face_recognition_model_v1'
Solution: The version of dlib you have installed is too old. You need version 19.7 or newer. Upgrade dlib.
Issue: Attribute Error: 'Module' object has no attribute 'cnn_face_detection_model_v1'
Solution: The version of dlib you have installed is too old. You need version 19.7 or newer. Upgrade dlib.
Issue: TypeError: imread() got an unexpected keyword argument 'mode'
Solution: The version of scipy you have installed is too old. You need version 0.17 or newer. Upgrade scipy.
Thanks
- Many, many thanks to Davis King (@nulhom) for creating dlib and for providing the trained facial feature detection and face encoding models used in this library. For more information on the ResNet that powers the face encodings, check out his blog post.
- Thanks to everyone who works on all the awesome Python data science libraries like numpy, scipy, scikit-image, pillow, etc, etc that makes this kind of stuff so easy and fun in Python.
- Thanks to Cookiecutter and the audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage project template for making Python project packaging way more tolerable.