Java Web+GeoTools工具+自定义几何对象构造器+简单应用
基于上一篇继续讲
一、相关依赖【不知道的继续看一遍】
(1)
1.8
17.0
42.1.4
osgeo
Open Source Geospatial Foundation Repository
http://download.osgeo.org/webdav/geotools/
(2)
org.geotools
gt-shapefile
${geotools.version}
org.geotools
gt-swing
${geotools.version}
org.geotools.jdbc
gt-jdbc-postgis
${geotools.version}
org.postgresql
postgresql
二、PostGis空间几何对象构造器
(1)GeometryCreator.java
package com.appleyk.geotools;
import java.util.List;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Coordinate;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Geometry;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryCollection;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.LineString;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.LinearRing;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.MultiLineString;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.MultiPoint;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.MultiPolygon;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Point;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Polygon;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.io.ParseException;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.io.WKTReader;
/**
* 几何对象构建器
*
* @author [email protected]
* @blob http://blog.csdn.net/appleyk
* @version V1.0.1
* @date 2017年12月8日10:38:49
*/
//单例模式
public class GeometryCreator {
public static GeometryCreator geometryCreator = null;
private GeometryFactory geometryFactory = new GeometryFactory();
private GeometryCreator() {
}
/**
* 返回本类的唯一实例
* @return
*/
public static GeometryCreator getInstance() {
if (geometryCreator == null) {
return new GeometryCreator();
}
return geometryCreator;
}
/**
* 1.构建点
*/
/**
* 1.1根据X,Y坐标构建一个几何对象: 点 【Point】
* @param x
* @param y
* @return
*/
public Point createPoint(double x,double y){
Coordinate coord = new Coordinate(x, y);
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint(coord);
return point;
}
/**
* 1.2根据几何对象的WKT描述【String】创建几何对象: 点 【Point】
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public Point createPointByWKT(String PointWKT) throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader(geometryFactory);
Point point = (Point) reader.read(PointWKT);
return point;
}
/**
* 1.3根据几何对象的WKT描述【String】创建几何对象:多点 【MultiPoint】
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public MultiPoint createMulPointByWKT(String MPointWKT)throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
MultiPoint mpoint = (MultiPoint) reader.read(MPointWKT);
return mpoint;
}
/**
* 2.构建线
*/
/**
* 2.1根据两点 创建几何对象:线 【LineString】
* @param ax
* @param ay
* @param bx
* @param by
* @return
*/
public LineString createLine(double ax,double ay,double bx,double by){
Coordinate[] coords = new Coordinate[] {new Coordinate(ax, ay), new Coordinate(bx, by)};
LineString line = geometryFactory.createLineString(coords);
return line;
}
/**
* 2.2根据线的WKT描述创建几何对象:线 【LineString】
* @param LineStringWKT
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public LineString createLineByWKT(String LineStringWKT) throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
LineString line = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 0, 2 0)");
return line;
}
/**
* 2.3根据点组合的线数组,创建几何对象:多线 【MultiLineString】
* @param list
* @return
*/
public MultiLineString createMLine(List list){
MultiLineString ms = null;
if(list == null){
return ms;
}
LineString[] lineStrings = new LineString[list.size()];
// Coordinate[] coords1 = new Coordinate[] {new Coordinate(2, 2), new Coordinate(2, 2)};
// LineString line1 = geometryFactory.createLineString(coords1);
//
// Coordinate[] coords2 = new Coordinate[] {new Coordinate(2, 2), new Coordinate(2, 2)};
// LineString line2 = geometryFactory.createLineString(coords2);
int i = 0;
for (Coordinate[] coordinates : list) {
lineStrings[i] = geometryFactory.createLineString(coordinates);
}
ms = geometryFactory.createMultiLineString(lineStrings);
return ms;
}
/**
* 2.4根据几何对象的WKT描述【String】创建几何对象 : 多线【MultiLineString】
* @param MLineStringWKT
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public MultiLineString createMLineByWKT(String MLineStringWKT)throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
MultiLineString line = (MultiLineString) reader.read(MLineStringWKT);
return line;
}
/**
* 3.构建多边形
*/
/**
* 3.1 根据几何对象的WKT描述【String】创建几何对象:多边形 【Polygon】
* @param PolygonWKT
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public Polygon createPolygonByWKT(String PolygonWKT) throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
Polygon polygon = (Polygon) reader.read(PolygonWKT);
return polygon;
}
/**
* 3.2 根据几何对象的WKT描述【String】创建几何对象: 多多边形 【MultiPolygon】
* @param MPolygonWKT
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public MultiPolygon createMulPolygonByWKT(String MPolygonWKT) throws ParseException{
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
MultiPolygon mpolygon = (MultiPolygon) reader.read(MPolygonWKT);
return mpolygon;
}
/**
* 4.构建几何对象集合
*/
/**
* 4.1 根据几何对象数组,创建几何对象集合:【GeometryCollection】
* @return
* @throws ParseException
*/
public GeometryCollection createGeoCollect(Geometry[] geoArray) throws ParseException{
// LineString line = createLine(125.12,25.4,85.63,99.99);
// Polygon poly = createPolygonByWKT("POLYGON((20 10, 30 0, 40 10, 30 20, 20 10))");
// Geometry g1 = geometryFactory.createGeometry(line);
// Geometry g2 = geometryFactory.createGeometry(poly);
// Geometry[] geoArray = new Geometry[]{g1,g2};
GeometryCollection gc = geometryFactory.createGeometryCollection(geoArray);
return gc;
}
/**
* 5.构建圆
*/
/**
* 5.1 根据圆点以及半径创建几何对象:特殊的多边形--圆 【Polygon】
* @param x
* @param y
* @param RADIUS
* @return
*/
public Polygon createCircle(double x, double y, final double RADIUS){
final int SIDES = 32;//圆上面的点个数
Coordinate coords[] = new Coordinate[SIDES+1];
for( int i = 0; i < SIDES; i++){
double angle = ((double) i / (double) SIDES) * Math.PI * 2.0;
double dx = Math.cos( angle ) * RADIUS;
double dy = Math.sin( angle ) * RADIUS;
coords[i] = new Coordinate( (double) x + dx, (double) y + dy );
}
coords[SIDES] = coords[0];
LinearRing ring = geometryFactory.createLinearRing(coords);
Polygon polygon = geometryFactory.createPolygon(ring, null);
return polygon;
}
}
(2)什么是WKT呢?
数据库 :【postgresql】
我们看一下,国家大剧院这个建筑物,在空间数据库的表中几的何形态的数据信息是什么,是什么类型
我们看下geom这个字段的类型
那我们怎么读取这个几何对象实际表示的空间信息呢?
三、空间数据库的简单操作+shapfile文件的读写应用
(1)GTDataBase.java
package com.appleyk.geotools;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.geotools.data.DataStore;
import org.geotools.data.DataStoreFinder;
import org.geotools.data.FeatureSource;
import org.geotools.data.FeatureWriter;
import org.geotools.data.Transaction;
import org.geotools.data.postgis.PostgisNGDataStoreFactory;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStoreFactory;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.files.ShpFiles;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.shp.ShapefileReader;
import org.geotools.feature.FeatureCollection;
import org.geotools.feature.FeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder;
import org.geotools.referencing.crs.DefaultGeographicCRS;
import org.opengis.feature.Property;
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
import org.opengis.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import com.appleyk.pojo.Geometry;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.GeometryFactory;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.MultiPolygon;
import com.vividsolutions.jts.geom.Polygon;
public class GTDataBase {
static Connection connection = null;
static DataStore pgDatastore = null;
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
static FeatureSource fSource = null;
static Statement statement = null ;
static GeometryCreator gCreator = GeometryCreator.getInstance();
/**
* 1.连接postgrepsql数据库
*
* @param ip
* @param port
* @param user
* @param password
* @param database
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private static boolean ConnDataBase(String ip, Integer port, String user, String password, String database)
throws Exception {
// "jdbc:postgresql://192.168.1.104:5432/test"
// user=postgres
// password=bluethink134
// 拼接url
String url = "jdbc:postgresql://" + ip + ":" + port + "/" + database;
Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver"); // 一定要注意和上面的MySQL语法不同
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
if (connection != null) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
/**
* 2.连接数据库 使用的postgis 链接代码如下:
*
* @param dbtype
* @param host
* @param port
* @param database
* @param userName
* @param password
*/
private static void ConnPostGis(String dbtype, String host, int port, String database, String userName,
String password) {
Map params = new HashMap();
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.DBTYPE.key, dbtype);
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.HOST.key, host);
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.PORT.key, new Integer(port));
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.DATABASE.key, database);
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.SCHEMA.key, "public");
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.USER.key, userName);
params.put(PostgisNGDataStoreFactory.PASSWD.key, password);
try {
pgDatastore = DataStoreFinder.getDataStore(params);
if (pgDatastore != null) {
System.out.println("系统连接到位于:" + host + "的空间数据库" + database + "成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("系统连接到位于:" + host + "的空间数据库" + database + "失败!请检查相关参数");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("系统连接到位于:" + host + "的空间数据库" + database + "失败!请检查相关参数");
}
}
// 3.针对某个地理图层,进行地理信息的读取
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void PostGisReading(String Schema) throws Exception {
fSource = pgDatastore.getFeatureSource(Schema);
// 一个用于处理FeatureCollection的实用工具类。提供一个获取FeatureCollection实例的机制
FeatureCollection result = fSource.getFeatures();
// 计算本图层中所有特征的数量
//System.out.println(result.size());
//1.迭代特征
FeatureIterator iterator = result.features();
//迭代 特征 只迭代30个 太大了,一下子迭代完,非常耗时
int stop = 0;
while(iterator.hasNext()){
if(stop >30){
break;
}
SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next();
Collection p = feature.getProperties();
Iterator it = p.iterator();
//2.特征里面的属性再迭代,属性里面有字段
System.out.println("================================");
while(it.hasNext()){
Property pro = it.next();
System.out.println(pro.getName()+"\t = "+pro.getValue());
}//end 里层while
stop++;
}//end 最外层 while
iterator.close();
}
/**4.Insert
* 插入一条特征
* @param geo
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static boolean Insert(Geometry geo) throws Exception{
boolean result = false;
String sql = "insert into geotable (osm_id,code,fclass,name,type,geom) values('"
+geo.getOsm_id()+"','"+geo.getCode()+"','"+geo.getFclass()
+"','"+geo.getName()+"','"+geo.getType()+"',"+"st_geomfromewkt('"+geo.getGeom().toString()+"'))";
PreparedStatement pstmt;
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//geometry = st_geomfromewkt(text WKT)
// System.out.println(sql);
int i = pstmt.executeUpdate();
if(i>0){
result = true;
}
pstmt.close();
return result;
}
// 4.取得POSTGIS中所有的地理图层
public static void getAllLayers() throws Exception {
String[] typeName = pgDatastore.getTypeNames();
for (int i = 0; i < typeName.length; i++) {
System.out.println((i + 1) + ":" + typeName[i]);
}
}
//2.3个文件一起读,以Point为例,读取后插入数据表
public static void ReadSHP(String path) throws Exception{
//A.建筑物的shapefile,多边形 MULTIPOLYGON
//String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_buildings_a_free_1.shp";
//B.路的shapefile,多线MULTILINESTRING
//String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_roads_free_1.shp";
//C.建筑物的点坐标 以Point为主
//String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_pois_free_1.shp";
//一个数据存储实现,允许从Shapefiles读取和写入
ShapefileDataStore shpDataStore = null;
shpDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(new File(path).toURI().toURL());
shpDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//获取这个数据存储保存的类型名称数组
//getTypeNames:获取所有地理图层
String typeName = shpDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
//通过此接口可以引用单个shapefile、数据库表等。与数据存储进行比较和约束
FeatureSource featureSource = null;
featureSource = (FeatureSource)shpDataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);
//一个用于处理FeatureCollection的实用工具类。提供一个获取FeatureCollection实例的机制
FeatureCollection result=featureSource.getFeatures();
//System.out.println(result.size());
FeatureIterator iterator = result.features();
//迭代 特征 只迭代30个 太大了,一下子迭代完,非常耗时
int stop = 0;
List geolist = new ArrayList<>();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
if(stop >100){
break;
}
SimpleFeature feature = iterator.next();
Collection p = feature.getProperties();
Iterator it = p.iterator();
Geometry geo = new Geometry();
//特征里面的属性再迭代,属性里面有字段
String name;
while(it.hasNext()){
Property pro = it.next();
name= pro.getName().toString();
if(name.equals("the_geom")){
geo.setGeom(pro.getValue());
}
if(name.equals("osm_id")){
geo.setOsm_id(pro.getValue().toString());
}
if(name.equals("code")){
geo.setCode(Integer.parseInt(pro.getValue().toString()));
}
if(name.equals("fclass")){
geo.setFclass(pro.getValue().toString());
}
if(name.equals("name")){
geo.setName(pro.getValue().toString());
}
if(name.equals("type")){
geo.setType(pro.getValue().toString());
}
}//end 里层while
geolist.add(geo);
stop++;
}//end 最外层 while
iterator.close();
boolean bRes = true;
for (Geometry geo : geolist) {
// System.out.println("================================");
// System.out.println(geo.getCode());
// System.out.println(geo.getFclass());
// System.out.println(geo.getGid());
// System.out.println(geo.getName());
// System.out.println(geo.getOsm_id());
// System.out.println(geo.getFclass());
if(!Insert(geo)){
bRes = false;
break;
}
}
if(bRes){
System.out.println("读取shapefile文件内容插入数据库成功!");
}
}
/**
* 将几何对象信息写入一个shapfile文件
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void WriteSHP(String path) throws Exception{
//String path="C:\\my.shp";
//1.创建shape文件对象
File file =new File(path);
Map params = new HashMap<>();
//用于捕获参数需求的数据类
//URLP:url to the .shp file.
params.put(ShapefileDataStoreFactory.URLP.key, file.toURI().toURL());
//2.创建一个新的数据存储——对于一个还不存在的文件。
ShapefileDataStore ds = (ShapefileDataStore) new ShapefileDataStoreFactory().createNewDataStore(params);
//3.定义图形信息和属性信息
//SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder 构造简单特性类型的构造器
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
//设置
//WGS84:一个二维地理坐标参考系统,使用WGS84数据
tBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
tBuilder.setName("shapefile");
//添加 一个几何对象:特殊的多边形:圆
tBuilder.add("the_geom", Polygon.class);
//添加一个id
tBuilder.add("osm_id", Long.class);
//添加名称
tBuilder.add("name", String.class);
//添加描述
tBuilder.add("des", String.class);
//设置此数据存储的特征类型
ds.createSchema(tBuilder.buildFeatureType());
//设置编码
ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
//设置writer
//为给定的类型名称创建一个特性写入器
//1.typeName:特征类型
//2.transaction :事物,写入失败,回滚
//3.ShapefileDataStore::getTypeNames:
/*public String[] getTypeNames()
获取这个数据存储保存的类型名称数组。
ShapefileDataStore总是返回一个名称
*/
FeatureWriter writer = ds.getFeatureWriter(
ds.getTypeNames()[0], Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT);
//Interface SimpleFeature:一个由固定列表值以已知顺序组成的SimpleFeatureType实例。
//写一个点
SimpleFeature feature = writer.next();
//SimpleFeature ::setAttribute(String attrName, Object val)
//给指定的属性名称添加一个对象 POINT
double x = 116.123; //X轴坐标
double y = 39.345 ; //Y轴坐标
/*
* Coordinate : GeoAPI几何接口的实现
一个轻量级的类,用于存储二维笛卡尔平面上的坐标。
它不同于点,它是几何的一个子类。
不同于类型点的对象(包含额外的信息,如信封、精确模型和空间引用系统信息),
坐标只包含有序值和访问方法。
*/
//Coordinate coordinate = new Coordinate(x, y);
//GeometryFactory:提供一套实用的方法,用于从坐标列表中构建几何对象。
//构造一个几何图形工厂,生成具有浮动精度模型的几何图形和一个0的空间引用ID。
//Point point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(coordinate);
// feature.setAttribute("the_geom",polygon);
// feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567890l);
// feature.setAttribute("name", "帅鱼");
// feature.setAttribute("des", "爱宝宝");
//利用几何对象构造器创建一个圆
Polygon polygon = gCreator.createCircle(x, y, 20);
feature.setAttribute("the_geom",polygon);
feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567890l);
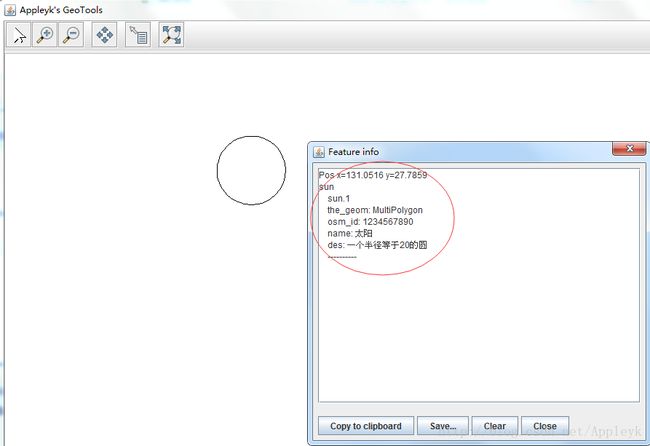
feature.setAttribute("name", "太阳");
feature.setAttribute("des", "一个半径等于20的圆");
//再来一个点
//
// feature = writer.next();
//
// x = 116.456;
// y = 39.678 ;
// coordinate = new Coordinate(x, y);
// point = new GeometryFactory().createPoint(coordinate);
//
// feature.setAttribute("the_geom",point);
// feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567891l);
// feature.setAttribute("name", "宝宝");
// feature.setAttribute("des", "爱帅鱼");
//写入
writer.write();
//关闭
writer.close();
//释放资源
ds.dispose();
//读取shapefile文件的图形信息
ShpFiles shpFiles = new ShpFiles(path);
/*ShapefileReader(
ShpFiles shapefileFiles,
boolean strict, --是否是严格的、精确的
boolean useMemoryMapped,--是否使用内存映射
GeometryFactory gf, --几何图形工厂
boolean onlyRandomAccess--是否只随机存取
)
*/
ShapefileReader reader = new ShapefileReader(shpFiles,
false, true, new GeometryFactory(), false);
while(reader.hasNext()){
System.out.println(reader.nextRecord().shape());
}
reader.close();
}
/**
* 3.根据几何对象名称 查询几何对象信息 [Query]
* @param name
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void Query(String name) throws Exception{
//String sql = "select st_astext(geom) from geotable where name ='"+name+"'";
String sql = "select st_geometrytype(geom) as type,st_astext(geom) as geom from geotable where name ='"+name+"'";
statement = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet result = statement.executeQuery(sql);
if(result!=null){
while(result.next()){
Object val = result.getString(1);
if(val.equals("ST_MultiPolygon")){
System.out.println("几何对象类型:多多边形");
MultiPolygon mPolygon = gCreator.createMulPolygonByWKT(result.getString(2));
System.out.println(mPolygon instanceof MultiPolygon);
System.out.println("获取几何对象中的点个数:"+mPolygon.getNumPoints());
}
}
}
}
// Main 方法测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.利用Provider连接 空间数据库
if (!ConnDataBase("192.168.1.104", 5432, "postgres", "123456", "test")) {
System.out.println("连接postgresql数据库失败,请检查参数!");
}
ConnPostGis("postgis", "192.168.1.104", 5432, "test", "postgres", "123456");
String path = "E:\\china-latest-free\\gis.osm_buildings_a_free_1.shp";
//2.读shapfile文件,并将内容写入空间数据库
//ReadSHP(path);
//3.获得空间数据库中所有的 地理图层
getAllLayers();
//4.根据空间几何对象的名称 查询几何对象信息
Query("国家大剧院");
//5.创建一个圆【多边形】,并写入shapfile文件
WriteSHP("C:\\Sun\\sun.shp");
}
}
(2)读取shapfile文件并写入空间数据库【所谓的空间数据库就是postgresql数据库加了postgis扩展】
选择数据库,执行下面的语句,就会把当前的数据库"变成"空间数据库
CREATE EXTENSION postgis
执行后,原本的数据库下面,自动多出一张表
(3)geotable表创建的sql脚本
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS "public"."geotable";
CREATE TABLE "public"."geotable" (
"gid" int4 DEFAULT nextval('geo_seq'::regclass) NOT NULL,
"osm_id" varchar(10) COLLATE "default",
"code" int2,
"fclass" varchar(20) COLLATE "default",
"name" varchar(100) COLLATE "default",
"type" varchar(20) COLLATE "default",
"geom" "public"."geometry"
)
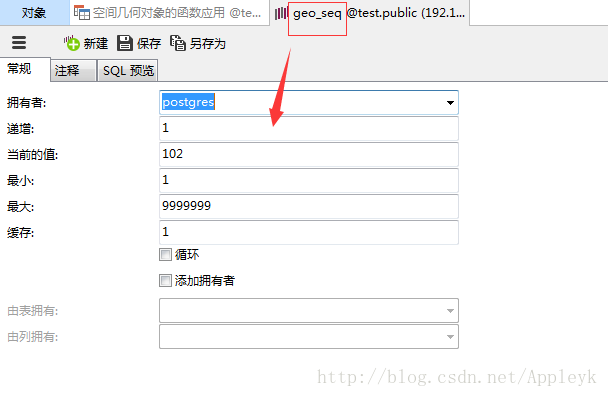
WITH (OIDS=FALSE);其中基于gid标识的序列是
(4)由于geotable已经插入数据了,代码里就给注释掉了
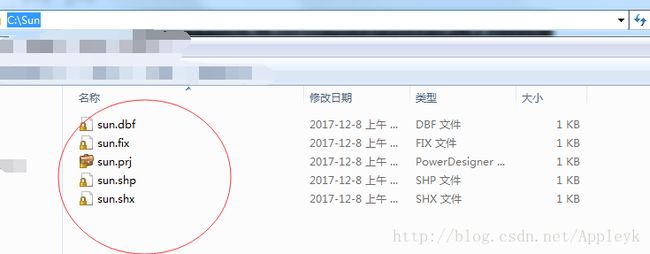
(5)运行Main方法,测试读取、查询和创建一个shapfile文件
A.
B.我们去这个路径下面,看一下我们的shapfile文件是否创建
C.
D.利用上一篇里面的内容,打开这个shp文件
E.利用空间范围查询几何对象集合【留个悬念】
补充说明:也就是在一个空间范围内,有哪些路,哪些建筑物,哪些物体等
几何对象存取函数:
获取几何对象的WKT描述 ST_AsText(geometry)
获取几何对象的WKB描述ST_AsBinary(geometry)
获取几何对象的空间参考ID ST_SRID(geometry)
获取几何对象的维数ST_Dimension(geometry)
获取几何对象的边界范围ST_Envelope(geometry)
判断几何对象是否为空 ST_IsEmpty(geometry)
判断几何对象是否不包含特殊点(比如自相交)ST_IsSimple(geometry)
判断几何对象是否闭合ST_IsClosed(geometry)
判断曲线是否闭合并且不包含特殊点 ST_IsRing(geometry)
获取多几何对象中的对象个数ST_NumGeometries(geometry)
获取多几何对象中第N个对象ST_GeometryN(geometry,int)
获取几何对象中的点个数ST_NumPoints(geometry)
获取几何对象的第N个点ST_PointN(geometry,integer)
获取多边形的外边缘ST_ExteriorRing(geometry)
获取多边形内边界个数ST_NumInteriorRings(geometry)
同上ST_NumInteriorRing(geometry)
获取多边形的第N个内边界ST_InteriorRingN(geometry,integer)
获取线的终点ST_EndPoint(geometry)
获取线的起始点 ST_StartPoint(geometry)
获取几何对象的类型GeometryType(geometry)
类似上,但是不检查M值,即POINTM对象会被判断为pointST_GeometryType(geometry)
获取点的X坐标 ST_X(geometry)
获取点的Y坐标 ST_Y(geometry)
获取点的Z坐标 ST_Z(geometry)
获取点的M值 ST_M(geometry)
番外篇:关于shape文件如何追加内容,我下面做个例子,demo结合实例来
先看支持追加写入shp文件的方法demo如下
/**
* 将几何对象信息写入一个shapefile文件并读取 == 可叠加写入 == MultiPolygon类型
* 目前shape文件被局限于只能包含同种shape类型,比如Point集合的shape文件中不能掺杂其他类型
* 但在将来shape文件可能会允许包含多种shape类型 == 混合shape?
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void writeSHP(String path, Geometry geometry,String desc) throws Exception {
// 1.创建shape文件对象
File file = new File(path);
ShapefileDataStore ds = new ShapefileDataStore(file.toURI().toURL());
if (!file.exists()) {
//如果文件不存在,创建schema,存在的话,就不创建了,防止覆盖
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder tBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
// 5.设置
// WGS84:一个二维地理坐标参考系统,使用WGS84数据
tBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84);
tBuilder.setName("shapefile");
// 6.置该shape文件几何类型
tBuilder.add( "the_geom", MultiPolygon.class );
// 7.添加一个id
tBuilder.add("osm_id", Long.class);
// 8.添加名称
tBuilder.add("name", String.class);
// 9.添加描述
tBuilder.add("des", String.class);
SimpleFeatureType buildFeatureType = tBuilder.buildFeatureType();
// 10.设置此数据存储的特征类型
ds.createSchema(buildFeatureType);
}
// 11.设置编码
ds.setCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
// 12.设置writer
// 为给定的类型名称创建一个特性写入器
String typeName = ds.getTypeNames()[0];
FeatureWriter writer = ds.getFeatureWriterAppend(typeName,
Transaction.AUTO_COMMIT);
// Interface SimpleFeature:一个由固定列表值以已知顺序组成的SimpleFeatureType实例。
// 13.写一个特征
SimpleFeature feature = writer.next();
feature.setAttribute("the_geom", geometry);
/**
* 下面的属性值,外面可以当做一个实体对象传进来,不写死!
*/
feature.setAttribute("osm_id", 1234567890l);
feature.setAttribute("name", "建筑物");
feature.setAttribute("des", desc);
// 14.写入
writer.write();
// 15.关闭
writer.close();
// 16.释放资源
ds.dispose();
// 17.读取shapefile文件的图形信息
ShpFiles shpFiles = new ShpFiles(path);
/*
* ShapefileReader( ShpFiles shapefileFiles, boolean strict,
* --是否是严格的、精确的 boolean useMemoryMapped,--是否使用内存映射 GeometryFactory gf,
* --几何图形工厂 boolean onlyRandomAccess--是否只随机存取 )
*/
ShapefileReader reader = new ShapefileReader(shpFiles, false, true, new GeometryFactory(), false);
while (reader.hasNext()) {
System.err.println(reader.nextRecord().shape());
}
reader.close();
} main方法作为测试的入口,主要是两次写入操作,一次是创建,一次是在上一次创建的基础上进行特征追加
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("===============创建自己的shp文件==============");
String MPolygonWKT1 = "MULTIPOLYGON(((121.5837313 31.2435225,121.5852142 31.2444795,121.5860999 31.2434539,121.586133 31.2433016,121.5856866 31.243208,121.5846169 31.2425171,121.5837313 31.2435225)))";
MultiPolygon multiPolygon1 = gCreator.createMulPolygonByWKT(MPolygonWKT1);
//写入一个多多边形 【建筑物】== 信合花园
writeSHP("C:/my/multipol.shp", multiPolygon1,"信合花园");
String MPolygonWKT2 = "MULTIPOLYGON(((121.5869337 31.2479069,121.5874496 31.248256,121.5877683 31.247914,121.5872516 31.2475652,121.5869337 31.2479069)))";
MultiPolygon multiPolygon2 = gCreator.createMulPolygonByWKT(MPolygonWKT2);
//再追加写入一个多多边形 【建筑物】== 信合花园
writeSHP("C:/my/multipol.shp", multiPolygon2,"新金桥大厦");
System.out.println("===============打开shp文件==============");
openShpFile();
}我们看一下数据库,这两个建筑物是存在的,而且位置挨的也比较近
运行main方法,最后的效果就是