android自定义View----通讯录导航栏(快速查找索引)
先上效果界面
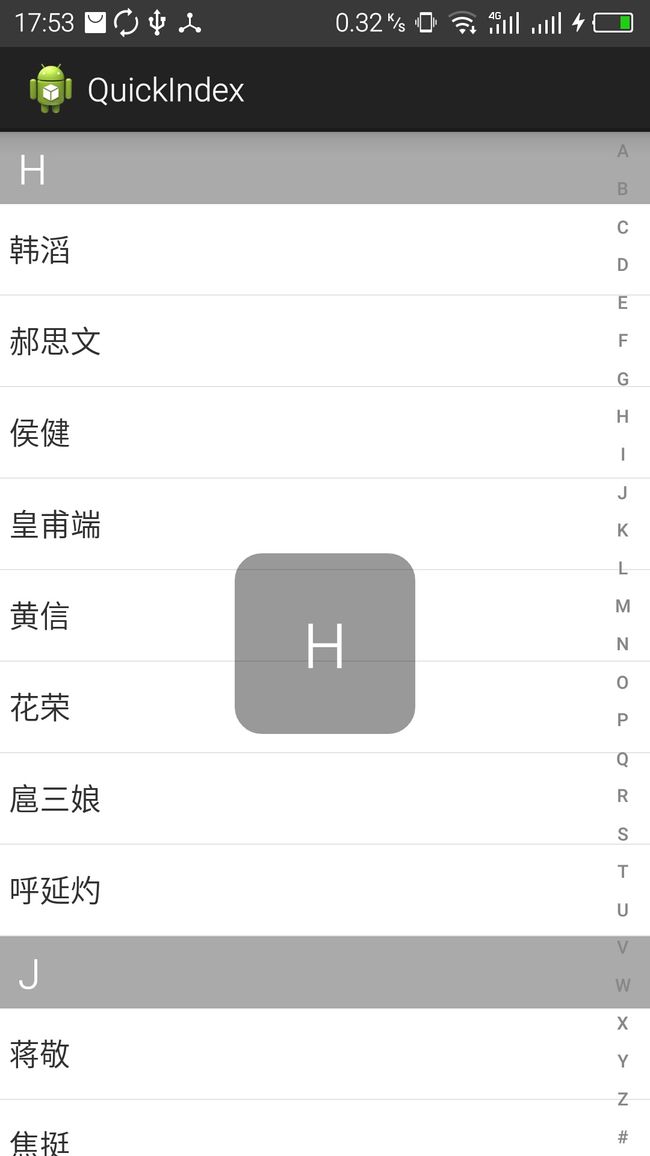
如图右侧竖排字母即为导航栏,通过自定义View实现。
实现导航思路:当用户点击这个控件时我们需要知道用户点击的哪个字母,并根据字母设置listview的从哪里开始显示,并在中心显示一个该字母的textview,给用户以提示。
所以这个控件的作用:在用户点击按钮时或滑动时,根据手指位置,实时获取字母(假设为M),将字母暴露出来,并提供事件的处理接口setOnLetterUpdateListener。在接口方法中,将listview设置到要显示的item项(listview.setSelection(N))方法。
程序源码地址:https://github.com/dronly/ImoocNews
QuickIndex源码如下
public class QuickIndexBar extends View {
private static final String[] LETTERS = new String[] { "A", "B", "C", "D",
"E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q",
"R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z","#" };
//画笔
private Paint mPaint;
//每个字母所在的矩形的宽高
private float cellWidth;
private float cellHeight;
//回调接口
private OnLetterUpdateListener mOnLetterUpdateListener;
/*
* 暴露一个字母的监听
*/
public interface OnLetterUpdateListener{
void letterUpdate(String letter);
}
public OnLetterUpdateListener getOnLetterUpdateListener() {
return mOnLetterUpdateListener;
}
/*
* 设置字母监听更新
* @param listener
*/
public void setOnLetterUpdateListener(OnLetterUpdateListener mOnLetterUpdateListener) {
this.mOnLetterUpdateListener = mOnLetterUpdateListener;
}
public QuickIndexBar(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public QuickIndexBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public QuickIndexBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
mPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
mPaint.setColor(0xff888888);
// int textSize = (int)cellHeight/2;
// mPaint.setTextSize(30);
mPaint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
for (int i = 0; i < LETTERS.length; i++) {
String text = LETTERS[i];
// 计算坐标
int x = (int) (cellWidth / 2.0f - mPaint.measureText(text) / 2.0f);
// 获取文本高度
Rect bounds = new Rect();
//设置字体大小为cellHeight的三分之二大小
mPaint.setTextSize(cellHeight/1.5f);
mPaint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), bounds);
int textHeight = bounds.height();
int y = (int) (cellHeight / 2.0f + textHeight / 2.0f + i
* cellHeight);
// 根据按下的字母, 设置画笔颜色
mPaint.setColor(touchIndex == i ? Color.BLACK : Color.GRAY);
canvas.drawText(text, x, y, mPaint);
}
}
int touchIndex = -1;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int index = -1;
switch (MotionEventCompat.getActionMasked(event)) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
index = (int) (event.getY() / cellHeight);
if (index >= 0 && index < LETTERS.length) {
if (index != touchIndex) {
mOnLetterUpdateListener.letterUpdate(LETTERS[index]);
}
touchIndex = index;
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
index = -1;
touchIndex = -1;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
index = (int) (event.getY() / cellHeight);
if (index >= 0 && index < LETTERS.length) {
if (index != touchIndex) {
mOnLetterUpdateListener.letterUpdate(LETTERS[index]);
Log.d("TAG", LETTERS[index]);
}
touchIndex = index;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
invalidate();
return true;
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
cellWidth = getMeasuredWidth();
int mHeight = getMeasuredHeight();
cellHeight = mHeight * 1.0f / LETTERS.length;
}
}