前言
虚拟机在解释执行字节码的时候一个重要的抽象就是要模拟 堆栈(Stack) 以及函数(方法)调用的栈帧(Frame),本文简要介绍 Zero 解释器中关于 Stack 和 Frame 的具体实现,相关源代码:
hotspot/src/cpu/zero/vm
hotspot/src/os_cpu/linux_zero
ZeroStack 类
相关源代码:
hotspot/src/cpu/zero/vm/stack_zero.hpp
hotspot/src/cpu/zero/vm/stack_zero.cpp
类属性
_base,the last available word,基地址
_top,the word past the end of the stack
_sp,the top word on the stack,当前栈顶指针
class ZeroStack {
private:
intptr_t *_base;
intptr_t *_top;
intptr_t *_sp;
}附上一张图形象描述 ZeroStack 所抽象的 Stack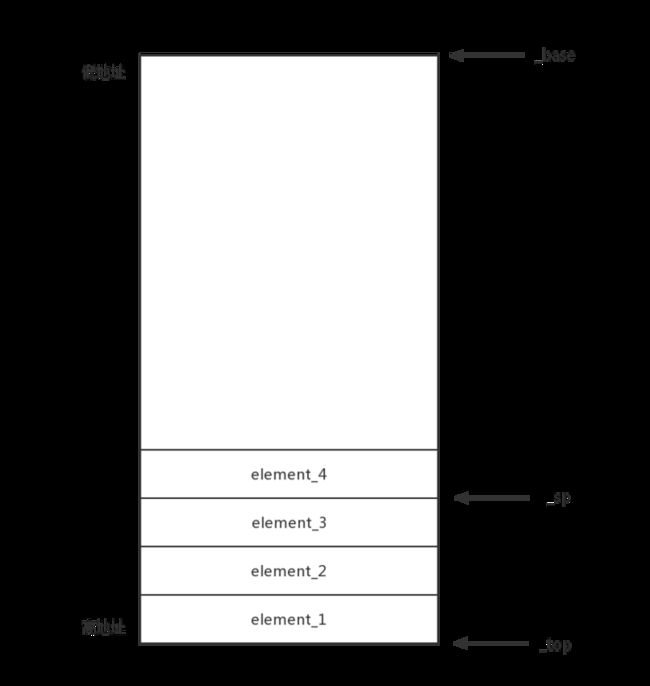
入栈
堆栈是从高地址向低地址伸展,先递减 _sp,再将 value 放入 _sp 指向的位置
void push(intptr_t value) {
assert(_sp > _base, "stack overflow");
*(-- _sp) = value;
}出栈
同理,先取出 _sp 指向的位置的值,再递增 _sp
intptr_t pop() {
assert(_sp < _top, "stack underflow");
return *(_sp++);
}ZeroFrame
相关源代码:
hotspot/src/cpu/zero/vm/stack_zero.hpp
ZeroFrame 是对栈帧的抽象,它是一个基类,定义了各个子类公用的 frame header(头部):
frame_type,frame 类型
next_frame,?
//
// | ... |
// +--------------------+ ------------------
// | ... | low addresses
// | frame_type |
// | next_frame | high addresses
// +--------------------+ ------------------
// | ... |Layout
Layout 枚举类型定义了 zero frame header 中的 next_frame 和 frame_type 偏移量
enum Layout {
next_frame_off,
frame_type_off,
jf_header_words
}访问字段
ZeroFrame 类和 hotspot 源代码中很多其它类一样,采用了"紧凑"的内存布局,没有将类字段声明在类定义里,而是通过 this 指针去操作字段,比如下面的这一组函数
intptr_t *addr_of_word(int offset) const {
return (intptr_t *) this - offset;
}
intptr_t value_of_word(int offset) const {
return *addr_of_word(offset);
}类型转换
ZeroFrame 提供了一组函数用于将 this 解析成指定的子类指针,因为不同的子类公用相同的头部,所以这种转换是 ok 的~
EntryFrame *as_entry_frame() const {
assert(is_entry_frame(), "should be");
return (EntryFrame *) this;
}
InterpreterFrame *as_interpreter_frame() const {
assert(is_interpreter_frame(), "should be");
return (InterpreterFrame *) this;
}
SharkFrame *as_shark_frame() const {
assert(is_shark_frame(), "should be");
return (SharkFrame *) this;
}
FakeStubFrame *as_fake_stub_frame() const {
assert(is_fake_stub_frame(), "should be");
return (FakeStubFrame *) this;
}Frame type
FrameType 枚举类型定义了各个不同的 frame type
enum FrameType {
ENTRY_FRAME = 1,
INTERPRETER_FRAME,
SHARK_FRAME,
FAKE_STUB_FRAME
}ZeroFrame 类提供了一组方法用于判断 frame type
bool is_entry_frame() const {
return type() == ENTRY_FRAME;
}
bool is_interpreter_frame() const {
return type() == INTERPRETER_FRAME;
}
bool is_shark_frame() const {
return type() == SHARK_FRAME;
}
bool is_fake_stub_frame() const {
return type() == FAKE_STUB_FRAME;
}InterpreterFrame
InterpreterFrame 类是 ZeroFrame 类的子类,和 java 方法调用相关,硬要从字面上翻译的化,姑且叫做 "解释器栈帧",它在 ZeroFrame 内存布局(header)的基础上 加了点自己的东西:
interpreter state,解释器上下文
monitor,synchronize 相关
local variable & parameters,局部变量和方法参数(是不是和 C/C++ 堆栈很像~)
// | ... |
// +--------------------+ ------------------
// | stack slot n-1 | low addresses
// | ... |
// | stack slot 0 |
// | monitor 0 (maybe) |
// | ... |
// | interpreter state |
// | ... |
// | frame_type |
// | next_frame | high addresses
// +--------------------+ ------------------
// | ... |build 函数中传入了一个 Method 类型的对象(指针),Method 类是 Java 中的方法在虚拟机的内部表示
InterpreterFrame 创建
参考之前相关文章,zero 解释器的入口函数 normal_entry 中会创建一个初始的 InterpreterFrame 并开始执行 byte code
// cppInterpreter_zero.cpp
int CppInterpreter::normal_entry(Method* method, intptr_t UNUSED, TRAPS) {
JavaThread *thread = (JavaThread *) THREAD;
// Allocate and initialize our frame.
InterpreterFrame *frame = InterpreterFrame::build(method, CHECK_0);
thread->push_zero_frame(frame);
// Execute those bytecodes!
main_loop(0, THREAD);
// No deoptimized frames on the stack
return 0;
}InterpreterFrame::build 函数比较长,仔细看来,无非就做了这几件事:
为本地变量,函数参数预留空间
在栈帧中创建解释器上下文(interpreter state)对象并进行初始化