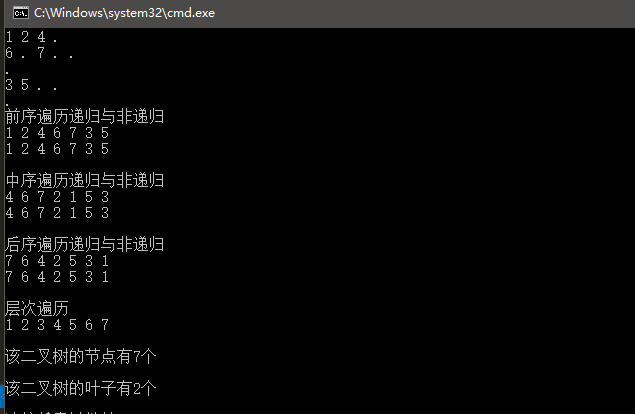
一:前言
本文主要讲解以下二叉树的4个部分:
(1)构造二叉树;
(2)前,中,后序遍历(递归与非递归)和层次遍历;
(3)求节点数;
(4)求叶子数。
在此先约定下二叉树的节点结构和类的结构:
struct Node
{
char data;
Node *left, *right;
};
class BiTree
{
public:
Node *root; //根节点
BiTree();
Node* create();
void pre_order_rec(Node *node); //前序遍历递归版
void pre_order_non_rec(); //前序遍历非递归版
void in_order_rec(Node *node); //中序
void in_order_non_rec(); //
void post_order_rec(Node *node); //后序
void post_order_non_rec(); //
void level_order(); //层次遍历
int count_node(Node *node); //求节点数
int count_leaf(Node *node); //求叶子数
};二:具体实现与代码分析
2.1 构造二叉树
BiTree::BiTree()
{
root = create();
}
Node * BiTree::create()
{
Node *p = nullptr;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '.') //结束输入
p = nullptr;
else
{
p = new Node;
p->data = ch;
p->left = create();
p->right = create();
}
return p;
}2.2 前序遍历
对于当前节点,先输出该节点,然后输出它的左孩子,最后输出它的右孩子。以上图为例,递归的过程如下:
(1)输出1,接着左孩子;
(2)输出2,接着左孩子;
(3)输出4,左孩子为空,再接着右孩子;
(4)输出6,左孩子为空,再接着右孩子;
(5)输出7,左右孩子都为空,此时2的左子树全部输出,2的右子树为空,此时1的左子树全部输出,接着1的右子树;
(6)输出3,接着左孩子;
(7)输出5,左右孩子为空,此时3的左子树全部输出,3的右子树为空,至此1的右子树全部输出,结束。
而非递归版本只是利用stack模拟上述过程而已,递归的过程也就是出入栈的过程。注意加粗部分的理解。
void BiTree::pre_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
cout << node->data << " "; //先输出当前节点
pre_order_rec(node->left); //然后输出左孩子
pre_order_rec(node->right); //最后输出右孩子
}
}
void BiTree::pre_order_non_rec()
{
stack S;
Node *p = root;
while (p || !S.empty())
{
while (p)
{
cout << p->data << " "; //先输出当前节点
S.push(p);
p = p->left; //然后输出左孩子
} //while结束意味着左孩子已经全部输出
if (!S.empty())
{
p = S.top()->right; //最后输出右孩子
S.pop();
}
}
} 2.3 中序遍历
对于当前节点,先输出它的左孩子,然后输出该节点,最后输出它的右孩子。以(2.2)图为例:
(1)1-->2-->4,4的左孩子为空,输出4,接着右孩子;
(2)6的左孩子为空,输出6,接着右孩子;
(3)7的左孩子为空,输出7,右孩子也为空,此时2的左子树全部输出,输出2,2的右孩子为空,此时1的左子树全部输出,输出1,接着1的右孩子;
(4)3-->5,5左孩子为空,输出5,右孩子也为空,此时3的左子树全部输出,而3的右孩子为空,至此1的右子树全部输出,结束。
注意加粗部分的理解。
void BiTree::in_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
in_order_rec(node->left); //先输出左孩子
cout << node->data << " "; //然后输出当前节点
in_order_rec(node->right); //最后输出右孩子
}
}
void BiTree::in_order_non_rec()
{
stack S;
Node *p = root;
while (p || !S.empty())
{
while (p)
{
S.push(p);
p = p->left;
} //while结束意味着左孩子为空
if (!S.empty())
{
cout << S.top()->data << " "; //左孩子已经全部输出,接着输出当前节点
p = S.top()->right; //左孩子全部输出,当前节点也输出后,最后输出右孩子
S.pop();
}
}
} 2.4 后序遍历
对于当前节点,先输出它的左孩子,然后输出它的右孩子,最后输出该节点。依旧以(2.2)图为例:
(1)1->2->4->6->7,7无左孩子,也无右孩子,输出7,此时6无左孩子,而6的右子树也全部输出,输出6,此时4无左子树,而4的右子树全部输出,输出4,此时2的左子树全部输出,且2无右子树,输出2,此时1的左子树全部输出,接着转向右子树;
(2)3->5,5无左孩子,也无右孩子,输出5,此时3的左子树全部输出,且3无右孩子,输出3,此时1的右子树全部输出,输出1,结束。
非递归版本中,对于一个节点,如果我们要输出它,只有它既没有左孩子也没有右孩子或者它有孩子但是它的孩子已经被输出(由此设置pre变量)。若非上述两种情况,则将该节点的右孩子和左孩子依次入栈,这样就保证了每次取栈顶元素的时候,先依次遍历左子树和右子树,然后输出再输出节点。
void BiTree::post_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
post_order_rec(node->left); //先输出左孩子
post_order_rec(node->right); //然后输出右孩子
cout << node->data << " "; //最后输出当前节点
}
}
void BiTree::post_order_non_rec()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Node *pre = nullptr;
Node *cur = root;
stack S;
S.push(cur);
while (!S.empty())
{
cur = S.top();
if ((!cur->left && !cur->right) || //第一个输出的必是无左右孩子的叶子节点,由(!cur->left && !cur->right)
(pre && (pre == cur->left || pre == cur->right))) //来判断,只要第一个节点输出,以后的pre就不会是空。此处的判断语句加入
{ //一个pre,只是用来确保输出正确的第一个节点。
cout << cur->data << " "; //左右孩子都全部输出,再输出当前节点
pre = cur;
S.pop();
}
else
{
if (cur->right)
S.push(cur->right); //先进右孩子,再进左孩子,取出来的才是左孩子
if (cur->left)
S.push(cur->left);
}
}
} 2.5 层次遍历
void BiTree::level_order()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Node *p = root;
queue Q; //队列
Q.push(p);
while (!Q.empty())
{
p = Q.front();
cout << p->data << " ";
Q.pop();
if (p->left)
Q.push(p->left); //注意顺序,先进左孩子
if (p->right)
Q.push(p->right);
}
} 2.6 计算节点和叶子数
int BiTree::count_node(Node *node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
return count_node(node->left) + count_node(node->right) + 1;
}
int BiTree::count_leaf(Node *node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
if (!node->left && !node->right)
return 1;
return count_leaf(node->left) + count_leaf(node->right);
}三:完整代码
/**
*
* author 刘毅(Limer)
* date 2017-03-19
* mode C++
*/
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
char data;
Node *left, *right;
};
class BiTree
{
public:
Node *root; //根节点
BiTree();
Node* create();
void pre_order_rec(Node *node); //前序遍历递归版
void pre_order_non_rec(); //前序遍历非递归版
void in_order_rec(Node *node); //中序
void in_order_non_rec(); //
void post_order_rec(Node *node); //后序
void post_order_non_rec(); //
void level_order(); //层次遍历
int count_node(Node *node); //求节点数
int count_leaf(Node *node); //求叶子数
};
int main()
{
BiTree myTree;
//1.
cout << "前序遍历递归与非递归\n";
myTree.pre_order_rec(myTree.root); cout << endl;
myTree.pre_order_non_rec(); cout << endl << endl;
//2.
cout << "中序遍历递归与非递归\n";
myTree.in_order_rec(myTree.root); cout << endl;
myTree.in_order_non_rec(); cout << endl << endl;
//3.
cout << "后序遍历递归与非递归\n";
myTree.post_order_rec(myTree.root); cout << endl;
myTree.post_order_non_rec(); cout << endl << endl;;
//4.
cout << "层次遍历\n";
myTree.level_order(); cout << endl << endl;;
//5.
cout << "该二叉树的节点有";
cout << myTree.count_node(myTree.root);
cout << "个\n\n";
//6.
cout << "该二叉树的叶子有";
cout << myTree.count_leaf(myTree.root);
cout << "个\n\n";
return 0;
}
BiTree::BiTree()
{
root = create();
}
Node * BiTree::create()
{
Node *p = nullptr;
char ch;
cin >> ch;
if (ch == '.') //结束输入
p = nullptr;
else
{
p = new Node;
p->data = ch;
p->left = create();
p->right = create();
}
return p;
}
void BiTree::pre_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
cout << node->data << " "; //先输出当前节点
pre_order_rec(node->left); //然后输出左孩子
pre_order_rec(node->right); //最后输出右孩子
}
}
void BiTree::pre_order_non_rec()
{
stack S;
Node *p = root;
while (p || !S.empty())
{
while (p)
{
cout << p->data << " "; //先输出当前节点
S.push(p);
p = p->left; //然后输出左孩子
} //while结束意味着左孩子已经全部输出
if (!S.empty())
{
p = S.top()->right; //最后输出右孩子
S.pop();
}
}
}
void BiTree::in_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
in_order_rec(node->left); //先输出左孩子
cout << node->data << " "; //然后输出当前节点
in_order_rec(node->right); //最后输出右孩子
}
}
void BiTree::in_order_non_rec()
{
stack S;
Node *p = root;
while (p || !S.empty())
{
while (p)
{
S.push(p);
p = p->left;
} //while结束意味着左孩子为空
if (!S.empty())
{
cout << S.top()->data << " "; //左孩子全部输出,接着输出当前节点
p = S.top()->right; //左孩子全部输出,当前节点也输出后,最后输出右孩子
S.pop();
}
}
}
void BiTree::post_order_rec(Node * node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return;
else
{
post_order_rec(node->left); //先输出左孩子
post_order_rec(node->right); //然后输出右孩子
cout << node->data << " "; //最后输出当前节点
}
}
void BiTree::post_order_non_rec()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Node *pre = nullptr;
Node *cur = root;
stack S;
S.push(cur);
while (!S.empty())
{
cur = S.top();
if ((!cur->left && !cur->right) || //第一个输出的必是无左右孩子的叶子节点,由(!cur->left && !cur->right)
(pre && (pre == cur->left || pre == cur->right))) //来判断,只要第一个节点输出,以后的pre就不会是空。此处的判断语句加入
{ //一个pre,只是用来确保输出正确的第一个节点。
cout << cur->data << " "; //左右孩子都全部输出,再输出当前节点
pre = cur;
S.pop();
}
else
{
if (cur->right)
S.push(cur->right); //先进右孩子,再进左孩子,取出来的才是左孩子
if (cur->left)
S.push(cur->left);
}
}
}
void BiTree::level_order()
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Node *p = root;
queue Q; //队列
Q.push(p);
while (!Q.empty())
{
p = Q.front();
cout << p->data << " ";
Q.pop();
if (p->left)
Q.push(p->left); //注意顺序,先进左孩子
if (p->right)
Q.push(p->right);
}
}
int BiTree::count_node(Node *node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
return count_node(node->left) + count_node(node->right) + 1;
}
int BiTree::count_leaf(Node *node)
{
if (node == nullptr)
return 0;
if (!node->left && !node->right)
return 1;
return count_leaf(node->left) + count_leaf(node->right);
} 文章转自我的个人博客:http://www.61mon.com/index.php/archives/189/