MariaDB Proxy读写分离的实现
1.创建用于存储数据目录lvm设备
安装mysql-proxy-0.8.3
为mysql-proxy提供SysV服务脚本,内容如下所示
# vim /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql-proxy
#!/bin/bash
#
# mysql-proxy Thisscript starts and stops the mysql-proxy daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 7830
# processname:mysql-proxy
# description:mysql-proxy is a proxy daemon for mysql
# Source functionlibrary.
./etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
prog="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/bin/mysql-proxy"
# Sourcenetworking configuration.
if [ -f/etc/sysconfig/network ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/network
fi
# Check thatnetworking is up.
[ ${NETWORKING} = "no"] && exit 0
# Set defaultmysql-proxy configuration.
ADMIN_USER="admin"
ADMIN_PASSWD="admin"
ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua"
PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon"
PROXY_PID=/var/run/mysql-proxy.pid
PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy"
# Sourcemysql-proxy configuration.
if [ -f/etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy ]; then
. /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy
fi
RETVAL=0
start() {
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $prog $PROXY_OPTIONS--pid-file=$PROXY_PID --proxy-address="$PROXY_ADDRESS"--user=$PROXY_USER --admin-username="$ADMIN_USER"--admin-lua-script="$ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT"--admin-password="$ADMIN_PASSWORD"
RETVAL=$?
echo
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then
touch /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy
fi
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc -p $PROXY_PID -d 3 $prog
RETVAL=$?
echo
if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then
rm -f /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy
rm -f $PROXY_PID
fi
}
# See how we werecalled.
case"$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
if status -p $PROXY_PIDFILE $prog>&/dev/null; then
stop
start
fi
;;
status)
status -p $PROXY_PID $prog
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0{start|stop|restart|reload|status|condrestart|try-restart}"
RETVAL=1
;;
esac
exit$RETVAL
将上述内容保存为/etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql-proxy,给予执行权限,而后加入到服务列表。
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/mysql-proxy
# chkconfig --add mysql-proxy
为服务脚本提供配置文件/etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy,内容如下所示:
# Options formysql-proxy
ADMIN_USER="admin"
ADMIN_PASSWORD="admin"
ADMIN_ADDRESS=""
ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua"
PROXY_ADDRESS=""
PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy"
PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon--log-level=info --log-use-syslog"
其中最后一行,需要按实际场景进行修改,例如:
PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon--log-level=info --log-use-syslog --plugins=proxy --plugins=admin--proxy-backend-addresses=172.16.251.68:3306--proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=172.16.251.69:3306--proxy-lua-script=/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/rw-splitting.lua"其中的proxy-backend-addresses选项和proxy-read-only-backend-addresses选项均可重复使用多次,以实现指定多个读写服务器或只读服务器。
复制如下内容建立admin.lua文件,将其保存至/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/目录中。
--[[$%BEGINLICENSE%$
Copyright (c) 2007, 2012, Oracle and/or itsaffiliates. All rights reserved.
This program is free software; you canredistribute it and/or
modify it under the terms of the GNU GeneralPublic License as
published by the Free Software Foundation;version 2 of the
License.
This program is distributed in the hope thatit will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even theimplied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULARPURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNUGeneral Public License
along with this program; if not, write to theFree Software
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor,Boston, MA
02110-1301USA
$%ENDLICENSE%$ --]]
functionset_error(errmsg)
proxy.response = {
type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_ERR,
errmsg = errmsg or "error"
}
end
functionread_query(packet)
if packet:byte() ~= proxy.COM_QUERY then
set_error("[admin] we only handletext-based queries (COM_QUERY)")
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end
local query = packet:sub(2)
local rows = { }
local fields = { }
if query:lower() == "select * frombackends" then
fields = {
{name = "backend_ndx",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG },
{ name = "address",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "state",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "type",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "uuid",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name ="connected_clients",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG },
}
for i = 1, #proxy.global.backends do
local states = {
"unknown",
"up",
"down"
}
local types = {
"unknown",
"rw",
"ro"
}
local b = proxy.global.backends[i]
rows[#rows + 1] = {
i,
b.dst.name,-- configured backend address
states[b.state + 1], -- the C-idis pushed down starting at 0
types[b.type + 1],-- the C-id is pushed down starting at 0
b.uuid,-- the MySQL Server's UUID if itis managed
b.connected_clients-- currently connected clients
}
end
elseif query:lower() == "select * fromhelp" then
fields = {
{ name = "command",
type =proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
{ name = "description",
type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING },
}
rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROMhelp", "shows this help" }
rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROMbackends", "lists the backends and their state" }
else
set_error("use 'SELECT * FROM help'to see the supported commands")
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end
proxy.response = {
type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_OK,
resultset = {
fields = fields,
rows = rows
}
}
return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT
end仅启动mysql-proxy就可以了,不要启动MariaDB,否则你只会看到mysql的3306端口
# service mysql-proxy start
# ss –tnl|egrep ":3306|:4401"
LISTEN 0 128 *:4041 *:* users:(("mysql-proxy",3592,11))
LISTEN 0 128 *:3306 *:* users:(("mysql-proxy",3592,10))
MySQL Master端
在MySQL Master端(172.16.251.69)授权
#mysql
mysql> GRANT ALL ON*.* TO 'admin'@'172.16.%.%' IDENTIFIED BY 'admin';
mysql> FLUSHPRIVILEGES;
MySQL Slave端
在MySQL Slave端的数据库上查看是否有授权的用户

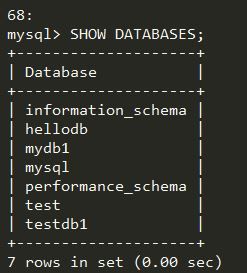
测试
下面的操作均在Maridb Proxy(172.16.251.70)上执行
管理功能测试
此时,若我们还试图以传统的方式连接Mysql的话,很显然是会失败的,如下:
# mysql
ERROR 2002(HY000): Can't connect to local MySQL server through socket '/tmp/mysql.sock'(2 "No such file or directory")
正确的方式:
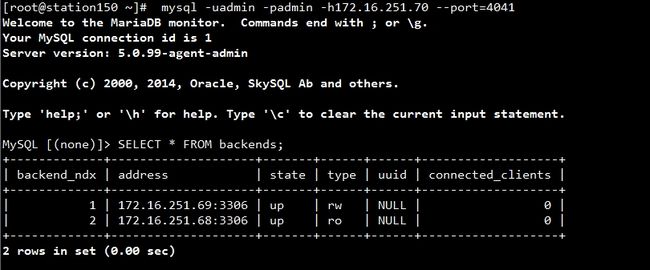
[root@station150 ~]#mysql-uadmin -padmin -h172.16.251.70 --port=4041
Welcome to theMariaDB monitor.Commands end with ; or\g.
Your MySQLconnection id is 1
Server version:5.0.99-agent-admin
MySQL [(none)]> SELECT* FROM HELP;
MySQL [(none)]>SELECT * FROM backends;
+-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+
| backend_ndx |address| state| type | uuid | connected_clients |
+-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+
|1 | 172.16.251.69:3306 | unknown |rw| NULL |0 |
|2 | 172.16.251.68:3306 | unknown |ro| NULL |0 |
+-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+
2 rows in set (0.01sec)
读写分离测试
通过MariadbProxy(172.16.251.70)访问Master MySQL(172.16.251.69)的数据库
# mysql -uadmin-padmin -h172.16.251.70 [--port=3306]
(1)测试写操作
# mysql -uadmin -padmin-h172.16.251.70
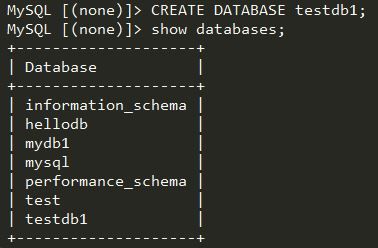
然后分别去Master端和Slave端,验证是否能看通过Mariadb Proxy新建的mydb1数据库
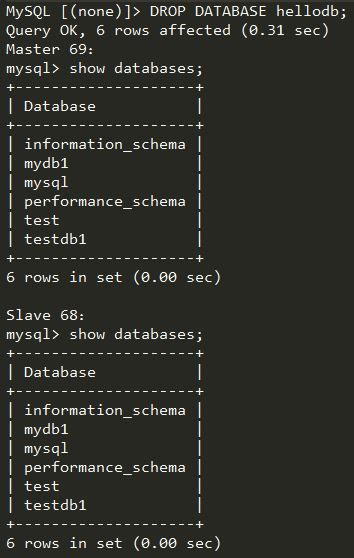
通过Mariadb Proxy删除hellodb数据库及其中的数据,并验证
MariaDB Proxy 70
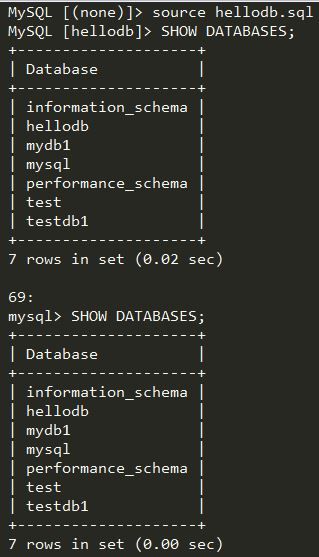
执行批量导入数据的操作:
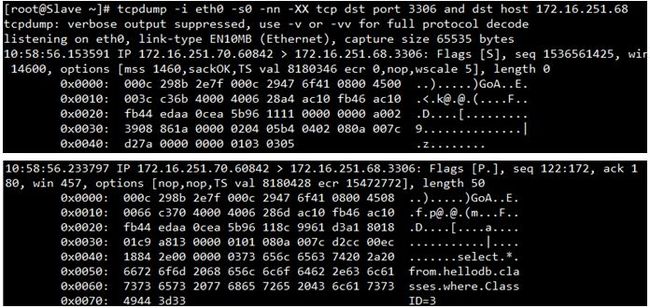
验证读写分离的最好办法是:分别在Master(可读写),Slave(只读)上使用tcpdump抓包工具,看可以捕捉到哪种操作的数据报文
测试读操作
在Master上捕获到的和读写操作相关的报文
由于在Master上可以进行读写操作,所以当读(查询)操作较少的时候,基本上Master自身就处理了,
所以想要验证效果就必须批量导入数据或执行查询操作。
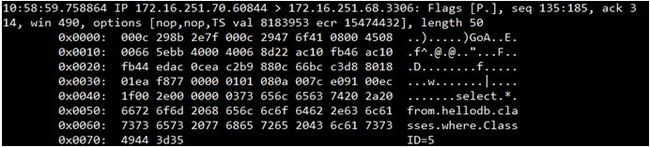
在MariadbProxy(70)执行批量读操作
# for i in `seq10`;do mysql -uadmin -padmin -h172.16.251.70 -e "select * fromhellodb.classes where ClassID=$i";done
下面是批量执行读操作时,在Slave上捕获到的和读写操作相关的报文
朋友,还记得之前在MariaDBProxy上执行SELECT * FROM backends;时state栏的状态信息吗?
刚开执行读写操作的时候,只有Master(172.16.251.69)的state是up状态,而在我批量执行读操作之后,
现在Slave(172.16.251.68)的state也变成了up状态,表示Slave端已接受到了读请求