ELKstack简介:
ELKstack是Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana三个开源软件的组合而成,形成一款强大的实时日志收集展示系统。
各组件作用如下:
Logstash:日志收集工具,可以从本地磁盘,网络服务(自己监听端口,接受用户日志),消息队列中收集各种各样的日志,然后进行过滤分析,并将日志输出到Elasticsearch中。
Elasticsearch:日志分布式存储/搜索工具,原生支持集群功能,可以将指定时间的日志生成一个索引,加快日志查询和访问。
Kibana:可视化日志Web展示工具,对Elasticsearch中存储的日志进行展示,还可以生成炫丽的仪表盘。
使用ELKstack对运维工作的好处:
1、应用程序的日志大部分都是输出在服务器的日志文件中,这些日志大多数都是开发人员来看,然后开发却没有登陆服务器的权限,如果开发人员需要查看日志就需要到服务器来拿日志,然后交给开发;试想下,一个公司有10个开发,一个开发每天找运维拿一次日志,对运维人员来说就是一个不小的工作量,这样大大影响了运维的工作效率,部署ELKstack之后,开发任意就可以直接登陆到Kibana中进行日志的查看,就不需要通过运维查看日志,这样就减轻了运维的工作。
2、日志种类多,且分散在不同的位置难以查找:如LAMP/LNMP网站出现访问故障,这个时候可能就需要通过查询日志来进行分析故障原因,如果需要查看apache的错误日志,就需要登陆到Apache服务器查看,如果查看数据库错误日志就需要登陆到数据库查询,试想一下,如果是一个集群环境几十台主机呢?这时如果部署了ELKstack就可以登陆到Kibana页面进行查看日志,查看不同类型的日志只需要电动鼠标切换一下索引即可。
ELKstack实验架构图:
redis消息队列作用说明:
1、防止Logstash和ES无法正常通信,从而丢失日志。
2、防止日志量过大导致ES无法承受大量写操作从而丢失日志。
3、应用程序(php,java)在输出日志时,可以直接输出到消息队列,从而完成日志收集。
补充:如果redis使用的消息队列出现扩展瓶颈,可以使用更加强大的kafka,flume来代替。
实验环境说明:
[root@es1 ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core) [root@es1 ~]# uname -rm 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 x86_64
使用软件说明:
1、jdk-8u92 官方rpm包
2、Elasticsearch 2.3.3 官方rpm包
3、Logstash 2.3.2 官方rpm包
4、Kibana 4.5.1 官方rpm包
5、Redis 3.2.1 remi rpm 包
6、nginx 1.10.0-1 官方rpm包
部署顺序说明:
1、Elasticsearch集群配置
2、Logstash客户端配置(直接写入数据到ES集群,写入系统messages日志)
3、Redis消息队列配置(Logstash写入数据到消息队列)
4、Kibana部署
5、nginx负载均衡Kibana请求
6、手机nginx日志
7、Kibana报表功能说明
配置注意事项:
1、时间必须同步
2、关闭防火墙,selinux
3、出了问题,检查日志
Elasticsearch集群安装配置
1、配置Java环境
[root@es1 ~]# yum -y install jdk1.8.0_92 [root@es1 ~]# java -version java version "1.8.0_92" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_92-b14) Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.92-b14, mixed mode)
2、安装Elasticsearch,因为我这里yum源已经创建好,所以可以直接安装
官方文档:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/index.html
官方下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch
[root@es1 ~]# yum -y install elasticstarch [root@es1 ~]# rpm -ql elasticsearch /etc/elasticsearch /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml #主配置文件 /etc/elasticsearch/logging.yml /etc/elasticsearch/scripts /etc/init.d/elasticsearch /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch /usr/lib/sysctl.d /usr/lib/sysctl.d/elasticsearch.conf /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service #启动脚本 /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/elasticsearch.conf
3、修改配置文件,这里的一些路径看个人习惯
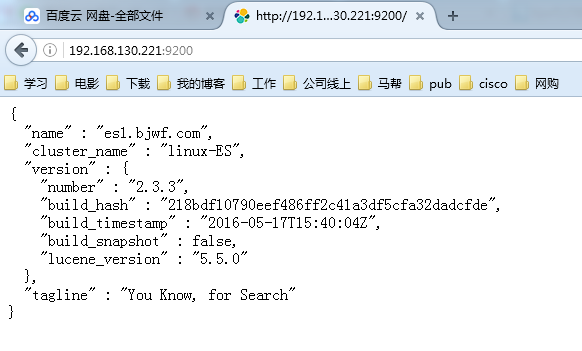
[root@es1 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 17 cluster.name: "linux-ES" 23 node.name: es1.bjwf.com 33 path.data: /elk/data 37 path.logs: /elk/logs 43 bootstrap.mlockall: true 54 network.host: 0.0.0.0 58 http.port: 9200 68 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.130.221", "192.168.130.222"]
4、创建相关目录并赋予权限
[root@es1 ~]# mkdir -pv /elk/{data,logs}
[root@es1 ~]# chown -R elasticsearch.elasticsearch /elk
[root@es1 ~]# ll /elk
drwxr-xr-x. 2 elasticsearch elasticsearch 6 Jun 28 03:51 data
drwxr-xr-x. 2 elasticsearch elasticsearch 6 Jun 28 03:51 logs
5、启动ES,并检查是否监听9200和9300端口
[root@es1 ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service [root@es1 ~]# netstat -tnlp|egrep "9200|9300" tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 17535/java tcp6 0 0 :::9300 :::* LISTEN 17535/java
6、安装另一台机器,步骤与第一台一样
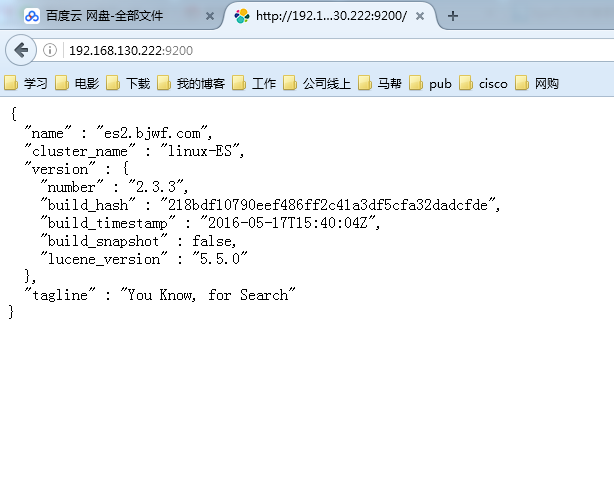
[root@es2 ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml 23 node.name: es2.bjwf.com #主要修改主机名
7、查看两个节点的状态
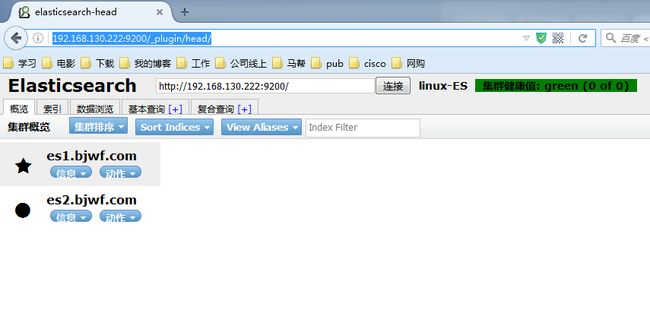
配置集群管理插件(head、kopf等)
官方提供了一个ES集群管理插件,可以非常直观的查看ES的集群状态和索引数据信息
[root@es1 ~]# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install mobz/elasticsearch-head [root@es1 ~]# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/plugin install lmenezes/elasticsearch-kopf
访问插件:
http://192.168.130.222:9200/_plugin/head/
http://192.168.130.222:9200/_plugin/kopf/
上面已经把ES集群配置完成了,下面就可以配置Logstash向ES集群中写入数据了
Logstash部署
1、配置Java环境,安装logstash
[root@logstash1 ~]# yum -y install jdk1.8.0_92 [root@logstash1 ~]# yum -y install logstash
2、通过配置文件验证Logstash的输入和输出
[root@logstash1 ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/stdout.conf
input {
stdin {}
}
output {
stdout {
codec => "rubydebug"
}
}
3、定义输出到Elasticsearch
[root@logstash1 ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf
input {
stdin {}
}
output {
input {
stdin {}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.130.221:9200","192.168.130.222:9200"]
index => "test"
}
}
[root@logstash1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf
Settings: Default pipeline workers: 4
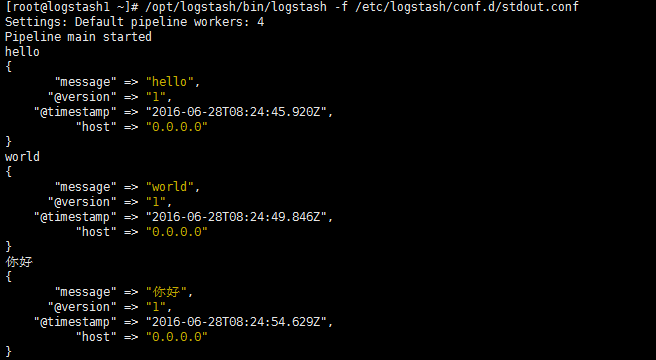
Pipeline main started
hello!
你好
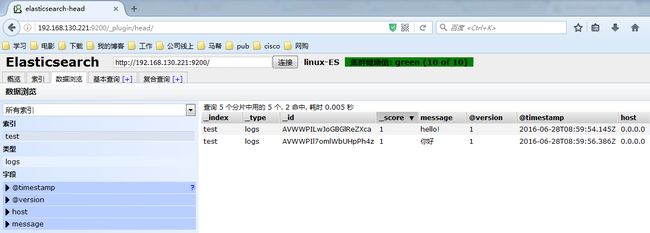 这个时候说明,Logstash接好Elasticsearch是可以正常工作的,下面介绍如何收集系统日志
这个时候说明,Logstash接好Elasticsearch是可以正常工作的,下面介绍如何收集系统日志
4、Logstash收集系统日志
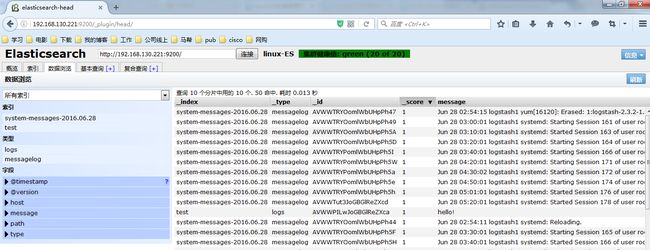
修改Logstash配置文件如下所示内容,并启动Logstash服务就可以在head中正常看到messages的日志已经写入到了ES中,并且创建了索引
[root@logstash1 ~]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf
input {
file {
type => "messagelog"
path => "/var/log/messages"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
file {
path => "/tmp/123.txt"
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.130.221:9200","192.168.130.222:9200"]
index => "system-messages-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
}
}
#检查配置文件语法:
/etc/init.d/logstash configtest
/opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf --configtest
#更改启动Logstash用户:
# vim /etc/init.d/logstash
LS_USER=root
LS_GROUP=root
#通过配置文件启动
[root@logstash1 ~]# /opt/logstash/bin/logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash.conf &
收集成功如图所示,自动生成了system-messages的索引
Kibana部署
说明:我这里是在两个ES节点部署kibana并且使用nginx实现负载均衡,如果没有特殊需要,可以只部署单台节点
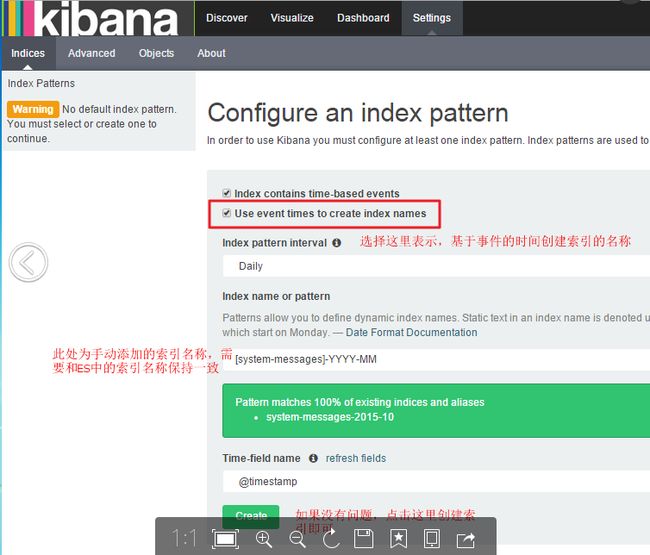
1、安装Kibana,每个ES节点部署一个 [root@es1 ~]# yum -y install kibana 2、配置Kibana,只需要指定ES地址其他配置保持默认即可 [root@es1 ~]# vim /opt/kibana/config/kibana.yml 15 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.130.221:9200" [root@es1 ~]# systemctl start kibana.service [root@es1 ~]# netstat -tnlp|grep 5601 #Kibana监听端口 tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5601 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 17880/node
查看效果,这个图是盗版的。。我做的这,忘记截图了
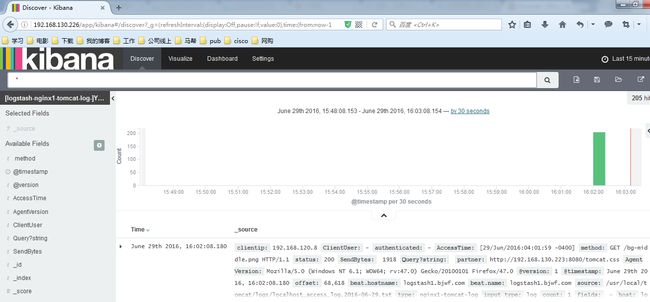
filebeat部署收集日志
1、安装nginx并将日志转换为json
[root@logstash1 ~]# yum -y install nginx
[root@logstash1 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
log_format access1 '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",'
'"host":"$server_addr",'
'"clientip":"$remote_addr",'
'"size":$body_bytes_sent,'
'"responsetime":$request_time,'
'"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",'
'"upstreamhost":"$upstream_addr",'
'"http_host":"$host",'
'"url":"$uri",'
'"domain":"$host",'
'"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",'
'"referer":"$http_referer",'
'"status":"$status"}';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log access1;
#保存配置文件,启动服务
[root@logstash1 ~]# systemctl start nginx
#验证nginx日志转json
[root@logstash1 ~]# tail /var/log/nginx/log/host.access.log
{"@timestamp":"2016-06-27T05:28:47-04:00",'"host":"192.168.130.223",''
"clientip":"192.168.120.222",''"size":15,''"responsetime":0.000,''"upstreamtime":"-",'
'"upstreamhost":"-",''"http_host":"192.168.130.223",''"url":"/index.html",''"domain":
"192.168.130.223",''"xff":"-",''"referer":"-",''"status":"200"}'
2、安装tomcat并将日志转换为json
[root@logstash1 ~]# tar xf apache-tomcat-8.0.36.tar.gz -C /usr/local
[root@logstash1 ~]# cd /usr/local
[root@logstash1 local]# ln -sv apache-tomcat-8.0.36/ tomcat
[root@logstash1 ~]# vim /usr/local/tomcat/conf/server.xml
配置nginx进行反向代理
[root@nginx ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
upstream kibana { #定义后端主机组
server 192.168.130.221:5601 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=2;
server 192.168.130.221:5602 weight=1 max_fails=2 fail_timeout=2;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.130.226;
location / { #定义反向代理,将访问自己的请求,都转发到kibana服务器
proxy_pass http://kibana/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
[root@nginx ~]# systemctl start nginx.service #启动服务
#查看Elasticsearch和Kibana输出结果
#到这里基本上结束了。以后在补充