在Android源码中添加自启服务
一、Android源码分析
在Android 系统源码中,服务的启动都是通过 SystemServer.java 这个类实现的。
1、源码位置:
2、源码部分展示:
(1)SystemServer.java (run())
private void run() {
......
// Start services.
try {
startBootstrapServices();
startCoreServices();
startOtherServices();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
}
......
}通过这部分源码,我们发现,系统服务分为了三类,下边我们一一分析。
(2)startBootstrapService()
private void startBootstrapServices() {
// Wait for installd to finish starting up so that it has a chance to
// create critical directories such as /data/user with the appropriate
// permissions. We need this to complete before we initialize other services.
Installer installer = mSystemServiceManager.startService(Installer.class);
// Activity manager runs the show.
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);
// Display manager is needed to provide display metrics before package manager
// starts up.
mDisplayManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(DisplayManagerService.class);
// Power manager needs to be started early because other services need it.
// Native daemons may be watching for it to be registered so it must be ready
// to handle incoming binder calls immediately (including being able to verify
// the permissions for those calls).
mPowerManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(PowerManagerService.class);
// Now that the power manager has been started, let the activity manager
// initialize power management features.
mActivityManagerService.initPowerManagement();
// We need the default display before we can initialize the package manager.
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_WAIT_FOR_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
// Only run "core" apps if we're encrypting the device.
String cryptState = SystemProperties.get("vold.decrypt");
if (ENCRYPTING_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Detected encryption in progress - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
} else if (ENCRYPTED_STATE.equals(cryptState)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Device encrypted - only parsing core apps");
mOnlyCore = true;
}
// Start the package manager.
Slog.i(TAG, "Package Manager");
mPackageManagerService = PackageManagerService.main(mSystemContext, installer,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_OFF, mOnlyCore);
mFirstBoot = mPackageManagerService.isFirstBoot();
mPackageManager = mSystemContext.getPackageManager();
Slog.i(TAG, "User Service");
ServiceManager.addService(Context.USER_SERVICE, UserManagerService.getInstance());
// Initialize attribute cache used to cache resources from packages.
AttributeCache.init(mSystemContext);
// Set up the Application instance for the system process and get started.
mActivityManagerService.setSystemProcess();
}通过这部分源码,我们发现,该方法负责启动系统中最重要的几个服务,PKMS,PMS,AMS等。
(3)startCoreService()
/**
* Starts some essential services that are not tangled up in the bootstrap process.
*/
private void startCoreServices() {
// Manages LEDs and display backlight.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(LightsService.class);
// Tracks the battery level. Requires LightService.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(BatteryService.class);
// Tracks application usage stats.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(UsageStatsService.class);
mActivityManagerService.setUsageStatsManager(
LocalServices.getService(UsageStatsManagerInternal.class));
// Update after UsageStatsService is available, needed before performBootDexOpt.
mPackageManagerService.getUsageStatsIfNoPackageUsageInfo();
// Tracks whether the updatable WebView is in a ready state and watches for update installs.
mSystemServiceManager.startService(WebViewUpdateService.class);
}通过注释我们可以看到,这些服务都是一些和系统引导,就是启动无关的一下服务。
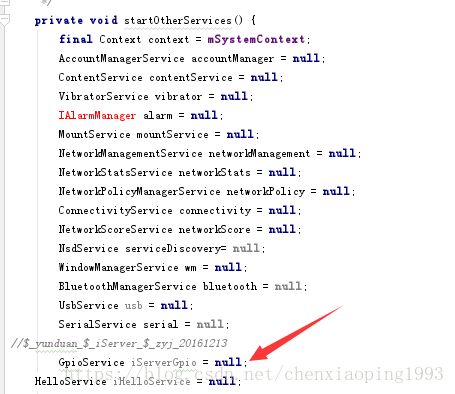
(4)startOtherServices()
所以说,剩下的这个方法就是我们需要添加服务的地方了
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "GPIO Service");
ServiceManager.addService("iServerGpio", new GpioService());
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting GpioService", e);
}3、服务存放位置

那么,这个存放位置是确定的吗?其实不是的。看下图:

我们可以看到,我们只要在SystemServer.java 中正确引包就可以了,但是为了代码的整洁,还是按规矩来比较好。
二、实现方法
为了阅读方便,我们以GpioService 为例:
1、将服务放置到源码中
2、在SystemServer.java 中添加代码
(1)引包
(2)创建对象
(3)开启服务
try {
Slog.i(TAG, "GPIO Service");
ServiceManager.addService("iServerGpio", new GpioService());
} catch (Throwable e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting GpioService", e);
}三、编译方法
具体编译方法,看RK3328-CC 官网,链接如下:
http://www.t-firefly.com/doc/product/info/id/252.html