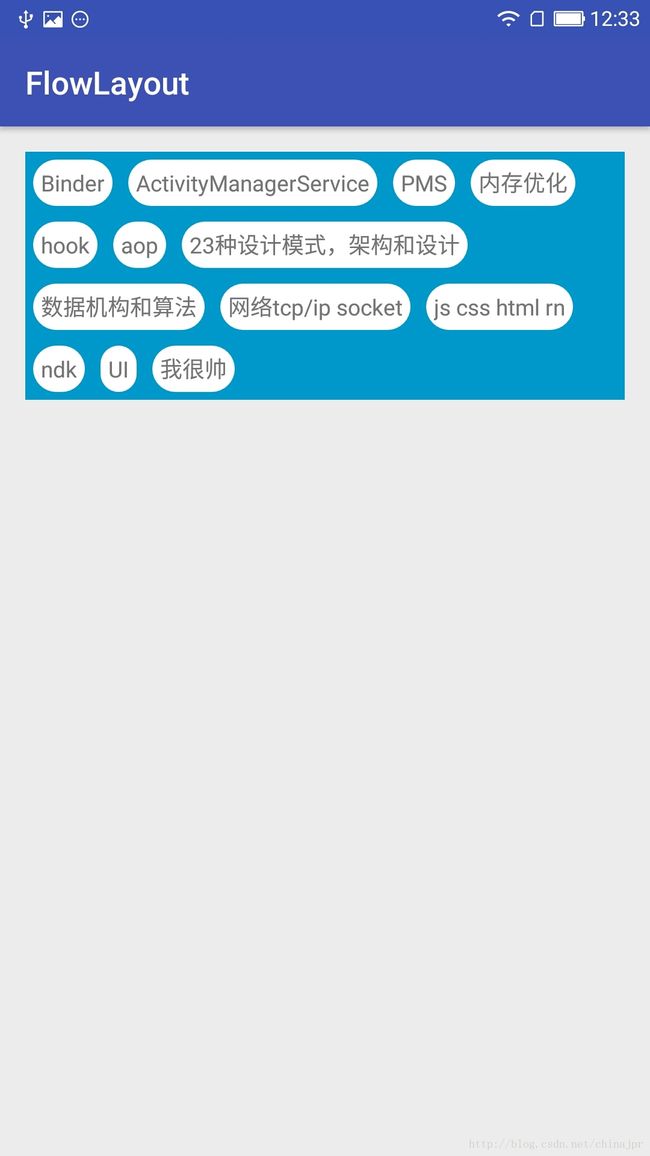
自适应布局FlowLayout
很明显,这是一个自定义ViewGroup,三个步骤,测量(onMeasure),布局(onLayout),绘制(onDraw,本例中用不到绘制哦);不叨叨,上代码
1.构造方法,在xml中引用,要实现2个参数的构造方法
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}2.onMeasrue,测量
FlowLayout的宽是:match_parent;高是:wrap_content,你知道的,自定义ViewGroup需要自己实现wrap_content,以及子view的margin(这个大家都很清楚了,就不赘述了。)
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//默认的高度,宽度以及模式
int widthMeasureSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMeasureMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMeasureMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
//viewgroup总的高度和宽度
int height = 0;
int width = 0;
//每一行的宽度和高度
int lineHeight = 0;
int lineWidth = 0;
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
//测量子view
measureChild(childAt, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获取子view的宽高
//LayoutParams layoutParams1 = childAt.getLayoutParams();
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = childAt.getMeasuredWidth() + layoutParams.leftMargin + layoutParams.rightMargin;
int childHeight = childAt.getMeasuredHeight() + layoutParams.topMargin + layoutParams.bottomMargin;
//开始测量
//需要换行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > widthMeasureSize) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);
height += lineHeight;
//换行后的行高和行宽
lineWidth = childWidth;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
//不需要换行
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
lineWidth += childWidth;
if (i == childCount - 1) {
height += lineHeight;
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(widthMeasureMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? widthMeasureSize : width
, heightMeasureMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? heightMeasureSize : height);
}
}
//LayoutParams是viewgroup提供给子view使用的,LayoutParams无法获取margin值,MarginLayoutParams可以获取margin值
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}前面说了,我们需要自己实现margin和wrap_content
实现wrap_content:for循环,遍历所有的子view,子view的高的和就是FlowLayout的高;实现子view的margin,需要重写generateLayoutParams().往下看:
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
//测量子view
measureChild(childAt, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//获取子view的宽高
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();这几行代码,分别是测量子View,获取子View的LayoutParams(别告诉我你不知道LayoutParams是啥),但是,默认情况下你的代码是这个样子的:
//LayoutParams layoutParams1 = childAt.getLayoutParams();LayoutParams 不包含margin信息,无法获取margin值,所以我们需要转成:
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();同时,重写:
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}原本该方法是返回LayoutParams 的,让他返回MarginLayoutParams,就是我们
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();中获得的MarginLayoutParams 。
onLayout 布局
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int childCount = getChildCount();
int lineWidth = 0, lineHeight = 0, left = 0, top = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childAt.getLayoutParams();
int leftMargin = layoutParams.leftMargin;
int rightMargin = layoutParams.rightMargin;
int topMargin = layoutParams.topMargin;
int bottomMargin = layoutParams.bottomMargin;
int childWidth = childAt.getMeasuredWidth() + leftMargin + rightMargin;
int childHeight = childAt.getMeasuredHeight() + topMargin + bottomMargin;
//开始布局
//换行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > getMeasuredWidth()) {
top += lineHeight;
left = 0;
//换行后,重新计算lineHeight,lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else {
//不换行
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(childHeight , lineHeight);
}
int cl = left + leftMargin;
int cr = cl + childAt.getMeasuredWidth();
int ct = top + topMargin;
int cb = ct + childAt.getMeasuredHeight();
childAt.layout(cl, ct, cr, cb);
left += childWidth;
}
}都是很简单的逻辑问题,我就不啰嗦了。
源码奉上