图片加载库Picasso和Glide对比
Android上图片加载库现在出现了有挺多了,比较出名的有ImageLoader、Picasso、Glide、Fresco,这里来对比一下两个比较相像的库,Picasso和Glide。
这两个库在API使用上非常的类似,都是很简单的链式调用法,但是实现上却有较大的不同,下载源码就能发现Glide复杂很多,Picasso相对就简单不少,下面就分几个方面来简单对比一下这两个库的不同之处和实现的关键点。
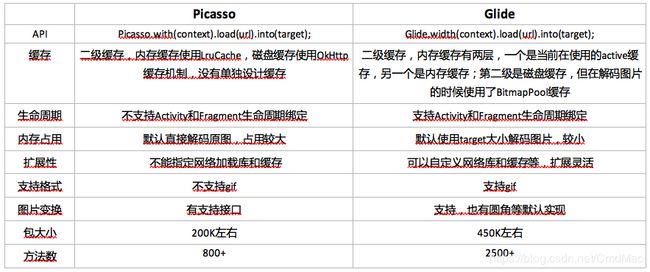
1.API使用
API使用上就不多做介绍,简单贴一下samle源码:
Picasso:
Picasso.get()
.load(url)
.placeholder(R.drawable.user_placeholder)
.error(R.drawable.user_placeholder_error)
.into(imageView);
Glide:
Glide.with(fragment)
.load(myUrl)
.placeholder(placeholder)
.fitCenter()
.into(imageView);
2.缓存实现
Picasso缓存比较简单,有两级,内存缓存实现是LruCache,源码在com.squareup.picasso3.PlatformLruCache类,里面有个LruCache
// RequestCreator.java
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(request.memoryPolicy)) {
Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(request.key);
if (bitmap != null) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
RequestHandler.Result result = new RequestHandler.Result(bitmap, MEMORY);
setResult(target, picasso.context, result, noFade, picasso.indicatorsEnabled);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, request.plainId(), "from " + MEMORY);
}
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
// Picasso.java
@Nullable Bitmap quickMemoryCacheCheck(String key) {
Bitmap cached = cache.get(key);
if (cached != null) {
stats.dispatchCacheHit();
} else {
stats.dispatchCacheMiss();
}
return cached;
}
磁盘缓存Picasso直接使用了OkHttp缓存机制,没有单独的磁盘缓存设计,关键代码在:
// NetworkRequestHandler.java
private static okhttp3.Request createRequest(Request request) {
CacheControl cacheControl = null;
int networkPolicy = request.networkPolicy;
if (networkPolicy != 0) {
if (NetworkPolicy.isOfflineOnly(networkPolicy)) {
cacheControl = CacheControl.FORCE_CACHE;
} else {
CacheControl.Builder builder = new CacheControl.Builder();
if (!NetworkPolicy.shouldReadFromDiskCache(networkPolicy)) {
builder.noCache();
}
if (!NetworkPolicy.shouldWriteToDiskCache(networkPolicy)) {
builder.noStore();
}
cacheControl = builder.build();
}
}
// ......
return builder.build();
}
而Glide则比较复杂,首先内存缓存分活动缓存即正在使用的和另一个内存缓存,关键代码:
// com.bumptech.glide.load.engine.Engine类的load方法
EngineKey key = keyFactory.buildKey(model, signature, width, height, transformations,
resourceClass, transcodeClass, options);
EngineResource active = loadFromActiveResources(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if (active != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(active, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from active resources", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
EngineResource cached = loadFromCache(key, isMemoryCacheable);
if (cached != null) {
cb.onResourceReady(cached, DataSource.MEMORY_CACHE);
if (VERBOSE_IS_LOGGABLE) {
logWithTimeAndKey("Loaded resource from cache", startTime, key);
}
return null;
}
// 默认是LruResourceCache,关键代码在GlideBuilder.java的build方法中可以看到
if (memoryCache == null) {
memoryCache = new LruResourceCache(memorySizeCalculator.getMemoryCacheSize());
}
if (diskCacheFactory == null) {
diskCacheFactory = new InternalCacheDiskCacheFactory(context);
}
而磁盘缓存是DiskLruCache,关键代码:
// DiskLruCacheFactory
@Override
public DiskCache build() {
File cacheDir = cacheDirectoryGetter.getCacheDirectory();
if (cacheDir == null) {
return null;
}
if (!cacheDir.mkdirs() && (!cacheDir.exists() || !cacheDir.isDirectory())) {
return null;
}
return DiskLruCacheWrapper.create(cacheDir, diskCacheSize);
}
// DiskLruCacheWrapper.java
private synchronized DiskLruCache getDiskCache() throws IOException {
if (diskLruCache == null) {
diskLruCache = DiskLruCache.open(directory, APP_VERSION, VALUE_COUNT, maxSize);
}
return diskLruCache;
}
而在decode图片时,Glide还独特做了优化,它使用BitmapPool缓存了option相同的图片,以减少内存开销,减少内存回收机率,从而提高性能,关键代码:
// Downsampler.java
private static void setInBitmap(
BitmapFactory.Options options, BitmapPool bitmapPool, int width, int height) {
@Nullable Bitmap.Config expectedConfig = null;
// ...
// BitmapFactory will clear out the Bitmap before writing to it, so getDirty is safe.
options.inBitmap = bitmapPool.getDirty(width, height, expectedConfig);
}
// Downsampler.java decodeStream方法
try {
result = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is, null, options);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
IOException bitmapAssertionException =
newIoExceptionForInBitmapAssertion(e, sourceWidth, sourceHeight, outMimeType, options);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.DEBUG)) {
Log.d(TAG, "Failed to decode with inBitmap, trying again without Bitmap re-use",
bitmapAssertionException);
}
if (options.inBitmap != null) {
try {
is.reset();
bitmapPool.put(options.inBitmap);
options.inBitmap = null;
return decodeStream(is, options, callbacks, bitmapPool);
} catch (IOException resetException) {
throw bitmapAssertionException;
}
}
throw bitmapAssertionException;
} finally {
TransformationUtils.getBitmapDrawableLock().unlock();
}
3.生命周期
Picasso没有生命周期绑定的功能,而Glide实现了,Glide是在Activity里插入一个没有界面的Fragment来达到绑定的,关键代码:
// RequestmanagerRetriever.java
private RequestManager fragmentGet(@NonNull Context context,
@NonNull android.app.FragmentManager fm,
@Nullable android.app.Fragment parentHint,
boolean isParentVisible) {
RequestManagerFragment current = getRequestManagerFragment(fm, parentHint, isParentVisible);
RequestManager requestManager = current.getRequestManager();
if (requestManager == null) {
// TODO(b/27524013): Factor out this Glide.get() call.
Glide glide = Glide.get(context);
requestManager =
factory.build(
glide, current.getGlideLifecycle(), current.getRequestManagerTreeNode(), context);
current.setRequestManager(requestManager);
}
return requestManager;
}
// RequestManagerFragment.java
@NonNull
ActivityFragmentLifecycle getGlideLifecycle() {
return lifecycle;
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
super.onStop();
lifecycle.onStop();
}
Glide将RequestMangerFragment的生命周期通过Lifecycle绑定到RequestManager上,原理是RequestMangerFragment.setRequestManager然后在RequestManager构造的时候调用lifecycle.addListener
if (Util.isOnBackgroundThread()) {
mainHandler.post(addSelfToLifecycle);
} else {
lifecycle.addListener(this);
}
不过要绑定Activity的生命周期需要使用Activity作为Context传入Glide中
Glide.width(Activity).load(url).into(target);
熟悉内存泄漏的你看到Activity传到单实例肯定担心,不过在RequestManger在收到生命周期Destory时会自动释放引用:
// RequestManager.java
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
targetTracker.onDestroy();
for (Target❔ target : targetTracker.getAll()) {
clear(target);
}
targetTracker.clear();
requestTracker.clearRequests();
lifecycle.removeListener(this);
lifecycle.removeListener(connectivityMonitor);
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(addSelfToLifecycle);
glide.unregisterRequestManager(this);
}
4.内存占用
Picasso内存占用较高的原因是默认decode的时候没有用实际的控件大小,关键代码:
// BitmapUtils.java
private static Bitmap decodeStreamPreP(Request request, BufferedSource bufferedSource)
throws IOException {
boolean isWebPFile = Utils.isWebPFile(bufferedSource);
boolean isPurgeable = request.purgeable && SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP;
BitmapFactory.Options options = createBitmapOptions(request);
boolean calculateSize = requiresInSampleSize(options);
Bitmap bitmap;
// We decode from a byte array because, a) when decoding a WebP network stream, BitmapFactory
// throws a JNI Exception, so we workaround by decoding a byte array, or b) user requested
// purgeable, which only affects bitmaps decoded from byte arrays.
if (isWebPFile || isPurgeable) {
byte[] bytes = bufferedSource.readByteArray();
if (calculateSize) {
BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(bytes, 0, bytes.length, options);
calculateInSampleSize(request.targetWidth, request.targetHeight,
checkNotNull(options, "options == null"), request);
}
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(bytes, 0, bytes.length, options);
} else {
if (calculateSize) {
BitmapFactory.decodeStream(bufferedSource.peek().inputStream(), null, options);
calculateInSampleSize(request.targetWidth, request.targetHeight,
checkNotNull(options, "options == null"), request);
}
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(bufferedSource.inputStream(), null, options);
}
if (bitmap == null) {
// Treat null as an IO exception, we will eventually retry.
throw new IOException("Failed to decode bitmap.");
}
return bitmap;
}
// BitmapUtils.java
@Nullable static BitmapFactory.Options createBitmapOptions(Request data) {
final boolean justBounds = data.hasSize();
BitmapFactory.Options options = null;
if (justBounds || data.config != null || data.purgeable) {
options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = justBounds;
options.inInputShareable = data.purgeable;
options.inPurgeable = data.purgeable;
if (data.config != null) {
options.inPreferredConfig = data.config;
}
}
return options;
}
// Request.java
public boolean hasSize() {
return targetWidth != 0 || targetHeight != 0;
}
可以看到Picasso在解码时需要判断Request的targetWidth和targetHeight是不是为0,需要在调用时调用resize指定大小才会触发到这里。而Glide默认就做了这个事,关键代码:
// SingleRequest.java begin方法
status = Status.WAITING_FOR_SIZE;
if (Util.isValidDimensions(overrideWidth, overrideHeight)) {
onSizeReady(overrideWidth, overrideHeight);
} else {
target.getSize(this);
}
// ViewTarget.java
void getSize(@NonNull SizeReadyCallback cb) {
int currentWidth = getTargetWidth();
int currentHeight = getTargetHeight();
if (isViewStateAndSizeValid(currentWidth, currentHeight)) {
cb.onSizeReady(currentWidth, currentHeight);
return;
}
// We want to notify callbacks in the order they were added and we only expect one or two
// callbacks to be added a time, so a List is a reasonable choice.
if (!cbs.contains(cb)) {
cbs.add(cb);
}
if (layoutListener == null) {
ViewTreeObserver observer = view.getViewTreeObserver();
layoutListener = new SizeDeterminerLayoutListener(this);
observer.addOnPreDrawListener(layoutListener);
}
}
//ViewTarget.java
private static final class SizeDeterminerLayoutListener
implements ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener {
//......
@Override
public boolean onPreDraw() {
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "OnGlobalLayoutListener called attachStateListener=" + this);
}
SizeDeterminer sizeDeterminer = sizeDeterminerRef.get();
if (sizeDeterminer != null) {
sizeDeterminer.checkCurrentDimens();
}
return true;
}
}
// SizeDeterminer类
private void notifyCbs(int width, int height) {
for (SizeReadyCallback cb : new ArrayList<>(cbs)) {
cb.onSizeReady(width, height);
}
}
可以看到在into的时候如果size不正确会调用ViewTarget的getSize,然后通过OnPrewDrawListener的回调获得大小后再回到onSizeReady到SingleRequest执行engine的load进行加载。
5.扩展性
扩展性方面Picasso比较差,比如网络只能使用OkHttp,关键代码:
// Picasso.java
@NonNull
public Builder client(@NonNull OkHttpClient client) {
checkNotNull(client, "client == null");
callFactory = client;
return this;
}
// NetworkRequestHandler.java
private static okhttp3.Request createRequest(Request request) {
//......
Uri uri = checkNotNull(request.uri, "request.uri == null");
okhttp3.Request.Builder builder = new okhttp3.Request.Builder().url(uri.toString());
if (cacheControl != null) {
builder.cacheControl(cacheControl);
}
return builder.build();
}
而Glide则可以使用OkHttp或Volley,扩展比较多,具体代码这里就不分析
6.图片格式/图形变换
Picasso默认不支持gif,而glide支持,只要这样使用:
Glide.width(context).asGif().load(url).into(target);
图形变换两个库都支持,但Picasso没有默认实现,只有Transformation接口,而Glide有默认实现,如圆角图片:
RequestOptions mRequestOptions = RequestOptions.circleCropTransform()
.diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.NONE)//不做磁盘缓存
.skipMemoryCache(true);//不做内存缓存
Glide.with(mContext).load(userInfo.getImage()).apply(mRequestOptions).into(mUserIcon);
总结
Picasso和Glide两个库各有优缺点,需要根据不同的需求进行选择,不过较为复杂的场景下,Glide还是更为推荐使用。Glide库里面的缓存实现等技术,非常值得学习,看了源码也会发现,其实最根本的还是要掌握android的基本功,比如BitmapPool技术其实就是用了decode图片时的内存复用技术。