Spring @Transactional 事务回滚机制
Srping 事务
在Spring 的世界里面我们一般使用@Transactional 注解在对应方法上面声明为一个事务方法。
但是在默认不写@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)默认回滚RuntimeException
今天就希望通过源码的方式了解一下@Transactional的回滚机制。
Spring 源码解析
首先我们先编写一个测试demo如下所示
@Service
public class TestService {
@Autowired
private ModelRepo modelRepo;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = {Exception.class,ClassNotFoundException.class,IOException.class} ,
noRollbackFor = FileNotFoundException.class)
public void test() throws Throwable{
Model model = new Model();
modelRepo.save(model);
throw new FileNotFoundException();
}
}
接着我们开始进入Debug
当我们的代码抛出异常时Spring容器会创建一个RuleBasedTransactionAttribute对象,该对象就是我们那个方法上面@Transactional的一个描述。
//基于规则的事务属性
public class RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
extends DefaultTransactionAttribute implements Serializable {
//这就是那些 rollbackFor noRollbackFor 异常的处理器
@Nullable
private List<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollbackRules;
...
}
//这个就是异常回滚处理器的类
//回滚规则属性
public class RollbackRuleAttribute implements Serializable{
/**
* The {@link RollbackRuleAttribute rollback rule} for
* {@link RuntimeException RuntimeExceptions}.
*/
//这里默认就有个RuntimeException处理
//但是 @Transactional 默认回滚和它貌似没有什么关系
public static final RollbackRuleAttribute ROLLBACK_ON_RUNTIME_EXCEPTIONS =
new RollbackRuleAttribute(RuntimeException.class);
private final String exceptionName;
//这里就将待处理类名称保存起来
public RollbackRuleAttribute(Class<?> clazz) {
Assert.notNull(clazz, "'clazz' cannot be null");
if (!Throwable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot construct rollback rule from [" + clazz.getName() + "]: it's not a Throwable");
}
this.exceptionName = clazz.getName();
}
//这两个方法是很关键的是Spring核心处理逻辑 后续会继续贴上代码
public int getDepth(Throwable ex) {
return getDepth(ex.getClass(), 0);
}
private int getDepth(Class<?> exceptionClass, int depth) {
//异常对象能够被代理吗? xxx.xxx.xxx.$xx 防止别人骚操作?
if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(this.exceptionName)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
// If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it...
//找不到而且已经找到头了
if (exceptionClass == Throwable.class) {
return -1;
}
//儿子找不到,就找他爹咯
return getDepth(exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1);
}
... //略
}
在初始化一个异常回滚判定的 基于规则的事务属性 RuleBasedTransactionAttribute对象之后就进入了TransactionAspectSupport(交易方面支持)的代码
public abstract class TransactionAspectSupport
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
...
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
// If the transaction attribute is null, the method is non-transactional.
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
//这还要是有 回调首选平台事务管理器 的才可以进入
//不够我们一般都是进入这个代码块逻辑进行处理的
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
//核心代码
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
//执行Service的相关方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// target invocation exception
//处理Exception判定回滚规则
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
else {
... //代码太多久不贴了
}
}
...
//进入 completeTransactionAfterThrowing 方法看看
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Completing transaction for [" + txInfo.getJoinpointIdentification() +
"] after exception: " + ex);
}
//核心关键的处理逻辑来了 txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
else {
// 发话了我们不会回滚这个异常
// We don't roll back on this exception.
// Will still roll back if TransactionStatus.isRollbackOnly() is true.
try {
txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
}
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
throw ex2;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", ex);
throw ex2;
}
}
}
}
}
搞事搞事 我们进入 txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex) 这个东西看看
第一层
public abstract class DelegatingTransactionAttribute
extends DelegatingTransactionDefinition
implements TransactionAttribute, Serializable {
...
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return this.targetAttribute.rollbackOn(ex);
}
...
}
进入this.targetAttribute.rollbackOn(ex);
没错就是上面的RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
public class RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
extends DefaultTransactionAttribute implements Serializable {
...
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Applying rules to determine whether transaction should rollback on " + ex);
}
RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//因为这里的处理器集合总是回滚的在前面,不回滚的在后面所以你认为不回滚一定无敌,那么你就错咯
if (this.rollbackRules != null) {
for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {
int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);
//骚还是Spring的人骚 这里他么是个就近原则
// 所以理论上 rollbackFor noRollbackFor 同一个类那么应该是回滚的 可以试试
//就近原则,一样近走回滚
if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {
deepest = depth;
winner = rule;
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Winning rollback rule is: " + winner);
}
// User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches.
if (winner == null) {
logger.trace("No relevant rollback rule found: applying default rules");
return super.rollbackOn(ex);
}
return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
}
...
}
rule.getDepth(ex);
public int getDepth(Throwable ex) {
//重0开始计数
return getDepth(ex.getClass(), 0);
}
//就是上面的rule.getDepth(ex); 获取深度,结合上下文 就近原则了
private int getDepth(Class<?> exceptionClass, int depth) {
if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(this.exceptionName)) {
// Found it!
return depth;
}
// If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it...
if (exceptionClass == Throwable.class) {
return -1;
}
return getDepth(exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1);
}
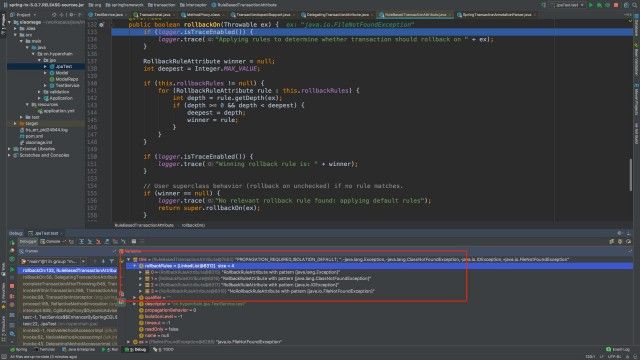
有张图片配合一下,可以看出里面的处理器总是前面的是允许回滚的,后面的是不进行回滚的。
可以看出里面的处理器总是前面的是允许回滚的,后面的是不进行回滚的。
以上就是@Transactional有配置 noRollbackFor ,rollbackFor 的执行流程
Spring @Transactional 无配置回滚执行
public class RuleBasedTransactionAttribute
extends DefaultTransactionAttribute
implements Serializable {
...
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Applying rules to determine whether transaction should rollback on " + ex);
}
RollbackRuleAttribute winner = null;
int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (this.rollbackRules != null) {
for (RollbackRuleAttribute rule : this.rollbackRules) {
int depth = rule.getDepth(ex);
if (depth >= 0 && depth < deepest) {
deepest = depth;
winner = rule;
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Winning rollback rule is: " + winner);
}
// User superclass behavior (rollback on unchecked) if no rule matches.
//无配置时 进入了这里了 找爹看看怎么操作
if (winner == null) {
logger.trace("No relevant rollback rule found: applying default rules");
return super.rollbackOn(ex);
}
return !(winner instanceof NoRollbackRuleAttribute);
}
...
}
看看爹怎么操作的
public class DefaultTransactionAttribute
extends DefaultTransactionDefinition
implements TransactionAttribute {
...
// 就这么直白 裁判杀死了比赛 RuntimeException Error 回滚,其他再见
@Override
public boolean rollbackOn(Throwable ex) {
return (ex instanceof RuntimeException || ex instanceof Error);
}
...
}