CJSON源码研究笔记
断断续续的CJSON源码看了也有一段时间了,研究一番还是收获颇多!很适合有一点C基础的想继续提高练手的开源源码!cJson.c代码只有700多行,官网上下的,代码风格个人感觉不是很方便阅读,如果全部展开的话代码估计至少不在1100行之下。网上也看了一些前辈们的cjson笔记!对于像我这这样初次接触CJSON还是相当有帮助的!下面就来一点一点的分析源码!这里记录一下自己对源码研究理解的笔记!同时也希望对别人作为参考也有一点点的帮助!
研究源码之前首先还是搞清楚CJSON到底是干啥的!这样可以对整个源码有个大体的把握!下面是举一些例子可以大致了解一下what is cjson?
CJSON:
解释一:
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,主要用于传送数据。JSON 可以将 JavaScript 对象中表示的一组数据转换为字符串,然后就可以在函数之间轻松地传递这个字符串,或者在异步应用程序中将字符串从 Web 客户机传递给服务器端程序。这个字符串看起来有点儿古怪,但是 JavaScript 很容易解释它,而且 JSON 可以表示比"名称 / 值对"更复杂的结构。例如,可以表示数组和复杂的对象,而不仅仅是键和值的简单列表。JSON采用完全独立于语言的文本格式,但是也使用了类似于C语言家族的习惯(包括C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Perl,Python等)。这些特性使JSON成为理想的数据交换语言。易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成。
解释二:
就是一种数据格式,不必过于纠结于此。就像一种交通工具,就像你上班要开车一样,可能骑自行车也是一种交通工具,但是json这种交通工具更方便,更快捷。
解释三:
对于cJSON的使用,我主要是用来模拟远程服务器端返回的一个json类型的目录结构,客户端进行获取并进行解析,把解析出来的目录按照原本的结构显示在本地
当然除了上面的一些解释最权威的还是CJSON官方解释!这个自己直接搜,百度谷歌!上面不仅有可供下载的各种编程语言版本的源码,也有很具体的介绍!下面就来逐步深入的分析研究源码了!(源码我是用SI来看的)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "cJSON.h"
static const char *global_ep;
const char *cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void) {return global_ep;}
static int cJSON_strcasecmp(const char *s1,const char *s2)
{
if (!s1) return (s1==s2)?0:1;
if (!s2) return 1;
for(; (*s1) == tolower(*s2); ++s1, ++s2)
if(*s1 == 0) return 0;
return tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s1) - tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s2);
} 除了上面两个地方,还有一个就是上图中第四个箭头所指的地方,
先来看看:
const char *cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void) {return global_ep;},/* If you supply a ptr in return_parse_end and parsing fails, then return_parse_end will contain a pointer to the error. If not, then cJSON_GetErrorPtr() does the job. */
这个函数可以看下.h文件中的英文注释,这个函数在官方的test.c中有一次调用!
if (!json) {printf("Error before: [%s]\n",cJSON_GetErrorPtr());}下面再来逐行分析下面的代码:
函数:int tolower(int c);
函数说明:若参数 c 为大写字母则将该对应的小写字母返回。
返回值:返回转换后的小写字母,若不须转换则将参数c 值返回。
函数说明
cJSON_strcasecmp()用来比较参数s1和s2字符串,比较时会自动忽略大小写的差异。static int cJSON_strcasecmp(const char *s1,const char *s2)
{
if (!s1) return (s1==s2)?0:1; //if语句里面的我习惯这样写if(s1 == NULL) 不过这里这样写感觉逼格要高一点的样子
if (!s2) return 1;
for(; (*s1) == tolower(*s2); ++s1, ++s2)
if(*s1 == 0) return 0;
return tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s1) - tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s2);
}而在ASCII码表中,NULL 就是0!
顺便查了下C库中的strcasecmp函数是这么实现的:
int strcasecmp(const char *s1, const char *s2)
{
int c1, c2;
do {
c1 = tolower(*s1++);
c2 = tolower(*s2++);
} while(c1 == c2 && c1 != 0);
return c1 - c2;
}static void *(*cJSON_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;//定义一个函数指针并初始化指向malloc函数
static void (*cJSON_free)(void *ptr) = free;//同上,这里有一个很巧妙灵活的功能,下边会提到//将传入的字符串复制一副本并返回新的字符串指针
static char* cJSON_strdup(const char* str)
{
size_t len;
char* copy;
len = strlen(str) + 1;
if (!(copy = (char*)cJSON_malloc(len))) return 0;
memcpy(copy,str,len);
return copy;
}//Hook内存管理函数,默认申请、释放内存函数malloc、free 也可以自定内存管理函数,增加灵活度,顺便这里的三目运算符还有函数指针结合用在这里简直是大写的赞!(代码的安全考虑的也比较全)
void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks)
{
if (!hooks) { /* Reset hooks */ //如果hooks为空,使用默认的内存管理
cJSON_malloc = malloc;
cJSON_free = free;
return;
}
cJSON_malloc = (hooks->malloc_fn)?hooks->malloc_fn:malloc;
cJSON_free = (hooks->free_fn)?hooks->free_fn:free;
}
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks {
void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void (*free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;//内存管理函数,new一个cJSON节点(对象)出来,并返回指向该节点的地址, 注意返回类型为(cJSON *)型
/* Internal constructor. */
static cJSON *cJSON_New_Item(void)
{
cJSON* node = (cJSON*)cJSON_malloc(sizeof(cJSON));//malloc出一个节点
if (node) memset(node,0,sizeof(cJSON));//将内存初始化为0
return node;
}
/* The cJSON structure: */
typedef struct cJSON {
struct cJSON *next,*prev; //双向链表指针
struct cJSON *child; //第一个儿子的指针 这个后边用到会具体说道
int type; /* The type of the item, as above. */
char *valuestring; /* The item's string, if type==cJSON_String */
int valueint; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
double valuedouble; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
char *string; //如果是对象的key_value元素的话, key值
} cJSON;type:
/* cJSON Types: */
#define cJSON_False (1 << 0)
#define cJSON_True (1 << 1)
#define cJSON_NULL (1 << 2)
#define cJSON_Number (1 << 3)
#define cJSON_String (1 << 4)
#define cJSON_Array (1 << 5)
#define cJSON_Object (1 << 6)//删除一个cJSON节点, 先删除儿子节点,然后删除自己。对于字符串,需要先释放字符串的内存然后再释放自己的这块内存,对于其他节点,直接释放自己这块内存(目前对这里的儿子节点还是有点不理解,儿子节点(struct cJSON类型)到底是什么?干嘛用的?删除的时候为啥要这样做?后边继续分析)
#define cJSON_IsReference 256
#define cJSON_StringIsConst 512
/* Delete a cJSON structure. */
void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c)
{
cJSON *next;
while (c)
{
next=c->next;
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->child)
cJSON_Delete(c->child); //先递归删除自己的儿子节点
if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->valuestring)
cJSON_free(c->valuestring);
if (!(c->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && c->string)
cJSON_free(c->string);
cJSON_free(c);
c=next;
}
}//解析数字,源码风格就是这样的,反正我阅读起来相当不方便!建议阅读之前格式还是自己先调整一下!
//解析输入文本生成一个数字,并填充结果项
//传入的参数有两个,这里先只关注num, 返回值是一个字符串
/* Parse the input text to generate a number, and populate the result into item. */
static const char *parse_number(cJSON *item,const char *num)
{
double n=0,sign=1,scale=0;int subscale=0,signsubscale=1;
if (*num=='-') sign=-1,num++; /* 判断是否为正负数 */
if (*num=='0') num++; /* is zero */
if (*num>='1' && *num<='9')
do n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'); while (*num>='0' && *num<='9'); //注意一下这里的语法,两个分号
if (*num=='.' && num[1]>='0' && num[1]<='9') //对小数点后边的部分进行处理 scale记录小数点后边的位数
{num++; do n=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'),scale--; while (*num>='0' && *num<='9');}
if (*num=='e' || *num=='E') /* 是否为指数,科学计数法 */
{ num++;if (*num=='+') num++; else if (*num=='-') signsubscale=-1,num++;//判断指数后边幂的正负号
while (*num>='0' && *num<='9') subscale=(subscale*10)+(*num++ - '0');//指数后边10的幂
}
//将字符串转换为相应的数值
n=sign*n*pow(10.0,(scale+subscale*signsubscale));/* number = +/- number.fraction * 10^+/- exponent */
item->valuedouble=n;//将算出来的值存入缓存
item->valueint=(int)n;//同上
item->type=cJSON_Number; //目标类型为数字
return num;
}其实上面的看着稍微有点复杂,但是仔细分析其实还是很简单的!最简单的就是随便写个数然后把自己当计算机一步一步执行上面的代码然后看结果!这里主要是字符串的科学计数法转变为数学上的科学计数法!
继续next one!
static int pow2gt (int x)
{ --x; x|=x>>1; x|=x>>2; x|=x>>4; x|=x>>8; x|=x>>16; return x+1; }
typedef struct {char *buffer; int length; int offset; } printbuffer;
/* ensure 函数 是一个 协助 printbuffer 分配内存的一个函数
* len 表示当前字符串的字符串起始偏移量 即 newbuffer+p->offset 起始的
*/
static char* ensure(printbuffer *p,int needed)
{
char *newbuffer;int newsize;
if (!p || !p->buffer) return 0;//传入参数合法性检测
needed+=p->offset;//需要额外分配的内存 也就是偏移量
if (needed<=p->length) return p->buffer+p->offset;//内存够用直接返回
newsize=pow2gt(needed);//不得不说这个用的很巧妙
newbuffer=(char*)cJSON_malloc(newsize);//malloc出新内存 用来放什么?后边来看是放buffer里面的内容
if (!newbuffer) {cJSON_free(p->buffer);p->length=0,p->buffer=0;return 0;}
if (newbuffer) memcpy(newbuffer,p->buffer,p->length);//复制内容 这一行有点不明白意图?为啥要这样做?
cJSON_free(p->buffer);//释放掉之前的buffer
p->length=newsize;
p->buffer=newbuffer;
return newbuffer+p->offset;//为什么要返回这个?这个函数到底要干吗?
}static int update(printbuffer *p)
{
char *str;
if (!p || !p->buffer) return 0;
str=p->buffer+p->offset;
return p->offset+strlen(str);
}//先看函数参数、返回值!返回值为一个字符串地址,这里看到sprintf的这种用法就知道是讲数字转换为字符串数组!
//也就是 300转换为“300”
static char *print_number(cJSON *item,printbuffer *p)
{
char *str=0;
double d=item->valuedouble;//取出item里面的valuedouble
if (d==0)
{
if (p) str=ensure(p,2);//申请两个字节内存 这个结合pow2gt函数
else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(2); /* special case for 0. */
if (str) strcpy(str,"0");//加一个字符0 ???
}
else if (fabs(((double)item->valueint)-d)<=DBL_EPSILON && d<=INT_MAX && d>=INT_MIN)
{
if (p) str=ensure(p,21);
else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(21); /* 2^64+1 can be represented in 21 chars. */
if (str) sprintf(str,"%d",item->valueint);
}
else
{
if (p) str=ensure(p,64);
else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(64); /* This is a nice tradeoff. */
if (str)
{
if (fpclassify(d) != FP_ZERO && !isnormal(d))
sprintf(str,"null");
else if (fabs(floor(d)-d)<=DBL_EPSILON && fabs(d)<1.0e60)
sprintf(str,"%.0f",d);
else if (fabs(d)<1.0e-6 || fabs(d)>1.0e9)
sprintf(str,"%e",d);
else sprintf(str,"%f",d);
}
}
return str;
}继续next one!
//将十六进制的字符串转换为数字表示!这个函数自己也可以单独写个小程序测试一下,比较简单明了!
static unsigned parse_hex4(const char *str)
{
unsigned h=0;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else return 0;
h=h<<4;str++;
if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0';
else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A';
else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a';
else return 0;
return h;
}//输入文本解析成一个因为保有的字符串,并填充项
static const unsigned char firstByteMark[7] = { 0x00, 0x00, 0xC0, 0xE0, 0xF0, 0xF8, 0xFC };
static const char *parse_string(cJSON *item,const char *str,const char **ep)
{
const char *ptr=str+1,*end_ptr=str+1;char *ptr2;char *out;int len=0;unsigned uc,uc2;
if (*str!='\"') {*ep=str;return 0;} /* not a string! */
while (*end_ptr!='\"' && *end_ptr && ++len) if (*end_ptr++ == '\\') end_ptr++; /* Skip escaped quotes. */
out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+1); /* This is how long we need for the string, roughly. */
if (!out) return 0;
item->valuestring=out; /* assign here so out will be deleted during cJSON_Delete() later */
item->type=cJSON_String;
ptr=str+1;ptr2=out;
while (ptr < end_ptr)
{
if (*ptr!='\\') *ptr2++=*ptr++;
else
{
ptr++;
switch (*ptr)
{
case 'b': *ptr2++='\b'; break;
case 'f': *ptr2++='\f'; break;
case 'n': *ptr2++='\n'; break;
case 'r': *ptr2++='\r'; break;
case 't': *ptr2++='\t'; break;
case 'u': /* transcode utf16 to utf8. */
uc=parse_hex4(ptr+1);ptr+=4; /* get the unicode char. */
if (ptr >= end_ptr) {*ep=str;return 0;} /* invalid */
if ((uc>=0xDC00 && uc<=0xDFFF) || uc==0) {*ep=str;return 0;}
if (uc>=0xD800 && uc<=0xDBFF) /* UTF16 surrogate pairs. */
{
if (ptr+6 > end_ptr) {*ep=str;return 0;} /* invalid */
if (ptr[1]!='\\' || ptr[2]!='u') {*ep=str;return 0;}
uc2=parse_hex4(ptr+3);ptr+=6;
if (uc2<0xDC00 || uc2>0xDFFF) {*ep=str;return 0;}
uc=0x10000 + (((uc&0x3FF)<<10) | (uc2&0x3FF));
}
len=4;
if (uc<0x80) len=1;
else if (uc<0x800) len=2;
else if (uc<0x10000) len=3;
ptr2+=len;
switch (len) {
case 4: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 3: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 2: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;
case 1: *--ptr2 =(uc | firstByteMark[len]);
}
ptr2+=len;
break;
default: *ptr2++=*ptr; break;
}
ptr++;
}
}
*ptr2=0;
if (*ptr=='\"') ptr++;
return ptr;
}//下面的一个函数功能和上面差不多,就是将数据填充成可以打印出来的字符串
static char *print_string_ptr(const char *str,printbuffer *p)
{
const char *ptr;char *ptr2,*out;int len=0,flag=0;unsigned char token;
if (!str)
{
if (p) out=ensure(p,3);
else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(3);
if (!out) return 0;
strcpy(out,"\"\"");
return out;
}
for (ptr=str;*ptr;ptr++) flag|=((*ptr>0 && *ptr<32)||(*ptr=='\"')||(*ptr=='\\'))?1:0;
if (!flag)
{
len=ptr-str;
if (p) out=ensure(p,len+3);
else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+3);
if (!out) return 0;
ptr2=out;*ptr2++='\"';
strcpy(ptr2,str);
ptr2[len]='\"';
ptr2[len+1]=0;
return out;
}
ptr=str;
while ((token=*ptr) && ++len)
{if (strchr("\"\\\b\f\n\r\t",token)) len++; else if (token<32) len+=5;ptr++;}
if (p) out=ensure(p,len+3);
else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+3);
if (!out) return 0;
ptr2=out;ptr=str;
*ptr2++='\"';
while (*ptr)
{
if ((unsigned char)*ptr>31 && *ptr!='\"' && *ptr!='\\') *ptr2++=*ptr++;
else
{
*ptr2++='\\';
switch (token=*ptr++)
{
case '\\': *ptr2++='\\'; break;
case '\"': *ptr2++='\"'; break;
case '\b': *ptr2++='b'; break;
case '\f': *ptr2++='f'; break;
case '\n': *ptr2++='n'; break;
case '\r': *ptr2++='r'; break;
case '\t': *ptr2++='t'; break;
default: sprintf(ptr2,"u%04x",token);ptr2+=5; break; /* escape and print */
}
}
}
*ptr2++='\"';*ptr2++=0;
return out;
}//做了一层封装 以字符的形式填充
static char *print_string(cJSON *item,printbuffer *p) {return print_string_ptr(item->valuestring,p);}//跳过空格
static const char *skip(const char *in) {while (in && *in && (unsigned char)*in<=32) in++; return in;}//解析对象,创建一个新的根并初始化,返回一个cJSON类型
cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated)
{
const char *end=0,**ep=return_parse_end?return_parse_end:&global_ep;
cJSON *c=cJSON_New_Item();
*ep=0;
if (!c) return 0; /* memory fail */
end=parse_value(c,skip(value),ep);
if (!end) {cJSON_Delete(c);return 0;} /* parse failure. ep is set. */
/* if we require null-terminated JSON without appended garbage, skip and then check for a null terminator */
if (require_null_terminated) {end=skip(end);if (*end) {cJSON_Delete(c);*ep=end;return 0;}}
if (return_parse_end) *return_parse_end=end;
return c;
}
/* Default options for cJSON_Parse */
cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value) {return cJSON_ParseWithOpts(value,0,0);}
/* Render a cJSON item/entity/structure to text. */
char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item) {return print_value(item,0,1,0);}
char *cJSON_PrintUnformatted(cJSON *item) {return print_value(item,0,0,0);}//先继续向下看
char *cJSON_PrintBuffered(cJSON *item,int prebuffer,int fmt)
{
printbuffer p;
p.buffer=(char*)cJSON_malloc(prebuffer);
p.length=prebuffer;
p.offset=0;
return print_value(item,0,fmt,&p);
}
static const char *parse_value(cJSON *item,const char *value,const char **ep)
{
if (!value) return 0; /* Fail on null. */
if (!strncmp(value,"null",4)) { item->type=cJSON_NULL; return value+4; }
if (!strncmp(value,"false",5)) { item->type=cJSON_False; return value+5; }
if (!strncmp(value,"true",4)) { item->type=cJSON_True; item->valueint=1;return value+4; }
if (*value=='\"') { return parse_string(item,value,ep); }
if (*value=='-' || (*value>='0' && *value<='9')) { return parse_number(item,value); }
if (*value=='[') { return parse_array(item,value,ep); }
if (*value=='{') { return parse_object(item,value,ep); }
*ep=value;return 0; /* failure. */
}//解析数组 终于看到了最核心的代码了 下面的代码大多是合法性检测,实际上代码没两行
static const char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value,const char **ep)
{
cJSON *child;
if (*value!='[') {*ep=value;return 0;} /* not an array! */
item->type=cJSON_Array;
value=skip(value+1);
if (*value==']') return value+1; /* empty array. */
item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!item->child) return 0; /* memory fail */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value),ep)); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
while (*value==',')
{
cJSON *new_item;
if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */
child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;//原来child指针是指向cJson节点的,还有两个指针作为双向链表指针
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1),ep));
if (!value) return 0; /* memory fail */
}
if (*value==']') return value+1; /* end of array */
*ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */
}//下面这个函数就比较长了,返回值为一个要out的字符串!关于下面的解析,代码稍微比较长一点,可以对照着后边的测试程序看,然后可以将测试例程塞进这个函数,看看out出的结果,然后还是把自己当计算机,照着代码一步一步执行!等大体吸收了下面编程的精华,然后就可以回过头来反观大局了!
static char *print_array(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p)
{
char **entries;
char *out=0,*ptr,*ret;int len=5;
cJSON *child=item->child;
int numentries=0,i=0,fail=0;
size_t tmplen=0;
/* How many entries in the array? */
while (child) numentries++,child=child->next;
/* Explicitly handle numentries==0 */
if (!numentries)
{
if (p) out=ensure(p,3);
else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(3);
if (out) strcpy(out,"[]");
return out;
}
if (p)
{
/* Compose the output array. */
i=p->offset;
ptr=ensure(p,1);if (!ptr) return 0; *ptr='['; p->offset++;
child=item->child;
while (child && !fail)
{
print_value(child,depth+1,fmt,p);
p->offset=update(p);
if (child->next)
{
len=fmt?2:1;ptr=ensure(p,len+1);
if (!ptr) return 0;*ptr++=',';
if(fmt)*ptr++=' ';*ptr=0;p->offset+=len;
}
child=child->next;
}
ptr=ensure(p,2);if (!ptr) return 0; *ptr++=']';*ptr=0;
out=(p->buffer)+i;
}
else
{
/* Allocate an array to hold the values for each */
entries=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));
if (!entries) return 0;
memset(entries,0,numentries*sizeof(char*));
/* Retrieve all the results: */
child=item->child;
while (child && !fail)
{
ret=print_value(child,depth+1,fmt,0);
entries[i++]=ret;
if (ret) len+=strlen(ret)+2+(fmt?1:0); else fail=1;
child=child->next;
}
/* If we didn't fail, try to malloc the output string */
if (!fail) out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len);
/* If that fails, we fail. */
if (!out) fail=1;
/* Handle failure. */
if (fail)
{
for (i=0;i下面两个函数是解析对象和out一个字符串形式的对象!和上面两个API一样
/* Build an object from the text. */
static const char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value,const char **ep)
{
cJSON *child;
if (*value!='{') {*ep=value;return 0;} /* not an object! */
item->type=cJSON_Object;
value=skip(value+1);
if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* empty array. */
item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!item->child) return 0;
value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value),ep));
if (!value) return 0;
child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;
if (*value!=':') {*ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1),ep)); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
while (*value==',')
{
cJSON *new_item;
if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */
child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;
value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value+1),ep));
if (!value) return 0;
child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;
if (*value!=':') {*ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! */
value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1),ep)); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */
if (!value) return 0;
}
if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* end of array */
*ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */
}
/* Render an object to text. */
static char *print_object(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p)
{
char **entries=0,**names=0;
char *out=0,*ptr,*ret,*str;int len=7,i=0,j;
cJSON *child=item->child;
int numentries=0,fail=0;
size_t tmplen=0;
/* Count the number of entries. */
while (child) numentries++,child=child->next;
/* Explicitly handle empty object case */
if (!numentries)
{
if (p) out=ensure(p,fmt?depth+4:3);
else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(fmt?depth+4:3);
if (!out) return 0;
ptr=out;*ptr++='{';
if (fmt) {*ptr++='\n';for (i=0;ioffset;
len=fmt?2:1; ptr=ensure(p,len+1); if (!ptr) return 0;
*ptr++='{'; if (fmt) *ptr++='\n'; *ptr=0; p->offset+=len;
child=item->child;depth++;
while (child)
{
if (fmt)
{
ptr=ensure(p,depth); if (!ptr) return 0;
for (j=0;joffset+=depth;
}
print_string_ptr(child->string,p);
p->offset=update(p);
len=fmt?2:1;
ptr=ensure(p,len); if (!ptr) return 0;
*ptr++=':';if (fmt) *ptr++='\t';
p->offset+=len;
print_value(child,depth,fmt,p);
p->offset=update(p);
len=(fmt?1:0)+(child->next?1:0);
ptr=ensure(p,len+1); if (!ptr) return 0;
if (child->next) *ptr++=',';
if (fmt) *ptr++='\n';*ptr=0;
p->offset+=len;
child=child->next;
}
ptr=ensure(p,fmt?(depth+1):2); if (!ptr) return 0;
if (fmt) for (i=0;ibuffer)+i;
}
else
{
/* Allocate space for the names and the objects */
entries=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));
if (!entries) return 0;
names=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));
if (!names) {cJSON_free(entries);return 0;}
memset(entries,0,sizeof(char*)*numentries);
memset(names,0,sizeof(char*)*numentries);
/* Collect all the results into our arrays: */
child=item->child;depth++;if (fmt) len+=depth;
while (child && !fail)
{
names[i]=str=print_string_ptr(child->string,0);
entries[i++]=ret=print_value(child,depth,fmt,0);
if (str && ret) len+=strlen(ret)+strlen(str)+2+(fmt?2+depth:0); else fail=1;
child=child->next;
}
/* Try to allocate the output string */
if (!fail) out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len);
if (!out) fail=1;
/* Handle failure */
if (fail)
{
for (i=0;i /* Get Array size/item / object item. */
int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array)
{cJSON *c=array->child;int i=0;while(c)i++,c=c->next;return i;}//返回节点的个数
cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array,int item)
{cJSON *c=array?array->child:0;while (c && item>0) item--,c=c->next; return c;}//返回第item个节点地址
cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string)//同上,只是类型不一样
{cJSON *c=object?object->child:0;while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string)) c=c->next; return c;}
int cJSON_HasObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string)//二次封装,暂时还没明白这样做的优势
{return cJSON_GetObjectItem(object,string)?1:0;}
/* Utility for array list handling. */
static void suffix_object(cJSON *prev,cJSON *item)
{prev->next=item;item->prev=prev;}//个人理解在链表尾插入一个节点
/* Utility for handling references. */
static cJSON *create_reference(cJSON *item)
{
cJSON *ref=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!ref) return 0;
memcpy(ref,item,sizeof(cJSON));
ref->string=0;
ref->type|=cJSON_IsReference;// 与256相与 1 0000 0000(256的二进制表示)这里暂时有点不明白
ref->next=ref->prev=0;//都置空
return ref;
}
/* Add item to array/object. */
void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item)//将item节点插入array链表
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
if (!item) return;
if (!c) {array->child=item;} //如果为空链表 直接插入
else
{while (c && c->next) c=c->next; suffix_object(c,item);}
}
//将字符串添加进对象
void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item)
{
if (!item) return;
if (item->string) cJSON_free(item->string);
item->string=cJSON_strdup(string);
cJSON_AddItemToArray(object,item);
}
void cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item)
{
if (!item) return;
if (!(item->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && item->string)
cJSON_free(item->string);
item->string=(char*)string;
item->type|=cJSON_StringIsConst;//512 (10 0000 0000b)
cJSON_AddItemToArray(object,item);
}void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(array,create_reference(item));
}
void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item)
{
cJSON_AddItemToObject(object,string,create_reference(item));
}
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which)//分离链表中第which位置的节点并返回
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
while (c && which>0) c=c->next,which--;//c指向第which个节点
if (!c) return 0;
if (c->prev)
c->prev->next=c->next;
if (c->next)
c->next->prev=c->prev;
if (c==array->child)
array->child=c->next;
c->prev=c->next=0;
return c;
}
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which)
{
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(array,which));
}
//功能同上差不多 只是类型不同
cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string)
{
int i=0;
cJSON *c=object->child;
while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string)) i++,c=c->next;
if (c)
return cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(object,i);
return 0;
}
void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string)
{
cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(object,string));
}//下面的API也是核心部分,要好好分析吸收
/* Replace array/object items with new ones. */
void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem)//在链表中插入一个新的节点
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
while (c && which>0) c=c->next,which--;//先定位到替换的位置
if (!c) {cJSON_AddItemToArray(array,newitem);return;}
newitem->next=c;
newitem->prev=c->prev;
c->prev=newitem;
if (c==array->child)
array->child=newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next=newitem;
}
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem)//用新的节点替换原有的某一个节点
{
cJSON *c=array->child;
while (c && which>0) c=c->next,which--;
if (!c) return;
newitem->next=c->next;
newitem->prev=c->prev;
if (newitem->next)
newitem->next->prev=newitem;
if (c==array->child)
array->child=newitem;
else
newitem->prev->next=newitem;
c->next=c->prev=0;
cJSON_Delete(c);
}
void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem)//同上,只是换个类型
{
int i=0;
cJSON *c=object->child;
while(c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))
i++,c=c->next;
if(c)
{
newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(string);
cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(object,i,newitem);
}
}【1】两个创建
【创建JSON对象】cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void);
【创建JSON数组】cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void);
【2】两种添加
【向对象中添加】voidcJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);
【向数组中添加】void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
【3】常用几招
【向对象中增加数字】cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "value", cJSON_CreateNumber(value));
【向对象中增加文件】cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "string", cJSON_CreateString(string));
【4】JSON嵌套
【向对象中增加数组】cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "rows", rows = cJSON_CreateArray());
【向数组中增加对象】cJSON_AddItemToArray(rows, row = cJSON_CreateObject());
【简单说明】
【1】cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "value", cJSON_CreateNumber(value));
【2】cJSON_AddNumberToObject(root, "value", value);
【1】和【2】效果完全相同。
【简单说明】
【1】 cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString(name));
【2】 cJSON_AddStringToObject(root, "name",name);
【1】和【2】效果完全相同。
//源码的格式稍微调整了了一下
/* Create basic types: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=cJSON_NULL;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=cJSON_True;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=cJSON_False;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=b?cJSON_True:cJSON_False;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
{
item->type=cJSON_Number;
item->valuedouble=num;
item->valueint=(int)num;
}
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
{
item->type=cJSON_String;
item->valuestring=cJSON_strdup(string);
if(!item->valuestring)
{
cJSON_Delete(item);
return 0;
}
}
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=cJSON_Array;
return item;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void)
{
cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();
if(item)
item->type=cJSON_Object;
return item;
}//下面的四个API都差不多,只是创建不同类型的数组
/* Create Arrays: */
cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers,int count)
{
int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();
for(i=0;a && ichild=n;
else
suffix_object(p,n);//插入节点
p=n;
}
return a;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers,int count)
{
int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();
for(i=0;a && ichild=n;
else
suffix_object(p,n);
p=n;
}
return a;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers,int count)
{
int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();
for(i=0;a && ichild=n;
else
suffix_object(p,n);
p=n;
}
return a;
}
cJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings,int count)
{
int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();
for(i=0;a && ichild=n;
else
suffix_object(p,n);
p=n;
}
return a;
} //最后两个API
/* Duplication */
cJSON *cJSON_Duplicate(cJSON *item,int recurse)//拷贝副本 是否递归拷贝
{
cJSON *newitem,*cptr,*nptr=0,*newchild;
if (!item) return 0;
/* Create new item */
newitem=cJSON_New_Item();
if (!newitem) return 0;
/* Copy over all vars */
newitem->type=item->type&(~cJSON_IsReference),newitem->valueint=item->valueint,newitem->valuedouble=item->valuedouble;
if (item->valuestring)
{
newitem->valuestring=cJSON_strdup(item->valuestring);
if (!newitem->valuestring) {cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}
}
if (item->string)
{
newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(item->string);
if (!newitem->string) {cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}
}
/* If non-recursive, then we're done! */
if (!recurse) return newitem;
/* Walk the ->next chain for the child. */
cptr=item->child;
while (cptr)
{
newchild=cJSON_Duplicate(cptr,1);
if (!newchild) {cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}
if (nptr)
{
nptr->next=newchild,newchild->prev=nptr;
nptr=newchild;
}
else {newitem->child=newchild;nptr=newchild;}
cptr=cptr->next;
}
return newitem;
}
void cJSON_Minify(char *json)
{
char *into=json;
while (*json)
{
if (*json==' ') json++;
else if (*json=='\t') json++; /* Whitespace characters. */
else if (*json=='\r') json++;
else if (*json=='\n') json++;
else if (*json=='/' && json[1]=='/') while (*json && *json!='\n') json++;
else if (*json=='/' && json[1]=='*') {while (*json && !(*json=='*' && json[1]=='/')) json++;json+=2;} /* multiline comments. */
else if (*json=='\"'){*into++=*json++;while (*json && *json!='\"'){if (*json=='\\') *into++=*json++;*into++=*json++;}*into++=*json++;}
else *into++=*json++; /* All other characters. */
}
*into=0; /* and null-terminate. */
}cJSON.h
#ifndef cJSON__h
#define cJSON__h
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C"
{
#endif
/* cJSON Types: */
#define cJSON_False (1 << 0)
#define cJSON_True (1 << 1)
#define cJSON_NULL (1 << 2)
#define cJSON_Number (1 << 3)
#define cJSON_String (1 << 4)
#define cJSON_Array (1 << 5)
#define cJSON_Object (1 << 6)
#define cJSON_IsReference 256
#define cJSON_StringIsConst 512
/* The cJSON structure: */
typedef struct cJSON {
/* next/prev allow you to walk array/object chains. Alternatively, use GetArraySize/GetArrayItem/GetObjectItem */
struct cJSON *next,*prev;
/* An array or object item will have a child pointer pointing to a chain of the items in the array/object. */
struct cJSON *child;
int type; /* The type of the item, as above. */
char *valuestring; /* The item's string, if type==cJSON_String */
int valueint; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
double valuedouble; /* The item's number, if type==cJSON_Number */
/* The item's name string, if this item is the child of, or is in the list of subitems of an object. */
char *string;
} cJSON;
typedef struct cJSON_Hooks {
void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);
void (*free_fn)(void *ptr);
} cJSON_Hooks;
/* Supply malloc, realloc and free functions to cJSON */
extern void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks);
extern cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value);
/* Render a cJSON entity to text for transfer/storage. Free the char* when finished. */
extern char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item);
extern char *cJSON_PrintUnformatted(cJSON *item);
/* Render a cJSON entity to text using a buffered strategy. prebuffer is a guess at the final size.
*guessing well reduces reallocation. fmt=0 gives unformatted, =1 gives formatted
*/
extern char *cJSON_PrintBuffered(cJSON *item,int prebuffer,int fmt);
/* Delete a cJSON entity and all subentities. */
extern void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c);
/* Returns the number of items in an array (or object). */
extern int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array);
/* Retrieve item number "item" from array "array". Returns NULL if unsuccessful. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array,int item);
/* Get item "string" from object. Case insensitive. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string);
extern int cJSON_HasObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string);
/* For analysing failed parses. This returns a pointer to the parse error.
* You'll probably need to look a few chars back to make sense of it.
Defined when cJSON_Parse() returns 0. 0 when cJSON_Parse() succeeds.
*/
extern const char *cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void);
/* These calls create a cJSON item of the appropriate type. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void);
/* These utilities create an Array of count items. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers,int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers,int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers,int count);
extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings,int count);
/* Append item to the specified array/object. */
extern void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);
/* Append reference to item to the specified array/object. Use this when you want to
* add an existing cJSON to a new cJSON, but don't want to corrupt your existing cJSON.
*/
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);
extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);
/* Remove/Detatch items from Arrays/Objects. */
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which);
extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string);
extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string);
/* Update array items. */
extern void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem);
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem);
extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem);
/* Duplicate a cJSON item */
extern cJSON *cJSON_Duplicate(cJSON *item,int recurse);
/* Duplicate will create a new, identical cJSON item to the one you pass, in new memory that will
*need to be released. With recurse!=0, it will duplicate any children connected to the item.
*The item->next and ->prev pointers are always zero on return from Duplicate.
*/
/* ParseWithOpts allows you to require (and check) that the JSON is null terminated,
*and to retrieve the pointer to the final byte parsed.
*/
extern cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated);
extern void cJSON_Minify(char *json);
Makefile (这个Makefile 可以将目标文件编译出动态库,静态库,自带的测试程序编译成目标文件,对于我这样的小白来说还是很值得学习研究的)
OBJ = cJSON.o
LIBNAME = libcjson
TESTS = test
PREFIX ?= /usr/local
INCLUDE_PATH ?= include/cjson
LIBRARY_PATH ?= lib
INSTALL_INCLUDE_PATH = $(DESTDIR)$(PREFIX)/$(INCLUDE_PATH)
INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH = $(DESTDIR)$(PREFIX)/$(LIBRARY_PATH)
INSTALL ?= cp -a
R_CFLAGS = -fpic $(CFLAGS) -Wall -Werror -Wstrict-prototypes -Wwrite-strings -D_POSIX_C_SOURCE=200112L
uname_S := $(shell sh -c 'uname -s 2>/dev/null || echo false')
## shared lib
DYLIBNAME = $(LIBNAME).so
DYLIBCMD = $(CC) -shared -o $(DYLIBNAME)
## create dynamic (shared) library on Darwin (base OS for MacOSX and IOS)
ifeq (Darwin, $(uname_S))
DYLIBNAME = $(LIBNAME).dylib
## create dyanmic (shared) library on SunOS
else ifeq (SunOS, $(uname_S))
DYLIBCMD = $(CC) -G -o $(DYLIBNAME)
INSTALL = cp -r
endif
## static lib
STLIBNAME = $(LIBNAME).a
.PHONY: all clean install
all: $(DYLIBNAME) $(STLIBNAME) $(TESTS)
$(DYLIBNAME): $(OBJ)
$(DYLIBCMD) $< $(LDFLAGS)
$(STLIBNAME): $(OBJ)
ar rcs $@ $<
$(OBJ): cJSON.c cJSON.h
.c.o:
$(CC) -ansi -pedantic -c $(R_CFLAGS) $<
$(TESTS): cJSON.c cJSON.h test.c
$(CC) cJSON.c test.c -o test -lm -I.
install: $(DYLIBNAME) $(STLIBNAME)
mkdir -p $(INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH) $(INSTALL_INCLUDE_PATH)
$(INSTALL) cJSON.h $(INSTALL_INCLUDE_PATH)
$(INSTALL) $(DYLIBNAME) $(INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH)
$(INSTALL) $(STLIBNAME) $(INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH)
uninstall:
rm -rf $(INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH)/$(DYLIBNAME)
rm -rf $(INSTALL_LIBRARY_PATH)/$(STLIBNAME)
rm -rf $(INSTALL_INCLUDE_PATH)/cJSON.h
clean:
rm -rf $(DYLIBNAME) $(STLIBNAME) $(TESTS) *.o
test.c
#include
#include
#include "cJSON.h"
/* Parse text to JSON, then render back to text, and print! */
void doit(char *text)
{
char *out;cJSON *json;
json=cJSON_Parse(text);
if (!json) {printf("Error before: [%s]\n",cJSON_GetErrorPtr());}
else
{
out=cJSON_Print(json);
cJSON_Delete(json);
printf("%s\n",out);
free(out);
}
}
/* Read a file, parse, render back, etc. */
void dofile(char *filename)
{
FILE *f;long len;char *data;
f=fopen(filename,"rb");fseek(f,0,SEEK_END);len=ftell(f);fseek(f,0,SEEK_SET);
data=(char*)malloc(len+1);fread(data,1,len,f);data[len]='\0';fclose(f);
doit(data);
free(data);
}
/* Used by some code below as an example datatype. */
struct record {const char *precision;double lat,lon;const char *address,*city,*state,*zip,*country; };
/* Create a bunch of objects as demonstration. */
void create_objects()
{
cJSON *root,*fmt,*img,*thm,*fld;char *out;int i; /* declare a few. */
/* Our "days of the week" array: */
const char *strings[7]={"Sunday","Monday","Tuesday","Wednesday","Thursday","Friday","Saturday"};
/* Our matrix: */
int numbers[3][3]={{0,-1,0},{1,0,0},{0,0,1}};
/* Our "gallery" item: */
int ids[4]={116,943,234,38793};
/* Our array of "records": */
struct record fields[2]={
{"zip",37.7668,-1.223959e+2,"","SAN FRANCISCO","CA","94107","US"},
{"zip",37.371991,-1.22026e+2,"","SUNNYVALE","CA","94085","US"}};
/* Here we construct some JSON standards, from the JSON site. */
/* Our "Video" datatype: */
root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "name", cJSON_CreateString("Jack (\"Bee\") Nimble"));
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "format", fmt=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fmt,"type", "rect");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"width", 1920);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"height", 1080);
cJSON_AddFalseToObject (fmt,"interlace");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fmt,"frame rate", 24);
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out); /* Print to text, Delete the cJSON, print it, release the string. */
/* Our "days of the week" array: */
root=cJSON_CreateStringArray(strings,7);
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out);
/* Our matrix: */
root=cJSON_CreateArray();
for (i=0;i<3;i++) cJSON_AddItemToArray(root,cJSON_CreateIntArray(numbers[i],3));
/* cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(root,1,cJSON_CreateString("Replacement")); */
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out);
/* Our "gallery" item: */
root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddItemToObject(root, "Image", img=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(img,"Width",800);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(img,"Height",600);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(img,"Title","View from 15th Floor");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(img, "Thumbnail", thm=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(thm, "Url", "http:/*www.example.com/image/481989943");
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(thm,"Height",125);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(thm,"Width","100");
cJSON_AddItemToObject(img,"IDs", cJSON_CreateIntArray(ids,4));
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out);
/* Our array of "records": */
root=cJSON_CreateArray();
for (i=0;i<2;i++)
{
cJSON_AddItemToArray(root,fld=cJSON_CreateObject());
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "precision", fields[i].precision);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fld, "Latitude", fields[i].lat);
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(fld, "Longitude", fields[i].lon);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Address", fields[i].address);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "City", fields[i].city);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "State", fields[i].state);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Zip", fields[i].zip);
cJSON_AddStringToObject(fld, "Country", fields[i].country);
}
/* cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON_GetArrayItem(root,1),"City",cJSON_CreateIntArray(ids,4)); */
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out);
root=cJSON_CreateObject();
cJSON_AddNumberToObject(root,"number", 1.0/0.0);
out=cJSON_Print(root); cJSON_Delete(root); printf("%s\n",out); free(out);
}
int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {
/* a bunch of json: */
char text1[]="{\n\"name\": \"Jack (\\\"Bee\\\") Nimble\", \n\"format\": {\"type\": \"rect\", \n\"width\": 1920, \n\"height\": 1080, \n\"interlace\": false,\"frame rate\": 24\n}\n}";
char text2[]="[\"Sunday\", \"Monday\", \"Tuesday\", \"Wednesday\", \"Thursday\", \"Friday\", \"Saturday\"]";
char text3[]="[\n [0, -1, 0],\n [1, 0, 0],\n [0, 0, 1]\n ]\n";
char text4[]="{\n \"Image\": {\n \"Width\": 800,\n \"Height\": 600,\n \"Title\": \"View from 15th Floor\",\n \"Thumbnail\": {\n \"Url\": \"http:/*www.example.com/image/481989943\",\n \"Height\": 125,\n \"Width\": \"100\"\n },\n \"IDs\": [116, 943, 234, 38793]\n }\n }";
char text5[]="[\n {\n \"precision\": \"zip\",\n \"Latitude\": 37.7668,\n \"Longitude\": -122.3959,\n \"Address\": \"\",\n \"City\": \"SAN FRANCISCO\",\n \"State\": \"CA\",\n \"Zip\": \"94107\",\n \"Country\": \"US\"\n },\n {\n \"precision\": \"zip\",\n \"Latitude\": 37.371991,\n \"Longitude\": -122.026020,\n \"Address\": \"\",\n \"City\": \"SUNNYVALE\",\n \"State\": \"CA\",\n \"Zip\": \"94085\",\n \"Country\": \"US\"\n }\n ]";
char text6[] = ""
"\n"
"\n"
" \n"
" \n"
"Application Error \n"
"\n"
"\n"
" \n"
"\n"
"\n";
/* Process each json textblock by parsing, then rebuilding: */
doit(text1);
doit(text2);
doit(text3);
doit(text4);
doit(text5);
doit(text6);
/* Parse standard testfiles: */
/* dofile("../../tests/test1"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test2"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test3"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test4"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test5"); */
/* dofile("../../tests/test6"); */
/* Now some samplecode for building objects concisely: */
create_objects();
return 0;
}
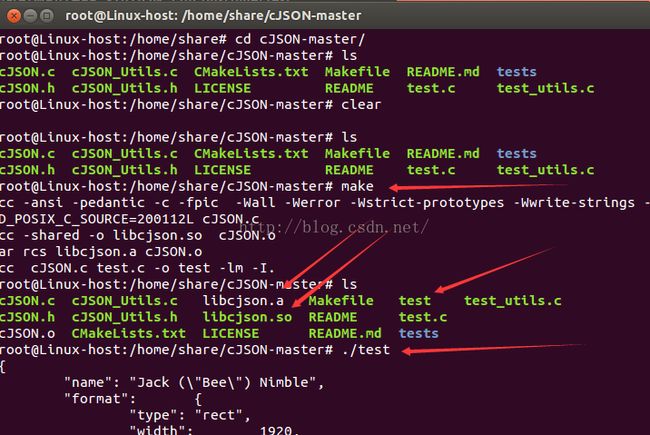
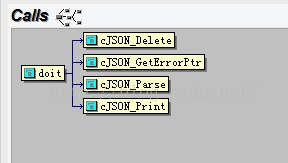
上面的test.c中也可以一个一个的测试,针对测试用例还有运行的结果再反过来分析源码!这样理解起来也会更容易一点!其中下面是doit函数调用的几个函数关系!
下面是其他网友关于cjson的博客文章,可以结合参考的来看:
http://blog.csdn.net/xukai871105/article/details/33013455
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a6fb6cc90101ffme.html
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_5f28333901017kql.html
http://www.0xffffff.org/2014/02/10/29-cjson-analyse/
源码后边接着分析!未完!