SpringBoot>08 - 配置文件、基本注解使用
简介:
SpringBoot采取的是约定优于配置的原则,旨在无需太多的配置快速启动,专注于业务代码的开发,提高开发效率,但有时个性化的配置、自定义的配置也是需要的。本章介绍 springboot1.5 版本部分自带配置属性、自定义属性以及读取方式,开发中常见注解的使用。
个人学习总结:
链接:【springboot、springcloud、docker 等,学习目录】
一、配置文件:
配置文件格式 分 application.properties 和 application.yml(官方推荐使用)。
1、常见的自带属性:
############ tomcat 相关 ############
#访问的根路径
server.context-path=/
#端口号
server.port=8080
#session失效时间 (秒)
server.session-timeout=30
#编码
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=utf-8
########### 数据库相关 #############
spring.datasource.url= #数据库地址
spring.datasource.username=
spring.datasource.password=
spring.datasource.driver-class-name= #数据库驱动
########### Mybatis 配置 ###########
mybatis.typeAliasesPackage= #别名,对应实体类包
mybatis.mapperLocations= #mybatis xml位置
########### 自带日志的配置 ##########
# 日志级别
logging.level.com.coolron.user.dao=debug
logging.file=my.log #日志名称
logging.path=./log #日志路径(默认日志名为 spring.log) 和 logging.file 只能出现一个
spring.output.ansi.enabled=DETECT # 控制台多彩输出
########### Redis 配置 ###########
## Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
## Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=191.250.49.120
## Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6333
## Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
## 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
## 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
## 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
## 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
## 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=3000
其他属性参看:http://blog.yuqiyu.com/spring-boot-chapter31.html
2、自定义属性:
application.properties文件中:
############## 自定义属性 #################
custom.properties.social.weixin.app-id = wxfd65ab1fadb2
custom.properties.social.weixin.app-secret = 66bb4566de776ac6ds1dbejhhcc3dd1
custom.properties.social.clients[0] = coolron
custom.properties.social.clients[1] = test
自定义属性的读取:
提供两种方式:使用@Value 读取,将配置文件的属性赋给实体类读取。
方式一、利用@Value 读取
1、测试controller:
/**
* @Auther: xf
* @Date: 2018/10/31 15:06
* @Description: 测试自定义属性
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class PropertiesController {
@Value("${custom.properties.social.weixin.app-id}")
private String appId;
@Value("${custom.properties.social.clients[0].clientId}")
private String clientId;
@GetMapping(value = "getProperties")
public ApiResult test(){
log.info("custom.properties.social.weixin.app-id,{}", appId);
log.info("custom.properties.social.clients[0].clientId,{}", clientId);
return ApiResult.ok(appId + ">>>>>>>>>>" + clientId);
}
}
方式二、利用实体类读取配置文件自定义属性:
注意: 以下各类中属性的命名一定要跟配置文件中自定义的属性名称相对应
1、配置文件读取器:对应配置文件中 custom.properties
/**
* 配置文件读取器 读取整个系统配置
*/
// 会读取 custom.properties 开头的配置项
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "custom.properties")
public class CustomProperties {
// social 会读取到 此类中去
private SocialProperties social = new SocialProperties();
}
2、social 实体类:对应配置文件中 social
@Data
public class SocialProperties {
private WeixinProperties weixin = new WeixinProperties();
private String[] clients = {}; // 默认空数组
}
3、weixin 实体类:对应配置文件中 weixin
@Data
public class WeixinProperties{
private String appId;
private String appSecret;
}
4、读取器配置类:
@Configuration
// 作用 : 使 CustomProperties 配置文件读取器生效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CustomProperties.class)
public class PropertiesCoreConfig {
}
5、在 Propertiescontroller 中新增代码:
// 注入配置文件读取器
@Autowired
private CustomProperties customProperties;
@GetMapping(value = "getBeanPro")
public ApiResult beanPro(){
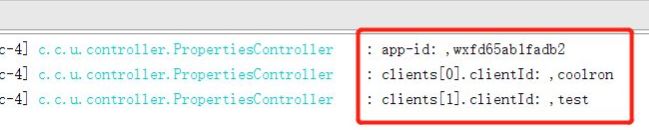
log.info("app-id: ,{}", customProperties.getSocial().getWeixin().getAppId());
log.info("clients[0].clientId: ,{}", customProperties.getSocial().getClients()[0]);
log.info("clients[1].clientId: ,{}", customProperties.getSocial().getClients()[1]);
return ApiResult.ok(appId + ">>>>>>>>>>" + clientId);
}
6、测试:请求接口:localhost:8080/getBeanPro 控制台如下:
二、多环境配置:
在开发、测试、生成不同的环境使用不同的配置文件,以swagger 为例,生产和测试环境不需要。Spring Boot中多环境配置文件名需要满足 application-{profile}.properties 的格式,其中{profile}对应你的环境标识。
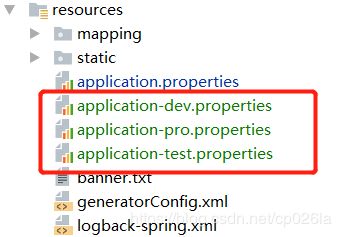
1、在src/main/resources 下新建:
2、选择配置文件
方式一、 在application.properties中指定使用dev/pro/test哪种环境:
# 指定配置文件
spring.profiles.active=dev
#spring.profiles.active=pro
#spring.profiles.active=test
效果:开发环境配置文件application-dev.properties 生效。
方式二: 运行 jar 包(后续章节涉及打包)的时候指定配置文件:
指定配置文件
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=test
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=pro
附加:自定义配置文件
若配置较多,不想都写到application.properties中,可以自定义配置文件,例如:custome.properties, 只需使用@PropertySource 注解映入即可。
// 建议写到启动类、自定义属性配置类(CustomProperties )上或者根据自身环境决定。
@PropertySource(value = “classpath:custom.properties”)
三、springboot 基本注解的使用
此处总结几个常用注解,其他注解遇到了再补充:
@Configuration:类上,表明这是一个IOC容器,相当于springMVC中的配置文件,springboot使用该注解用作java配置。
@Bean: 方法上,常结合@Configuration使用,往spring容器中添加一个组件。
@Component: 类上,将备被注解的类交给spring容器管理,例如本章的 CustomProperties类
@ComponentScan:类上,相当于 xml配置文件中的context:component-scan标签,对标注了@Controller、@Service、@Respoitory、@Component等的类扫描,注册为bean
@SpringBootConfiguration:启动类上,包含@SpringBootConfiguration(继承@Configuration)、 @EnableAutoConfiguration和 @ComponentScan注解
@RestController:包含@ResponseBody 和 @Controller 的注解
@PathVariable、@RequestParam、@RequestMapping、@Controller、@Service、@RequestBody、@ResponseBody:跟SpringMVC相同。
# 请求路径 PUT、DELETE、PATCH 同下
@GetMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@PostMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@EnableScheduling:建议加到启动类上,开启springboot定时支持,结合@Scheduled做定时任务。
@PropertySource:加载指定的配置文件,例如本章中附加:自定义配置文件
至此,springboot配置中常见的自带属性、按需自定义属性,以及它们的两种读取方式:@Value 和 实体类映射,自定义配置文件的引入,常用的几种注解,重点为利用实体类读取配置文件自定义属性。
