Weblogic-学习笔记(1-2课)
Overview
该系列文章为播布客(www.boobooke.com)黑弓老师的Weblogic视频教程学习笔记。
1:Setting up a Weblogic Server Environment(安装)
2 : Configure a Weblogic Server Environment(配置)
3 : Managing and Monitoring a Weblogic Server Environment(监视&管理)
4 : Basic Deployment(基础部署)
5 : Understanding JNDI
6 : Setting up JDBC
7 : Setting up JMS Applications
8 : Setting up JMS Applications(Contd)
9 : Managing Transactions()(分布式事务管理)
10 : Securing Weblogic Server Resources and Applications
11 : Advanced Deployment
12 : Introduction to Clustering
13 : Configuring a Cluster
14 : Managing Clusters
15 : Clustering EJB Objects
16 : Clustering Services
17 : Virtualization
Distributed systems
- Distributed systems divide the work amongst several indpendent modules
- Failure of a single module has less impact on the overall system,which makes them more:
- Available(可用性)
- Scalable(灵活性)
- Maintainable(可管理性)
How Standards Help
- Many of the advantages of distributed systems come from standards.
- Standards:
- Provide separation of difficult problems to separate platforms
- Allow modularization of complex hardware and software
- Allow a larger portion of project costes to go toward solving business software needs
The J2EE Standard
Java Platform 2 Enterprise Edition(J2EE) helps to overcome distribution liabilities.
- Stardardized(标准的)
- Adherent to specification guidelines
- Written in Java
- Deployable in any compliant application server
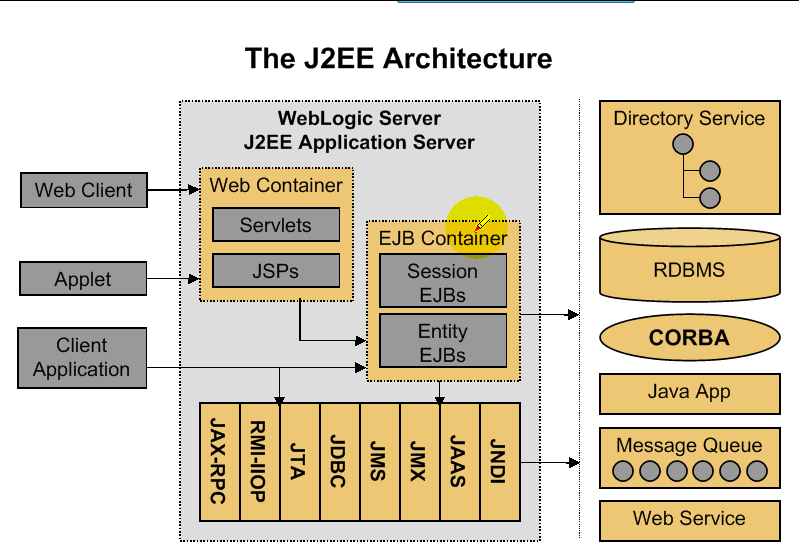
The J2EE Architecture
- JNDI : java目录服务
- JAAS : 安全访问控制
- JMX : 管理扩展
- JMS : 消息管理
- JDBC : 数据库访问
- JTA : 分布式事务处理
- RMI-IIOP : 远程对象访问
- JAX-RPC :
Java Servlets
A servlet is a java “program” that executes on the server,acepting client rquests and generating dynamic responses.
The most prevalent type of servlet is an HttpServlet that acceptes HTTP requests and generates HTTP responses.
Servlets:
- Do not just generate HTML
- Can also be used to generate other MIME types,such as images
JavaServer Pages(JSPs)
- Are HTML documents interweaved with java
- Provide a dynamic response that is based on the client’s request
- Provide for the separation of responsibilities between Web presentation and dynamic content
- Are protable(write once,run anywhere)
- Compile and run as servlets
Enterprise JavaBeans(EJBs)
Enterprise JavaBean(EJBs) are software components written in java that encapsulate a system’s business logic and data access and make it available to Java clients running anywhere on the network.
The J2EE specification mandates that EJBs run within an EJB container that not only provides a runtime environment for them,but also provides the enterprise-class services that I mentioned before : high availability,transactions,session management,persistence,and security.
The container must also provide support for declarative services,.which allow the users of EJBs(referred to in J2EE parlance as application assemblers)to configure many aspects of EJB runtime behavior through the use of XML deployment descriptors.
Weblogic Server’s EJB container provides all these services and more,as you will see in the rest of this chapter.
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)
- Is a standard Java interface for accessing heterogeneous databases
- Is a specification that defines four different driver types for connection to databases
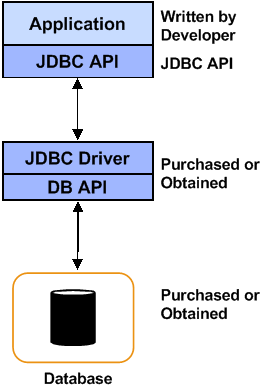
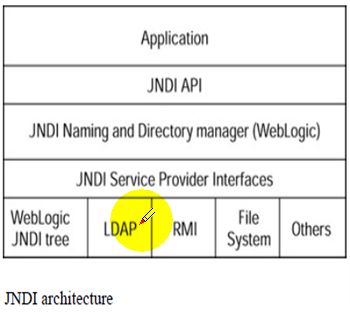
Java Naming and Directory Interface(JNDI)
At the top is Java application code,implemented as a servlet,EJB,or other component,which makes calls to the JNDI API.
These calls are routed by the naming and directory manager(in your case,Weblogic Server)to the appropriate JNDI server provider interface(SPI),which translates the JNDI calls into native commands for the naming or directory resource being accessed.
This resource can be the JNDI tree built into Weblogic,an external LDAP directory,an RMI registry,a file system,or virtually any other resource for which an appropriate JNDI SPI can be written.
Java Transaction API(JTA)
- JTA is a standard java API for demarcating transactions within a program.
- Weblogic Server supports local and distributed transactions.
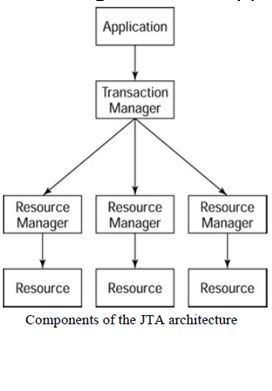
The top layer of the architecture is the application,which can be implemented as a servlet,JSP,RMI application,EJB,or stand-alone java application.
The application makes calls to the transaction manager,which manages communications between the application and the transaction’s resource managers.
Weblogic Server has embedded within it a transaction manager that is fully J2EE compliant.
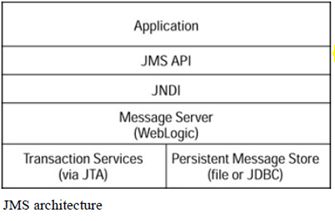
Java Message Service(JMS)
A Java application(or application component)accesses a IMS-enabled message server through the JMS API.
References to the message server are obtained via JNDI lookups.
Weblogic Server contains a complete,feature-rich message server of its own;third-party message servers that run outside of Weblogic Server(such as IBM MQSeries)can also be used if their vendors provide JMS API implementations for them
Java Authentication and Authorization
Java Authentication and Authorization Service(JAAS) is a java-based security management framework.
- Single sign-on
- A Pluggable Authentication Module(PAM)
JAAS enables flexible control over authorization whether it is based on:
- Users
- Groups
- Roles
JMX
The Java Management Extensions(JMX):
- Defines a standard infrastructure to manage a device from java programs.
- Decouples the managed device from the management tools
The specification describes MBeans,which are the building blocks of JMX