行人属性“Attributed Grammars for Joint Estimation of Human Attributes, Part and Pose”
相关工作
1.属性模型:
人脸:性别,发型,是否戴眼镜
Poselet:检测身体parts
Panda: HOG based Poselet 检测parts,CNN分类。重在数据和微调。本文重在建模和表示。
2.Part定位模型:
pictorial structural model,geometry based tree model,DPM,POselet,CNN。
3.Grammar模型:
phrase structural grammars(PG)
dependancy grammars(DG)
And-or Grammar
Attributed Grammar Model
part用状态变量表示位置及属性,part状态(x,y,s),属性状态:属性。parse tree的概率模型使用Gibbs能量模型表示:
p(pt|I)=1Zexp{−EPA(I|pt)−EAA(I|pt)−EPR(I|pt)−EAR(I|pt)}
似然项用于appearance响应,先验项描述语法的关系。 EPA(I|pt) 是appearance想, EPR(I|pt) 是relation项。能量可以描述为得分函数。
Part 模型
1.定义
part定义的三种方法:one part(whole body)
three parts(head, upper body, lower body)
find-grained parts(eyes, writs, hands, and etc.)
首先寻找合适的Part数目,下图使用keypoint定义part,目的是找到P个窗口覆盖所有的特征点,步骤是:
(1) Randomly select the example which has all visible keypoints.
(2) Draw P bounding boxes by avoiding overlap with other bounding boxes until each part region includes N/P keypoints approximately.
(3) Visit training examples one by one and check whether it can be described with current part design.
2.Part 关系模型
共享最多的part作为根节点,然后加入最近的part扩展树结构,树结构如下:
Part关系使用And-rule定义,通过part之间的几何约束,part与其type的articulation约束计算,part使用Or-rule定义。

3.Part Appearance模型
考虑到各种变化,对剪切的part聚类,对每种part训练逻辑回归检测器,每个part定义了10种类型,下图显示了两个part的其中五种类型,

appearance 特征使用4种:CNN,梯度HOG,颜色直方图,RGB。appearance得分是part及type特征与权值的内积。
SPA(I|P)=<λPap,ϕPa(I,p)>
SPA(I|w)=<λPap,ϕPa(I,w)>
属性模型
属性与part的关系比较密切,对于part定义属性A(p),(1)假设part与每个属性都有联系,(2)对每个part类型使用逻辑回归训练二类属性分类器,(3)忽略平均预测率<0.5的part与属性关系,下表显示了预测准确率。

A(p)可认为是两层树,根节点And-rule定义,包含对应的属性,每个属性遵循OR-rule,示例如下:

1.属性关系模型
下图中,每个属性节点A(P)用蓝边与part相连,关系反映了给定part类型属性的出现频率。

属性关系得分是:
SAR(pt)=∑pi∈ptSAR(wi,A(pi))
其中,
SAR(w,A(p))=<λattw,ϕatt(A(p))>
2.属性外观模型
下图显示了5种类型的p1,对应4种属性。属性外观得分是:
SAA(I|a)=<λAaa,ϕAa(I,a)>
a是属性的类型, ϕAa(I,a) 是模板响应向量, λAaa 是类型a外形特征权值,对于pt的总得分是:
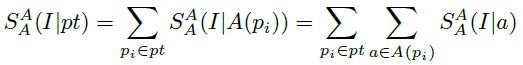
Parsing and Inference
对给定图像寻找parse tree,最大化之前的得分函数:

parsing定义为最大化得分函数 S(p0,I) , p0 是根节点,对每个part,part type及属性计算外形图及关系图。对外形得分图,每个part,part type及属性计算外形响应。对关系图,最大化父节点组合。子节点条件独立,可以独立最大化。
给定节点 pi ,得分函数是:

Learning
parse tree得分是模型参数 λ 与特征响应 ϕ(pt,I) 的内积,学习任务可认为是寻找最小化风险的参数 λ 。定义了两个损失函数,part loc损失和part 选择损失,
![]()
实验结果




