Yen 的k_shortest paths 算法的C++实现
具体介绍见:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yen%27s_algorithm
还有具体步骤见:https://blog.csdn.net/sharpdew/article/details/446510?tdsourcetag=s_pctim_aiomsg
我也不知道我对这个算法理解是否完全正确,但是大体的数据结构和逻辑是正确的,希望大家指点,后期我更理解了,会做相应修改。
在这个算法里需要改进的地方是:我没有用堆去插入,这个等有时间再做
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
static const unsigned int INF(std::numeric_limits::max());
static const unsigned undefined = INF;
class K_Shortest_Path {
public:
vector> run(
const unsigned int kPath, // K Path
const vector>& NW, // network
const unsigned int src, // source node
const unsigned int dst); // destination node
};
//
//结构体用于保存两点之间的最短路径和长度
//
class DijPath
{
public:
vector onePath;
int cost;
bool operator <(const DijPath &n2);
//判断两条路径是否相等
bool operator ==(const DijPath &n2);
};
bool DijPath::operator <(const DijPath &n2)
{
return cost < n2.cost;
}
//判断两条路径是否相等
bool DijPath::operator ==(const DijPath &n2)
{
if (onePath.size() == n2.onePath.size())
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < onePath.size(); i++)
{
if (onePath[i] != n2.onePath[i])
return false;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
//
//最短路径算法,返回一个DijPath结构体
//
DijPath dijkstra(
const vector> &NW,
const int src,
const int dst
)
{
//图中节点个数
unsigned int sizeNW = NW.size();
//知道每一个节点都被访问过结束
vector visited(sizeNW);
//到达dst顶点的最短路径的前一个顶点
vector prev(sizeNW);
//下一个距离当前访问过的最小的一个点
int minPos = 0;
//用于记录每个顶点到源节点的距离,如果最终len[dst]=INF,
//说明src和dst不可到达,讲cost设置为INF,用于ksp做判断舍弃这条路径
vector len(sizeNW);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < NW.size(); i++) //初始化
{
visited[i] = false; //一开始均被访问
len[i] = NW[src][i];
prev[i] = INF;
}
//初始节点被设置为访问过
visited[src] = true;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < sizeNW; ++i)
{
unsigned int min = INF; //记录访问过的节点到没访问过的节点的最小路径长度
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < sizeNW; ++j)
{
if (!visited[j] && min > len[j])
{
minPos = j; //记录找到了下一个节点
min = len[j];
}
}
visited[minPos] = true;
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < sizeNW; ++j)
{
//如果j节点没有被访问过,且通过j节点发现到其他节点更短的len[j]值
if (!visited[j] && len[j] > (len[minPos] + NW[minPos][j]))
{
prev[j] = minPos;
len[j] = len[minPos] + NW[minPos][j];
}
}
}
unsigned int beforeVertex = dst;
//通过一个栈将prev[]中的节点给倒过去,实现正序排列
stack st;
while (prev[beforeVertex] != INF)
{
st.push(beforeVertex);
beforeVertex = prev[beforeVertex];
}
st.push(beforeVertex);
//st栈中保存了第二个节点到dst的最短路径的正序
DijPath oneDijPath;
oneDijPath.onePath.resize(st.size() + 1);
oneDijPath.onePath[0] = src;
for (unsigned int i = 1; !st.empty(); i++)
{
oneDijPath.onePath[i] = st.top();
st.pop();
}
oneDijPath.cost = len[dst]; //返回最短路径的值,如果不可到达,设置为INF
return oneDijPath;
}
//
//用于裁剪掉kSP所有路径中root节点后面的所有的边和当前路径的前一条边
//返回一个vector>的被裁剪后的图
vector> cutEdge(
const vector>& NW,
vector< DijPath> kSPCost,
unsigned int root)
{
vector>NWCopy = NW;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < kSPCost.size(); i++)
{
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < kSPCost[i].onePath.size(); j++)
{
if (kSPCost[i].onePath[j] == root)
{
unsigned int nextVertex = kSPCost[i].onePath[j + 1];
if (j >= 1)
{
unsigned int beforeVertex = kSPCost[i].onePath[j - 1];
NWCopy[root][beforeVertex] = INF;
}
NWCopy[root][nextVertex] = INF; //设置为不可连接
break;
}
}
}
return NWCopy;
}
//
//Yen_k-shortest-path
//
vector> K_Shortest_Path::run(
const unsigned int kPath, // K Path
const vector>& NW, // network
const unsigned int src, // source node
const unsigned int dst) // destination node
{
vector>NWCopy = NW;
vector< DijPath> kSPCost(1); //不仅包含最短路径,还包含路径长度
vector< DijPath>B; //一个用于记录没有上一代通过裁剪边得到的下一代路径
DijPath newPath = dijkstra(NW, src, dst); //第一条最短路径
vector> kSP; //返回的路径
if (newPath.cost==INF) //判断最开始是否可以到达
{
kSP.resize(0);
return kSP;
}
kSPCost[0] = newPath; //用于储存找到的路径
vectorforwardPath; //记录裁剪边前面的
int nowCost; //用于记录到裁剪掉边前面一段路径的长度
for (unsigned int k = 1; k < kPath; k++) //用于找到所有的kPath
{
nowCost = 0;
bool flag = false;
//将这一代中B的节点加到kSP中去,当时必须等待上一代的所有边遍历完成
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < B.size() && kSPCost.size() < kPath&&kSPCost.size() >= k - 1; i++)
{
kSPCost.push_back(B[i]);
flag = true;
}
if (flag) //如果将B的路径加到A中,就置空B
{
B.resize(0);
}
//找不到路径了,直接返回
if (kSPCost.size() < k)
{
sort(kSPCost.begin(), kSPCost.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < kSPCost.size(); i++)
{
kSP.push_back(kSPCost[i].onePath);
}
return kSP;
}
forwardPath.resize(0);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < kSPCost[k - 1].onePath.size() - 1; i++) //用于第k-1条路径所有的边尝试去除去
{
forwardPath.push_back(kSPCost[k - 1].onePath[i]);
if (i != 0)
{
unsigned int forwardVertex = kSPCost[k - 1].onePath[i];
unsigned int nextVertex = kSPCost[k - 1].onePath[i - 1];
nowCost += NW[forwardVertex][nextVertex];
}
NWCopy = cutEdge(NW, kSPCost, kSPCost[k - 1].onePath[i]);
//找到一条从剪掉边的前面的那个节点到终点的一条最短路径
DijPath secondPath = dijkstra(NWCopy, kSPCost[k - 1].onePath[i], dst);
if (secondPath.cost > 100000)//判断两点不可以到达
{
continue;
}
//找到新的路径
newPath.onePath = forwardPath;
for (unsigned int j = 1; j < secondPath.onePath.size(); j++)
{
newPath.onePath.push_back(secondPath.onePath[j]);
}
newPath.cost = secondPath.cost + nowCost;
//判断newPath是不是已经存在了
secondPath.onePath.resize(0);
DijPath tmp;
tmp.cost = newPath.cost;
bool flag = true;
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < kSPCost.size(); j++)
{
tmp.onePath = kSPCost[j].onePath;
if (tmp == newPath)
{
flag = false; //已经存在了
break;
}
}
if (flag) //不存在,加到新的路径中
{
B.push_back(newPath);
}
if (kSPCost.size() >= kPath)
{
sort(kSPCost.begin(), kSPCost.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < kSPCost.size(); i++)
{
kSP.push_back(kSPCost[i].onePath);
}
return kSP;
}
}
}
sort(kSPCost.begin(), kSPCost.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < kSPCost.size(); i++)
{
kSP.push_back(kSPCost[i].onePath);
}
return kSP;
}
int main()
{
const string funcReturn("int");
const string funcName("main(int argc, char *argv[])");
try {
//unsigned int NODE = 5;
////vector> NW(NODE, vector(NODE, 0));
//vector> NW = {
// {0, 0, 0, 1, 1}, // A(0)
// {0, 0, 1, 0, 1}, // B(1)
// {0, 1, 0, 1, 1}, // C(2)
// {1, 0, 1, 0, 1}, // D(3)
// {1, 1, 1, 1, 0}, // E(4)
//};
//// NW 2
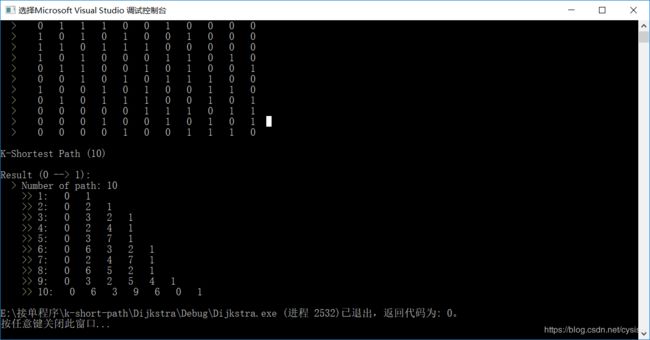
vector> NW = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
};
for (unsigned int i(0); i < NW.size(); i++) {
for (unsigned int j(0); j < NW.size(); j++) {
if (NW[i][j] == 0) {
NW[i][j] = INF;
}
}
}
//创建network
cout << "Network: " << endl;
for (unsigned int i(0); i < NW.size(); i++) {
cout << " > ";
for (unsigned int j(0); j < NW[i].size(); j++) {
if (NW[i][j] !=INF)
cout << " " << NW[i][j];
else
cout << " " << 0;
}
cout << endl;
}
// K-Shortest Path
unsigned int kPath = 10;
cout << endl << "K-Shortest Path (" << kPath << ")" << endl;
K_Shortest_Path KSP;
vector> kSP = KSP.run(kPath, NW, 0, 1);
cout << endl << "Result (0 --> 1): " << endl;
cout << " > Number of path: " << kSP.size() << endl;
for (unsigned int i(0); i < kSP.size(); i++) {
cout << " >> " << (i + 1) << ":";
for (unsigned int j(0); j < kSP[i].size(); j++) {
cout << " " << kSP[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
// vector ary1(NODE, 0);
// vector> ary2(NODE, ary1);
}
//++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
// 例外処理
// エラーが発生した場合にエラーを受け取って表示する処理
//++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
// 入出力ストリームでの例外処理
catch (std::ios_base::failure& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::ios_base::failure" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 範囲外へのアクセスによる例外処理(実行前)
catch (std::out_of_range& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::out_of_range" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 引数の値が不正な場合の例外処理(実行前)
catch (std::invalid_argument& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::invalid_argument" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 最大の長さを超える長さの値による例外処理(実行前)
catch (std::length_error& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::length_error" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// その他の実行前に発生する例外処理(実行前)
catch (std::domain_error& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::domain_error" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 数値演算を行った結果、アンダーフローが発生したときの例外処理(演算関係)
catch (std::underflow_error& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::underflow_error" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 数値演算を行った結果、オーバーフローが発生したときの例外処理(演算関係)
catch (std::overflow_error& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::overflow_error" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 演算処理の過程において、有効な範囲外の値となったときに発生する例外処理(演算関係)
catch (std::range_error& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::range_error" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// メモリ確保失敗の例外処理
catch (std::bad_alloc& err) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : std::bad_alloc" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
cout << "Error Content:" << endl
<< err.what() << endl;
}
// 前述していない例外処理を受け取る
catch (...) {
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-*-" << endl;
cout << "Exception : unknown" << endl;
cout << " >> " << funcReturn << " " << funcName << endl;
}
return 0;
}