C++最小二乘法拟合-(线性拟合和多项式拟合)
在进行曲线拟合时用的最多的是最小二乘法,其中以一元函数(线性)和多元函数(多项式)居多,下面这个类专门用于进行多项式拟合,可以根据用户输入的阶次进行多项式拟合,算法来自于网上,和GSL的拟合算法对比过,没有问题。此类在拟合完后还能计算拟合之后的误差:SSE(剩余平方和),SSR(回归平方和),RMSE(均方根误差),R-square(确定系数)。
1.fit类的实现
先看看fit类的代码:(只有一个头文件方便使用)
这是用网上的代码实现的,下面有用GSL实现的版本
#ifndef CZY_MATH_FIT
#define CZY_MATH_FIT
#include
/*
尘中远,于2014.03.20
主页:http://blog.csdn.net/czyt1988/article/details/21743595
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/maozefa/article/details/1725535
*/
namespace czy{
///
/// \brief 曲线拟合类
///
class Fit{
std::vector factor; ///<拟合后的方程系数
double ssr; ///<回归平方和
double sse; ///<(剩余平方和)
double rmse; /// fitedYs;///<存放拟合后的y值,在拟合时可设置为不保存节省内存
public:
Fit():ssr(0),sse(0),rmse(0){factor.resize(2,0);}
~Fit(){}
///
/// \brief 直线拟合-一元回归,拟合的结果可以使用getFactor获取,或者使用getSlope获取斜率,getIntercept获取截距
/// \param x 观察值的x
/// \param y 观察值的y
/// \param isSaveFitYs 拟合后的数据是否保存,默认否
///
template
bool linearFit(const std::vector& x, const std::vector& y,bool isSaveFitYs=false)
{
return linearFit(&x[0],&y[0],getSeriesLength(x,y),isSaveFitYs);
}
template
bool linearFit(const T* x, const T* y,size_t length,bool isSaveFitYs=false)
{
factor.resize(2,0);
typename T t1=0, t2=0, t3=0, t4=0;
for(int i=0; issr,this->sse,this->rmse,isSaveFitYs);
return true;
}
///
/// \brief 多项式拟合,拟合y=a0+a1*x+a2*x^2+……+apoly_n*x^poly_n
/// \param x 观察值的x
/// \param y 观察值的y
/// \param poly_n 期望拟合的阶数,若poly_n=2,则y=a0+a1*x+a2*x^2
/// \param isSaveFitYs 拟合后的数据是否保存,默认是
///
template
void polyfit(const std::vector& x
,const std::vector& y
,int poly_n
,bool isSaveFitYs=true)
{
polyfit(&x[0],&y[0],getSeriesLength(x,y),poly_n,isSaveFitYs);
}
template
void polyfit(const T* x,const T* y,size_t length,int poly_n,bool isSaveFitYs=true)
{
factor.resize(poly_n+1,0);
int i,j;
//double *tempx,*tempy,*sumxx,*sumxy,*ata;
std::vector tempx(length,1.0);
std::vector tempy(y,y+length);
std::vector sumxx(poly_n*2+1);
std::vector ata((poly_n+1)*(poly_n+1));
std::vector sumxy(poly_n+1);
for (i=0;i<2*poly_n+1;i++){
for (sumxx[i]=0,j=0;jssr,this->sse,this->rmse,isSaveFitYs);
}
///
/// \brief 获取系数
/// \param 存放系数的数组
///
void getFactor(std::vector& factor){factor = this->factor;}
///
/// \brief 获取拟合方程对应的y值,前提是拟合时设置isSaveFitYs为true
///
void getFitedYs(std::vector& fitedYs){fitedYs = this->fitedYs;}
///
/// \brief 根据x获取拟合方程的y值
/// \return 返回x对应的y值
///
template
double getY(const T x) const
{
double ans(0);
for (size_t i=0;i
size_t getSeriesLength(const std::vector& x
,const std::vector& y)
{
return (x.size() > y.size() ? y.size() : x.size());
}
///
/// \brief 计算均值
/// \return 均值
///
template
static T Mean(const std::vector& v)
{
return Mean(&v[0],v.size());
}
template
static T Mean(const T* v,size_t length)
{
T total(0);
for (size_t i=0;i
void calcError(const T* x
,const T* y
,size_t length
,double& r_ssr
,double& r_sse
,double& r_rmse
,bool isSaveFitYs=true
)
{
T mean_y = Mean(y,length);
T yi(0);
fitedYs.reserve(length);
for (int i=0; i
void gauss_solve(int n
,std::vector& A
,std::vector& x
,std::vector& b)
{
gauss_solve(n,&A[0],&x[0],&b[0]);
}
template
void gauss_solve(int n
,T* A
,T* x
,T* b)
{
int i,j,k,r;
double max;
for (k=0;k=0;x[i]/=A[i*n+i],i--)
for (j=i+1,x[i]=b[i];j GSL实现版本,此版本依赖于GSL需要先配置GSL,GSL配置方法网上很多,我的blog也有一篇介绍win + Qt环境下的配置,其它大同小异:http://blog.csdn.net/czyt1988/article/details/39178975
#ifndef CZYMATH_FIT_H
#define CZYMATH_FIT_H
#include
namespace gsl{
#include
#include /* 提供了 gammaq 函数 */
#include /* 提供了向量结构*/
#include
#include
}
namespace czy {
///
/// \brief The Math class 用于处理简单数学计算
///
namespace Math{
using namespace gsl;
///
/// \brief 拟合类,封装了gsl的拟合算法
///
/// 实现线性拟合和多项式拟合
///
class fit{
public:
fit(){}
~fit(){}
private:
std::map m_factor;//记录各个点的系数,key中0是0次方,1是1次方,value是对应的系数
std::map m_err;
double m_cov;//相关度
double m_ssr;//回归平方和
double m_sse;//(剩余平方和)
double m_rmse;//RMSE均方根误差
double m_wssr;
double m_goodness;//基于wssr的拟合优度
void clearAll(){
m_factor.clear();m_err.clear();
}
public:
//计算拟合的显著性
static void getDeterminateOfCoefficient(
const double* y,const double* yi,size_t length
,double& out_ssr,double& out_sse,double& out_sst,double& out_rmse,double& out_RSquare)
{
double y_mean = mean(y,y+length);
out_ssr = 0.0;
for (size_t i =0;isecond;
}
///
/// \brief 获取系数的个数
/// \return
///
size_t getFactorSize()
{
return m_factor.size();
}
///
/// \brief linearFit 线性拟合的静态函数
/// \param x 数据点的横坐标值数组
/// \param xstride 横坐标值数组索引步长 xstride 与 ystride 的值设为 1,表示数据点集 {(xi,yi)|i=0,1,⋯,n−1} 全部参与直线的拟合;
/// \param y 数据点的纵坐标值数组
/// \param ystride 纵坐标值数组索引步长
/// \param n 数据点的数量
/// \param out_intercept 计算的截距
/// \param out_slope 计算的斜率
/// \param out_interceptErr 计算的截距误差
/// \param out_slopeErr 计算的斜率误差
/// \param out_cov 计算的斜率和截距的相关度
/// \param out_wssr 拟合的wssr值
/// \return
///
static int linearFit(
const double *x
,const size_t xstride
,const double *y
,const size_t ystride
,size_t n
,double& out_intercept
,double& out_slope
,double& out_interceptErr
,double& out_slopeErr
,double& out_cov
,double& out_wssr
)
{
return gsl_fit_linear(x,xstride,y,ystride,n
,&out_intercept,&out_slope,&out_interceptErr,&out_slopeErr,&out_cov,&out_wssr);
}
///
/// \brief 线性拟合
/// \param x 拟合的x值
/// \param y 拟合的y值
/// \param n x,y值对应的长度
/// \return
///
bool linearFit(const double *x,const double *y,size_t n)
{
clearAll();
m_factor[0]=0;m_err[0]=0;
m_factor[1]=1;m_err[1]=0;
int r = linearFit(x,1,y,1,n
,m_factor[0],m_factor[1],m_err[0],m_err[1],m_cov,m_wssr);
if (0 != r)
return false;
m_goodness = gsl_cdf_chisq_Q(m_wssr/2.0,(n-2)/2.0);//计算优度
{
std::vector yi;
getYis(x,n,yi);
double t;
getDeterminateOfCoefficient(y,&yi[0],n,m_ssr,m_sse,t,m_rmse,t);
}
return true;
}
bool linearFit(const std::vector& x,const std::vector& y)
{
size_t n = x.size() > y.size() ? y.size() :x.size();
return linearFit(&x[0],&y[0],n);
}
///
/// \brief 多项式拟合
/// \param poly_n 阶次,如c0+C1x是1,若c0+c1x+c2x^2则poly_n是2
static int polyfit(const double *x
,const double *y
,size_t xyLength
,unsigned poly_n
,std::vector& out_factor
,double& out_chisq)//拟合曲线与数据点的优值函数最小值 ,χ2 检验
{
gsl_matrix *XX = gsl_matrix_alloc(xyLength, poly_n + 1);
gsl_vector *c = gsl_vector_alloc(poly_n + 1);
gsl_matrix *cov = gsl_matrix_alloc(poly_n + 1, poly_n + 1);
gsl_vector *vY = gsl_vector_alloc(xyLength);
for(size_t i = 0; i < xyLength; i++)
{
gsl_matrix_set(XX, i, 0, 1.0);
gsl_vector_set (vY, i, y[i]);
for(unsigned j = 1; j <= poly_n; j++)
{
gsl_matrix_set(XX, i, j, pow(x[i], int(j) ));
}
}
gsl_multifit_linear_workspace *workspace = gsl_multifit_linear_alloc(xyLength, poly_n + 1);
int r = gsl_multifit_linear(XX, vY, c, cov, &out_chisq, workspace);
gsl_multifit_linear_free(workspace);
out_factor.resize(c->size,0);
for (size_t i=0;isize;++i)
{
out_factor[i] = gsl_vector_get(c,i);
}
gsl_vector_free(vY);
gsl_matrix_free(XX);
gsl_matrix_free(cov);
gsl_vector_free(c);
return r;
}
bool polyfit(const double *x
,const double *y
,size_t xyLength
,unsigned poly_n)
{
double chisq;
std::vector factor;
int r = polyfit(x,y,xyLength,poly_n,factor,chisq);
if (0 != r)
return false;
m_goodness = gsl_cdf_chisq_Q(chisq/2.0,(xyLength-2)/2.0);//计算优度
clearAll();
for (unsigned i=0;i yi;
getYis(x,xyLength,yi);
double t;//由于没用到,所以都用t代替
getDeterminateOfCoefficient(y,&yi[0],xyLength,m_ssr,m_sse,t,m_rmse,t);
return true;
}
bool polyfit(const std::vector& x
,const std::vector& y
,unsigned plotN)
{
size_t n = x.size() > y.size() ? y.size() :x.size();
return polyfit(&x[0],&y[0],n,plotN);
}
double getYi(double x) const
{
double ans(0);
for (auto ite = m_factor.begin();ite != m_factor.end();++ite)
{
ans += (ite->second)*pow(x,ite->first);
}
return ans;
}
void getYis(const double* x,size_t length,std::vector& yis) const
{
yis.clear();
yis.resize(length);
for(size_t i=0;i 为了防止重命名,把其放置于czy的命名空间中,此类主要两个函数:
1.求解线性拟合:
///
/// \brief 直线拟合-一元回归,拟合的结果可以使用getFactor获取,或者使用getSlope获取斜率,getIntercept获取截距
/// \param x 观察值的x
/// \param y 观察值的y
/// \param length x,y数组的长度
/// \param isSaveFitYs 拟合后的数据是否保存,默认否
///
template
bool linearFit(const std::vector& x, const std::vector& y,bool isSaveFitYs=false);
template
bool linearFit(const T* x, const T* y,size_t length,bool isSaveFitYs=false); 2.多项式拟合:
///
/// \brief 多项式拟合,拟合y=a0+a1*x+a2*x^2+……+apoly_n*x^poly_n
/// \param x 观察值的x
/// \param y 观察值的y
/// \param length x,y数组的长度
/// \param poly_n 期望拟合的阶数,若poly_n=2,则y=a0+a1*x+a2*x^2
/// \param isSaveFitYs 拟合后的数据是否保存,默认是
///
template
void polyfit(const std::vector& x,const std::vector& y,int poly_n,bool isSaveFitYs=true);
template
void polyfit(const T* x,const T* y,size_t length,int poly_n,bool isSaveFitYs=true); 这两个函数都用模板函数形式写,主要是为了能使用于float和double两种数据类型
2.fit类的MFC示范程序
下面看看如何使用这个类,以MFC示范,使用了开源的绘图控件Hight-Speed Charting,使用方法见 http://blog.csdn.net/czyt1988/article/details/8740500新建对话框文件,
对话框资源文件如图所示:
加入下面的这些变量:
std::vector m_x,m_y,m_yploy;
const size_t m_size;
CChartLineSerie *m_pLineSerie1;
CChartLineSerie *m_pLineSerie2; 由于m_size是常量,因此需要在构造函数进行初始化,如:
ClineFitDlg::ClineFitDlg(CWnd* pParent /*=NULL*/)
: CDialogEx(ClineFitDlg::IDD, pParent)
,m_size(512)
,m_pLineSerie1(NULL)CChartAxis *pAxis = NULL;
pAxis = m_chartCtrl.CreateStandardAxis(CChartCtrl::BottomAxis);
pAxis->SetAutomatic(true);
pAxis = m_chartCtrl.CreateStandardAxis(CChartCtrl::LeftAxis);
pAxis->SetAutomatic(true);
m_x.resize(m_size);
m_y.resize(m_size);
m_yploy.resize(m_size);
for(size_t i =0;iSetSeriesOrdering(poNoOrdering);//设置为无序
m_pLineSerie1->AddPoints(&m_x[0], &m_y[0], m_size);
m_pLineSerie1->SetName(_T("线性数据"));
m_pLineSerie2 = m_chartCtrl.CreateLineSerie();
m_pLineSerie2->SetSeriesOrdering(poNoOrdering);//设置为无序
m_pLineSerie2->AddPoints(&m_x[0], &m_yploy[0], m_size);
m_pLineSerie2->SetName(_T("多项式数据")); rangf是随机数生成函数,实现如下:
double ClineFitDlg::randf(double min,double max)
{
int minInteger = (int)(min*10000);
int maxInteger = (int)(max*10000);
int randInteger = rand()*rand();
int diffInteger = maxInteger - minInteger;
int resultInteger = randInteger % diffInteger + minInteger;
return resultInteger/10000.0;
}运行程序,如图所示
线性拟合的使用如下:
void ClineFitDlg::OnBnClickedButton1()
{
CString str,strTemp;
czy::Fit fit;
fit.linearFit(m_x,m_y);
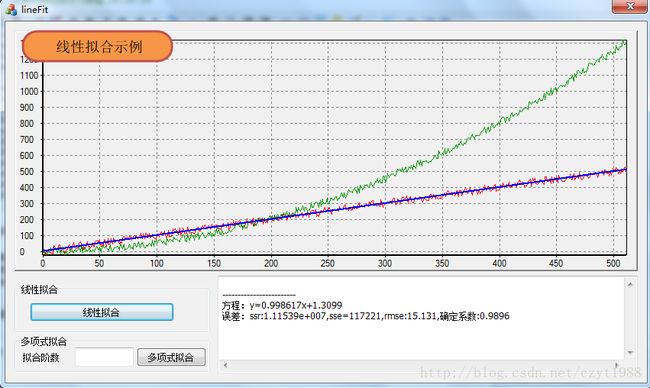
str.Format(_T("方程:y=%gx+%g\r\n误差:ssr:%g,sse=%g,rmse:%g,确定系数:%g"),fit.getSlope(),fit.getIntercept()
,fit.getSSR(),fit.getSSE(),fit.getRMSE(),fit.getR_square());
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT,strTemp);
SetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT,strTemp+_T("\r\n------------------------\r\n")+str);
//在图上绘制拟合的曲线
CChartLineSerie* pfitLineSerie1 = m_chartCtrl.CreateLineSerie();
std::vector x(2,0),y(2,0);
x[0] = 0;x[1] = m_size-1;
y[0] = fit.getY(x[0]);y[1] = fit.getY(x[1]);
pfitLineSerie1->SetSeriesOrdering(poNoOrdering);//设置为无序
pfitLineSerie1->AddPoints(&x[0], &y[0], 2);
pfitLineSerie1->SetName(_T("拟合方程"));//SetName的作用将在后面讲到
pfitLineSerie1->SetWidth(2);
} 需要如下步骤:
- 声明Fit类,用于头文件在czy命名空间中,因此需要显示声明命名空间名称czy::Fit fit;
- 把观察数据输入进行拟合,由于是线性拟合,可以使用LinearFit函数,此函数把观察量的x值和y值传入即可进行拟合
- 拟合完后,拟合的相关结果保存在czy::Fit里面,可以通过相关方法调用,方法在头文件中都有详细说明
运行结果如图所示:
多项式拟合的使用如下:
void ClineFitDlg::OnBnClickedButton2()
{
CString str;
GetDlgItemText(IDC_EDIT1,str);
if (str.IsEmpty())
{
MessageBox(_T("请输入阶次"),_T("警告"));
return;
}
int n = _ttoi(str);
if (n<0)
{
MessageBox(_T("请输入大于1的阶数"),_T("警告"));
return;
}
czy::Fit fit;
fit.polyfit(m_x,m_yploy,n,true);
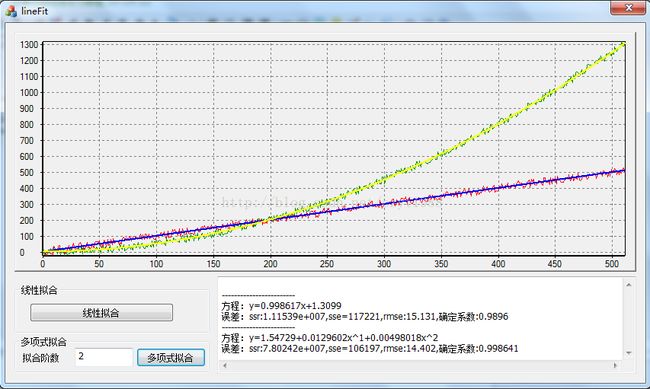
CString strFun(_T("y=")),strTemp(_T(""));
for (int i=0;i yploy;
fit.getFitedYs(yploy);
CChartLineSerie* pfitLineSerie1 = m_chartCtrl.CreateLineSerie();
pfitLineSerie1->SetSeriesOrdering(poNoOrdering);//设置为无序
pfitLineSerie1->AddPoints(&m_x[0], &yploy[0], yploy.size());
pfitLineSerie1->SetName(_T("多项式拟合方程"));//SetName的作用将在后面讲到
pfitLineSerie1->SetWidth(2);
} 步骤如下:
- 和线性拟合一样,声明Fit变量
- 输入观察值,同时输入需要拟合的阶次,这里输入2阶,就是2项式拟合,最后的布尔变量是标定是否需要把拟合的结果点保存起来,保存点会根据观察的x值计算拟合的y值,保存结果点会花费更多的内存,如果拟合后需要绘制,设为true会更方便,如果只需要拟合的方程,可以设置为false
- 拟合完后,拟合的相关结果保存在czy::Fit里面,可以通过相关方法调用,方法在头文件中都有详细说明
代码:
for (int i=0;i是用于生成方程的,由于系数小于时,打印时会把负号“-”显示,而正数时却不会显示正号,因此需要进行判断,如果小于0就不用添加“+”号,如果大于0就添加“+”号
结果如下:
源代码下载:
C++最小二乘法拟合-(线性拟合和多项式拟合)