View的事件分发机制最新源码剖析
先抛出几个问题
1:触发View事件dispatchTouchEvent与onTouchEvent那个函数先执行?
2:onTouch消费事件的具体含义是什么?
3:onTouch,onClick回调方法的先后执行顺序?
Button分别监听onTouchListener & onClickListener
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sb.append("onclick is called!" + "\n");
}
}); button1.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
sb.append("ontouch is called! event = " + event.getAction() + "\n");
return isCheck;
}
});isCheck由Checkbox控制默认为false;
默认情况下点击button,打印日志如下:
02-19 10:20:48.154 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 0
02-19 10:20:48.154 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 2
02-19 10:20:48.154 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 2
02-19 10:20:48.154 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 1
02-19 10:20:48.154 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: onclick is called
选择CheckBox,消费掉OnTouch事件,打印日志如下:
02-19 10:23:43.694 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 0
02-19 10:23:43.694 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 2
02-19 10:23:43.694 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 2
02-19 10:23:43.694 19082-19082/com.example.hongentao.touchdemo I/ViewActivity: ontouch is called! event = 1
查看打印日志,发现消费掉Ontouch事件后(也就是将返回值设为true),onClick事件没有得到执行。
那到底是什么原因导致的呢?
打开源码我们来分析一下:
Button是自定义的View,代码如下:
public class MyButton extends Button {
private String TAG = MyButton.class.getSimpleName();
public MyButton(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "disPatchTouchEvent is called!");
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
Log.i(TAG, "onTouchEvent is called!");
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}这里打印日志发现永远都是dispatchTouchEvent事件先执行,只要触发View的任何事件都会首先触发该方法。
源码为api-23, 老版本源码略有不同
我们找找dispatchTouchEvent到底在哪里?
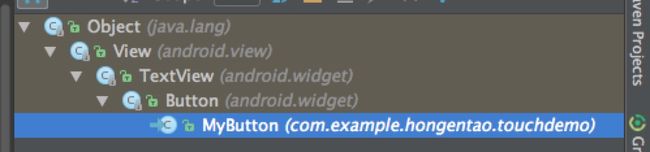
分别在Button,TextView中都没有找到dispatchTouchEvent事件,最终在View中找到了该方法。
进入源码瞅一下:
/**
* Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
* view if it is the target.
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first.
if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) {
// We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event.
if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {
return false;
}
// We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch.
event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
boolean result = false;
if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0);
}
final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked();
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
// Defensive cleanup for new gesture
stopNestedScroll();
}
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {
mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);
}
// Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture;
// also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest
// of the gesture.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP ||
actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL ||
(actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) {
stopNestedScroll();
}
return result;
}分析关键代码:
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)是判断改点击事件是否应该被传递,然后进入下一级判断条件,分别为四级判断条件
1:li != null
2: li.mOntouchListener != null
3:(mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
4:li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)
首先分析第一个判断条件:
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
mListenerInfo在那里被赋值的呢?
跟踪源码:
ListenerInfo getListenerInfo() {
if (mListenerInfo != null) {
return mListenerInfo;
}
mListenerInfo = new ListenerInfo();
return mListenerInfo;
} public void setOnClickListener(@Nullable OnClickListener l) {
if (!isClickable()) {
setClickable(true);
}
getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener = l;
}
在Button setOnclickListener监听事件的时候,调用getListenerInfo方法,getListenerInfo就是一个单例事件,从而li被赋值。
分析第二个判断条件:
li.mOntouchListener != null
这个又是什么鬼?
来来来,继续看源码
/**
* Register a callback to be invoked when a touch event is sent to this view.
* @param l the touch listener to attach to this view
*/
public void setOnTouchListener(OnTouchListener l) {
getListenerInfo().mOnTouchListener = l;
}通过查看源码,mTouchListener就是在setOntouchListener的时候被赋值的,一目了然。
再来看第三个判断条件:
(mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
这个比较简单,就是判断当前的View是否是可点击的。
第四个判断条件为:
li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)
这个更直接,直接获取onTouch的返回值:
借用这四种判断条件显而易见可以分析出,当Button消费掉ontouch事件之后,直接renturn true,onclick不会被执行。 而如果ontouch没有被消费,通过源码onclick肯定是在onTouchEvent(event)事件中被执行。
查看下源码:
/**
* Implement this method to handle touch screen motion events.
*
* If this method is used to detect click actions, it is recommended that
* the actions be performed by implementing and calling
* {@link #performClick()}. This will ensure consistent system behavior,
* including:
*
* - obeying click sound preferences
*
- dispatching OnClickListener calls
*
- handling {@link AccessibilityNodeInfo#ACTION_CLICK ACTION_CLICK} when
* accessibility features are enabled
*
*
* @param event The motion event.
* @return True if the event was handled, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final float x = event.getX();
final float y = event.getY();
final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;
final int action = event.getAction();
if ((viewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
setPressed(false);
}
// A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch
// events, it just doesn't respond to them.
return (((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE
|| (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)
|| (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE);
}
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
if (((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE ||
(viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) ||
(viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in
// touch mode.
boolean focusTaken = false;
if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {
focusTaken = requestFocus();
}
if (prepressed) {
// The button is being released before we actually
// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed
// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure
// the user sees it.
setPressed(true, x, y);
}
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed state
if (!focusTaken) {
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClick();
}
}
}
if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {
mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();
}
if (prepressed) {
postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,
ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());
} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {
// If the post failed, unpress right now
mUnsetPressedState.run();
}
removeTapCallback();
}
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (performButtonActionOnTouchDown(event)) {
break;
}
// Walk up the hierarchy to determine if we're inside a scrolling container.
boolean isInScrollingContainer = isInScrollingContainer();
// For views inside a scrolling container, delay the pressed feedback for
// a short period in case this is a scroll.
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// Not inside a scrolling container, so show the feedback right away
setPressed(true, x, y);
checkForLongClick(0);
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
setPressed(false);
removeTapCallback();
removeLongPressCallback();
mInContextButtonPress = false;
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
drawableHotspotChanged(x, y);
// Be lenient about moving outside of buttons
if (!pointInView(x, y, mTouchSlop)) {
// Outside button
removeTapCallback();
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {
// Remove any future long press/tap checks
removeLongPressCallback();
setPressed(false);
}
}
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}源码好长直接挑重点:
当Event为 ACTION_UP之后,经过一系列的判断会进入该段代码:
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {performClick();} 进入performClick源码中看下:
public boolean performClick() {
final boolean result;
final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {
playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);
li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);
return result;
}果然看见了onclick事件被执行,现在答案也一一被解答了。
现在分别解答下开篇提出的三个问题:
1:触发View事件dispatchTouchEvent与onTouchEvent那个函数先执行?
答:只要是触发View的任何事件,都会首先触发dispatchTouchEvent事件。
2:onTouch消费事件的具体含义是什么?
答:ouTouch消费事件后,后续注册的事件回调都不会被执行,例如onClick。
3:onTouch,onClick回调方法的先后执行顺序?
答:分两种情况:1:onTouch消费掉事件, onTouch事件会被执行,onClick事件不会被执行。 2:onTouch没有消费掉事件,onTouch先执行,onCLick事件后执行。
