CTR预估 论文实践(五)--Practical Lessons from Predicting Clicks on Ads at Facebook (GBDT+LR)
博客代码均以上传至GitHub,欢迎follow和start~~!
1. GBDT构造组合特征的方式
利用GBDT进行特征构造依据其模型组合方式一共有两种方式:
-
GBDT + LR
与原论文的实现方式一样,利用GBDT构造组合特征,再将组合特征进行one-hot编码(本实践代码也属此类);
-
GBDT + FFM 或者 GBDT + 树模型
此时,使用利用GBDT构造的组合特征不再进行one-hot编码,而是直接利用输出叶节点的索引信息,如果将GBDT组合特征输出到其他树模型,则可直接利用节点索引信息;若是将GBDT信息输出到FFM中,依旧是利用索引信息,但是需要将索引信息组织成FFM数据输入形式。
2. GBDT组合特征实现方式
GBDT实现特征组合主要有两种实现方式:
- 可以设置pre_leaf=True获得每个样本在每颗树上的
leaf_Index,可以查看下XGBoost官方文档查阅一下API:
原来这个参数是在predict里面,在对原始特征进行简单调参训 练后,对原始数据以及测试数据进行new_feature= bst.predict(d_test, pred_leaf=True)即可得到一个(nsample, ntrees) 的结果矩阵,即每个样本在每个树上的index。
-
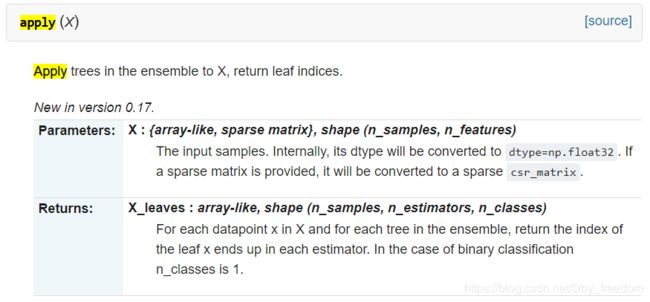
通过设置apply实现 (注意结合LR时候,后接[:,:,0]进行降维):
可以看到他用的是apply()方法,这里就有点疑惑了,在XGBoost官方API并没有看到这个方法,于是我去SKlearn GBDT API看了下,果然有apply()方法可以获得leaf indices:
因为XGBoost有自带接口和Scikit-Learn接口,所以代码上有所差异。
值得注意的是,当使用apply方式时候,返回比直接调用XGBoost的多了
n_classes:这也是为什么在GBDT+LR使用apply方式获得GBDT的组合特征时往往加上[:,:,0],为的就是去掉n_class那一维,如下:
实例代码:
'''
使用X_train训练GBDT模型,后面用此模型构造特征
'''
grd.fit(X_train, y_train)
# fit one-hot编码器
grd_enc.fit(grd.apply(X_train)[:, :, 0])
'''
使用训练好的GBDT模型构建特征,然后将特征经过one-hot编码作为新的特征输入到LR模型训练。
'''
grd_lm.fit(grd_enc.transform(grd.apply(X_train_lr)[:, :, 0]), y_train_lr)
# 用训练好的LR模型多X_test做预测
y_pred_grd_lm = grd_lm.predict_proba(grd_enc.transform(grd.apply(X_test)[:, :, 0]))[:, 1]
# 根据预测结果输出
fpr_grd_lm, tpr_grd_lm, _ = roc_curve(y_test, y_pred_grd_lm)
3. 代码实践
3.1 介绍
针对CTR预估,测试LR + GBDT的方案效果.
3.2 数据集
这里提供两份数据集,第一份比较好是CTR的,第二份也还凑合,之前在DeepFm中有用过。按理来说用第一个数据更好,但是压缩包大小为4G+ 有点大.
所以我采用的是第二个数据。感兴趣的同学,可以尝试下用第一个的数据进行试验。非常欢迎分享下实验结果~
3.3 kaggle CTR比赛
使用kaggle 2014年比赛 criteo-Display Advertising Challenge比赛的数据集。第一名的方案就是参考了Facebook的论文,使用GBDT进行特征转换,后面跟FFM
比赛地址: https://www.kaggle.com/c/criteo-display-ad-challenge/data
数据集下载:http://labs.criteo.com/2014/02/kaggle-display-advertising-challenge-dataset/
第一名方案参考
https://www.kaggle.com/c/criteo-display-ad-challenge/discussion/10555
PPT: https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r01922136/kaggle-2014-criteo.pdf
3.4 kaggle 比赛
kaggle上一个预测任务
https://www.kaggle.com/c/porto-seguro-safe-driver-prediction
其中数据集及jupyter notebook版说明均已上传至个人GitHub
采用了LightGBM树集成架构实现的GBDT,当然也可采用XGBoost或者sklearn自带的GBDT实现;
Code:
import gc
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 1. 读取数据
path = "./data/"
train_file = "train.csv"
test_file = "test.csv"
trainDf = pd.read_csv(path + train_file)
# testDf = pd.read_csv(path + train_file, nrows=1000, skiprows=range(1, 10000))
pos_trainDf = trainDf[trainDf['target'] == 1]
neg_trainDf = trainDf[trainDf['target'] == 0].sample(n=20000, random_state=2018)
trainDf = pd.concat([pos_trainDf, neg_trainDf], axis=0).sample(frac=1.0, random_state=2018)
del pos_trainDf
del neg_trainDf
gc.collect()
print(trainDf.shape, trainDf['target'].mean())
trainDf, testDf, _, _ = train_test_split(trainDf, trainDf['target'], test_size=0.25, random_state=2018)
print(trainDf['target'].mean(), trainDf.shape)
print(testDf['target'].mean(), testDf.shape)
"""
一共59个特征,包括id, target
bin特征17个;cat特征14个;连续特征26个;
Code:
columns = trainDf.columns.tolist()
bin_feats = []
cat_feats = []
con_feats = []
for col in columns:
if 'bin' in col:
bin_feats.append(col)
continue
if 'cat' in col:
cat_feats.append(col)
continue
if 'id' != col and 'target' != col:
con_feats.append(col)
print(len(bin_feats), bin_feats)
print(len(cat_feats), cat_feats)
print(len(con_feats), con_feats)
"""
bin_feats = ['ps_ind_06_bin', 'ps_ind_07_bin', 'ps_ind_08_bin', 'ps_ind_09_bin', 'ps_ind_10_bin', 'ps_ind_11_bin',
'ps_ind_12_bin', 'ps_ind_13_bin', 'ps_ind_16_bin', 'ps_ind_17_bin', 'ps_ind_18_bin', 'ps_calc_15_bin',
'ps_calc_16_bin', 'ps_calc_17_bin', 'ps_calc_18_bin', 'ps_calc_19_bin', 'ps_calc_20_bin']
cat_feats = ['ps_ind_02_cat', 'ps_ind_04_cat', 'ps_ind_05_cat', 'ps_car_01_cat', 'ps_car_02_cat', 'ps_car_03_cat',
'ps_car_04_cat', 'ps_car_05_cat', 'ps_car_06_cat', 'ps_car_07_cat', 'ps_car_08_cat', 'ps_car_09_cat',
'ps_car_10_cat', 'ps_car_11_cat']
con_feats = ['ps_ind_01', 'ps_ind_03', 'ps_ind_14', 'ps_ind_15', 'ps_reg_01', 'ps_reg_02', 'ps_reg_03', 'ps_car_11',
'ps_car_12', 'ps_car_13', 'ps_car_14', 'ps_car_15', 'ps_calc_01', 'ps_calc_02', 'ps_calc_03', 'ps_calc_04',
'ps_calc_05', 'ps_calc_06', 'ps_calc_07', 'ps_calc_08', 'ps_calc_09', 'ps_calc_10', 'ps_calc_11',
'ps_calc_12', 'ps_calc_13', 'ps_calc_14']
# 2. 特征处理
trainDf = trainDf.fillna(0)
testDf = testDf.fillna(0)
train_sz = trainDf.shape[0]
combineDf = pd.concat([trainDf, testDf], axis=0)
del trainDf
del testDf
gc.collect()
# 2.1 连续特征全部归一化
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
for col in con_feats:
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
combineDf[col] = scaler.fit_transform(np.array(combineDf[col].values.tolist()).reshape(-1, 1))
# 2.2 离散特征one-hot
for col in bin_feats + cat_feats:
onehotret = pd.get_dummies(combineDf[col], prefix=col)
combineDf = pd.concat([combineDf, onehotret], axis=1)
# 3. 训练模型
label = 'target'
onehot_feats = [col for col in combineDf.columns if col not in ['id', 'target'] + con_feats + cat_feats + bin_feats]
train = combineDf[:train_sz]
test = combineDf[train_sz:]
print("Train.shape: {0}, Test.shape: {0}".format(train.shape, test.shape))
del combineDf
# 3.1 LR模型
lr_feats = con_feats + onehot_feats
lr = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=1)
lr.fit(train[lr_feats], train[label].values)
def do_model_metric(y_true, y_pred, y_pred_prob):
print("Predict 1 percent: {0}".format(np.mean(y_pred)))
print("Label 1 percent: {0}".format(train[label].mean()))
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, accuracy_score
print("AUC: {0:.3}".format(roc_auc_score(y_true=y_true, y_score=y_pred_prob[:, 1])))
print("Accuracy: {0}".format(accuracy_score(y_true=y_true, y_pred=y_pred)))
print("Train............")
do_model_metric(y_true=train[label], y_pred=lr.predict(train[lr_feats]), y_pred_prob=lr.predict_proba(train[lr_feats]))
print("\n\n")
print("Test.............")
do_model_metric(y_true=test[label], y_pred=lr.predict(test[lr_feats]), y_pred_prob=lr.predict_proba(test[lr_feats]))
# 3.2 GBDT
lgb_feats = con_feats + cat_feats + bin_feats
categorical_feature_list = cat_feats + bin_feats
import lightgbm as lgb
lgb_params = {
'objective': 'binary',
'boosting_type': 'gbdt',
'metric': 'auc',
'learning_rate': 0.01,
'num_leaves': 5,
'max_depth': 4,
'min_data_in_leaf': 100,
'bagging_fraction': 0.8,
'feature_fraction': 0.8,
'bagging_freq': 10,
'lambda_l1': 0.2,
'lambda_l2': 0.2,
'scale_pos_weight': 1,
}
lgbtrain = lgb.Dataset(train[lgb_feats].values, label=train[label].values,
feature_name=lgb_feats,
categorical_feature=categorical_feature_list
)
lgbvalid = lgb.Dataset(test[lgb_feats].values, label=test[label].values,
feature_name=lgb_feats,
categorical_feature=categorical_feature_list
)
evals_results = {}
print('train')
lgb_model = lgb.train(lgb_params,
lgbtrain,
valid_sets=lgbvalid,
evals_result=evals_results,
num_boost_round=1000,
early_stopping_rounds=60,
verbose_eval=50,
categorical_feature=categorical_feature_list,
)
# 3.3 LR + GBDT
train_sz = train.shape[0]
combineDf = pd.concat([train, test], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
# 得到叶节点编号 Feature Transformation
gbdt_feats_vals = lgb_model.predict(combineDf[lgb_feats], pred_leaf=True)
gbdt_columns = ["gbdt_leaf_indices_" + str(i) for i in range(0, gbdt_feats_vals.shape[1])]
combineDf = pd.concat(
[combineDf, pd.DataFrame(data=gbdt_feats_vals, index=range(0, gbdt_feats_vals.shape[0]), columns=gbdt_columns)],
axis=1)
# onehotencoder(gbdt_feats)
origin_columns = combineDf.columns
for col in gbdt_columns:
combineDf = pd.concat([combineDf, pd.get_dummies(combineDf[col], prefix=col)], axis=1)
gbdt_onehot_feats = [col for col in combineDf.columns if col not in origin_columns]
# 恢复train, test
train = combineDf[:train_sz]
test = combineDf[train_sz:]
del combineDf;
gc.collect();
lr_gbdt_feats = lr_feats + gbdt_onehot_feats
lr_gbdt_model = LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=1)
lr_gbdt_model.fit(train[lr_gbdt_feats], train[label])
print("Train................")
do_model_metric(y_true=train[label], y_pred=lr_gbdt_model.predict(train[lr_gbdt_feats]),
y_pred_prob=lr_gbdt_model.predict_proba(train[lr_gbdt_feats]))
print("Test..................")
do_model_metric(y_true=test[label], y_pred=lr_gbdt_model.predict(test[lr_gbdt_feats]),
y_pred_prob=lr_gbdt_model.predict_proba(test[lr_gbdt_feats]))
3.5 使用apply方式生成GBDT特征
Code:
# coding: utf-8
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn import metrics
from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier
import numpy as np
class XgboostFeature():
##可以传入xgboost的参数
##常用传入特征的个数 即树的个数 默认30
def __init__(self,n_estimators=30,learning_rate =0.3,max_depth=3,min_child_weight=1,gamma=0.3,subsample=0.8,colsample_bytree=0.8,objective= 'binary:logistic',nthread=4,scale_pos_weight=1,reg_alpha=1e-05,reg_lambda=1,seed=27):
self.n_estimators=n_estimators
self.learning_rate=learning_rate
self.max_depth=max_depth
self.min_child_weight=min_child_weight
self.gamma=gamma
self.subsample=subsample
self.colsample_bytree=colsample_bytree
self.objective=objective
self.nthread=nthread
self.scale_pos_weight=scale_pos_weight
self.reg_alpha=reg_alpha
self.reg_lambda=reg_lambda
self.seed=seed
print 'Xgboost Feature start, new_feature number:',n_estimators
def mergeToOne(self,X,X2):
X3=[]
for i in xrange(X.shape[0]):
tmp=np.array([list(X[i]),list(X2[i])])
X3.append(list(np.hstack(tmp)))
X3=np.array(X3)
return X3
##切割训练
def fit_model_split(self,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test):
##X_train_1用于生成模型 X_train_2用于和新特征组成新训练集合
X_train_1, X_train_2, y_train_1, y_train_2 = train_test_split(X_train, y_train, test_size=0.6, random_state=0)
clf = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =self.learning_rate,
n_estimators=self.n_estimators,
max_depth=self.max_depth,
min_child_weight=self.min_child_weight,
gamma=self.gamma,
subsample=self.subsample,
colsample_bytree=self.colsample_bytree,
objective= self.objective,
nthread=self.nthread,
scale_pos_weight=self.scale_pos_weight,
reg_alpha=self.reg_alpha,
reg_lambda=self.reg_lambda,
seed=self.seed)
clf.fit(X_train_1, y_train_1)
y_pre= clf.predict(X_train_2)
y_pro= clf.predict_proba(X_train_2)[:,1]
print "pred_leaf=T AUC Score : %f" % metrics.roc_auc_score(y_train_2, y_pro)
print"pred_leaf=T Accuracy : %.4g" % metrics.accuracy_score(y_train_2, y_pre)
new_feature= clf.apply(X_train_2)
X_train_new2=self.mergeToOne(X_train_2,new_feature)
new_feature_test= clf.apply(X_test)
X_test_new=self.mergeToOne(X_test,new_feature_test)
print "Training set of sample size 0.4 fewer than before"
return X_train_new2,y_train_2,X_test_new,y_test
##整体训练
def fit_model(self,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test):
clf = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =self.learning_rate,
n_estimators=self.n_estimators,
max_depth=self.max_depth,
min_child_weight=self.min_child_weight,
gamma=self.gamma,
subsample=self.subsample,
colsample_bytree=self.colsample_bytree,
objective= self.objective,
nthread=self.nthread,
scale_pos_weight=self.scale_pos_weight,
reg_alpha=self.reg_alpha,
reg_lambda=self.reg_lambda,
seed=self.seed)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pre= clf.predict(X_test)
y_pro= clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1]
print "pred_leaf=T AUC Score : %f" % metrics.roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pro)
print"pred_leaf=T Accuracy : %.4g" % metrics.accuracy_score(y_test, y_pre)
new_feature= clf.apply(X_train)
X_train_new=self.mergeToOne(X_train,new_feature)
new_feature_test= clf.apply(X_test)
X_test_new=self.mergeToOne(X_test,new_feature_test)
print "Training set sample number remains the same"
return X_train_new,y_train,X_test_new,y_test
4. 模板
4.1 GBDT + LR 模板
from scipy.sparse.construct import hstack
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets.svmlight_format import load_svmlight_file
from sklearn.ensemble.gradient_boosting import GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model.logistic import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics.ranking import roc_auc_score
from sklearn.preprocessing.data import OneHotEncoder
import numpy as np
def gbdt_lr_train(libsvmFileName):
# load样本数据
X_all, y_all = load_svmlight_file(libsvmFileName)
# 训练/测试数据分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_all, y_all, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 42)
# 定义GBDT模型
gbdt = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=40, max_depth=3, verbose=0,max_features=0.5)
# 训练学习
gbdt.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_gbdt = gbdt.predict_proba(X_test.toarray())[:, 1]
gbdt_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_gbdt)
print('gbdt auc: %.5f' % gbdt_auc)
# lr对原始特征样本模型训练
lr = LogisticRegression()
lr.fit(X_train, y_train) # 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_test = lr.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
lr_test_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test)
print('基于原有特征的LR AUC: %.5f' % lr_test_auc)
# GBDT编码原有特征
X_train_leaves = gbdt.apply(X_train)[:,:,0]
X_test_leaves = gbdt.apply(X_test)[:,:,0]
# 对所有特征进行ont-hot编码
(train_rows, cols) = X_train_leaves.shape
gbdtenc = OneHotEncoder()
X_trans = gbdtenc.fit_transform(np.concatenate((X_train_leaves, X_test_leaves), axis=0))
# 定义LR模型
lr = LogisticRegression()
# lr对gbdt特征编码后的样本模型训练
lr.fit(X_trans[:train_rows, :], y_train)
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_gbdtlr1 = lr.predict_proba(X_trans[train_rows:, :])[:, 1]
gbdt_lr_auc1 = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_gbdtlr1)
print('基于GBDT特征编码后的LR AUC: %.5f' % gbdt_lr_auc1)
# 定义LR模型
lr = LogisticRegression(n_jobs=-1)
# 组合特征
X_train_ext = hstack([X_trans[:train_rows, :], X_train])
X_test_ext = hstack([X_trans[train_rows:, :], X_test])
print(X_train_ext.shape)
# lr对组合特征的样本模型训练
lr.fit(X_train_ext, y_train)
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_gbdtlr2 = lr.predict_proba(X_test_ext)[:, 1]
gbdt_lr_auc2 = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_gbdtlr2)
print('基于组合特征的LR AUC: %.5f' % gbdt_lr_auc2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
gbdt_lr_train('data/sample_libsvm_data.txt')
4.2 XGBoost + LR 模板
#!/usr/bin python
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.datasets import load_svmlight_file
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve, auc, roc_auc_score
from sklearn.externals import joblib
import numpy as np
from scipy.sparse import hstack
def xgb_feature_encode(libsvmFileNameInitial):
# load样本数据
X_all, y_all = load_svmlight_file(libsvmFileNameInitial)
# 训练/测试数据分割
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_all, y_all, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 42)
# 定义模型
xgboost = xgb.XGBClassifier(nthread=4, learning_rate=0.08,
n_estimators=50, max_depth=5, gamma=0, subsample=0.9, colsample_bytree=0.5)
# 训练学习
xgboost.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_test = xgboost.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
xgb_test_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test)
print('xgboost test auc: %.5f' % xgb_test_auc)
# xgboost编码原有特征
X_train_leaves = xgboost.apply(X_train)
X_test_leaves = xgboost.apply(X_test)
# 训练样本个数
train_rows = X_train_leaves.shape[0]
# 合并编码后的训练数据和测试数据
X_leaves = np.concatenate((X_train_leaves, X_test_leaves), axis=0)
X_leaves = X_leaves.astype(np.int32)
(rows, cols) = X_leaves.shape
# 记录每棵树的编码区间
cum_count = np.zeros((1, cols), dtype=np.int32)
for j in range(cols):
if j == 0:
cum_count[0][j] = len(np.unique(X_leaves[:, j]))
else:
cum_count[0][j] = len(np.unique(X_leaves[:, j])) + cum_count[0][j-1]
print('Transform features genenrated by xgboost...')
# 对所有特征进行ont-hot编码
for j in range(cols):
keyMapDict = {}
if j == 0:
initial_index = 1
else:
initial_index = cum_count[0][j-1]+1
for i in range(rows):
if X_leaves[i, j] not in keyMapDict:
keyMapDict[X_leaves[i, j]] = initial_index
X_leaves[i, j] = initial_index
initial_index = initial_index + 1
else:
X_leaves[i, j] = keyMapDict[X_leaves[i, j]]
# 基于编码后的特征,将特征处理为libsvm格式且写入文件
print('Write xgboost learned features to file ...')
xgbFeatureLibsvm = open('data/xgb_feature_libsvm', 'w')
for i in range(rows):
if i < train_rows:
xgbFeatureLibsvm.write(str(y_train[i]))
else:
xgbFeatureLibsvm.write(str(y_test[i-train_rows]))
for j in range(cols):
xgbFeatureLibsvm.write(' '+str(X_leaves[i, j])+':1.0')
xgbFeatureLibsvm.write('\n')
xgbFeatureLibsvm.close()
def xgboost_lr_train(xgbfeaturefile, origin_libsvm_file):
# load xgboost特征编码后的样本数据
X_xg_all, y_xg_all = load_svmlight_file(xgbfeaturefile)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_xg_all, y_xg_all, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 42)
# load 原始样本数据
X_all, y_all = load_svmlight_file(origin_libsvm_file)
X_train_origin, X_test_origin, y_train_origin, y_test_origin = train_test_split(X_all, y_all, test_size = 0.3, random_state = 42)
# lr对原始特征样本模型训练
lr = LogisticRegression(n_jobs=-1, C=0.1, penalty='l1')
lr.fit(X_train_origin, y_train_origin)
joblib.dump(lr, 'model/lr_orgin.m')
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_test = lr.predict_proba(X_test_origin)[:, 1]
lr_test_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test_origin, y_pred_test)
print('基于原有特征的LR AUC: %.5f' % lr_test_auc)
# lr对load xgboost特征编码后的样本模型训练
lr = LogisticRegression(n_jobs=-1, C=0.1, penalty='l1')
lr.fit(X_train, y_train)
joblib.dump(lr, 'model/lr_xgb.m')
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_test = lr.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
lr_test_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test)
print('基于Xgboost特征编码后的LR AUC: %.5f' % lr_test_auc)
# 基于原始特征组合xgboost编码后的特征
X_train_ext = hstack([X_train_origin, X_train])
del(X_train)
del(X_train_origin)
X_test_ext = hstack([X_test_origin, X_test])
del(X_test)
del(X_test_origin)
# lr对组合后的新特征的样本进行模型训练
lr = LogisticRegression(n_jobs=-1, C=0.1, penalty='l1')
lr.fit(X_train_ext, y_train)
joblib.dump(lr, 'model/lr_ext.m')
# 预测及AUC评测
y_pred_test = lr.predict_proba(X_test_ext)[:, 1]
lr_test_auc = roc_auc_score(y_test, y_pred_test)
print('基于组合特征的LR AUC: %.5f' % lr_test_auc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
xgb_feature_encode("data/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
xgboost_lr_train("data/xgb_feature_libsvm","data/sample_libsvm_data.txt")
5. 参考文献
- GBDT原理及利用GBDT构造新的特征-Python实现
- sklearn.ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier
- XGBoost Plotting API以及GBDT组合特征实践
- 利用GBDT模型构造新特征
- python机器学习案例系列教程——GBDT构建新特征