tensorflow训练验证码识别模型
tensorflow训练验证码识别模型的样本可以使用captcha生成,captcha在linux中的安装也很简单:
pip install captcha
生成验证码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from captcha.image import ImageCaptcha # pip install captcha
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import random
import cv2
import os
# 验证码中的字符
number = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
# alphabet = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u',
# 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z']
# ALPHABET = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U',
# 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z']
# 验证码长度为4个字符
def random_captcha_text(char_set=number, captcha_size=4):
captcha_text = []
for i in range(captcha_size):
c = random.choice(char_set)
captcha_text.append(c)
return captcha_text
# 生成字符对应的验证码
def gen_captcha_text_and_image():
image = ImageCaptcha()
captcha_text = random_captcha_text()
captcha_text = ''.join(captcha_text)
captcha = image.generate(captcha_text)
captcha_image = Image.open(captcha)
captcha_image = np.array(captcha_image)
return captcha_text, captcha_image
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 训练集和测试集数量
train_num = 10000
valid_num = 3000
#保存路径
path_train = './trainImage'
path_valid = './validImage'
if not os.path.exists(path_train):
os.mkdir(path_train)
if not os.path.exists(path_valid):
os.mkdir(path_valid)
for i in range(train_num):
text, image = gen_captcha_text_and_image()
fullPath = os.path.join(path_train, text + ".jpg")
cv2.imwrite(fullPath, image)
print "Creating train data: {0}/{1}".format(i,train_num)
for i in range(valid_num):
text, image = gen_captcha_text_and_image()
fullPath = os.path.join(path_valid, text + ".jpg")
cv2.imwrite(fullPath, image)
print "Creating valid data: {0}/{1}".format(i, valid_num)
print "Done!"
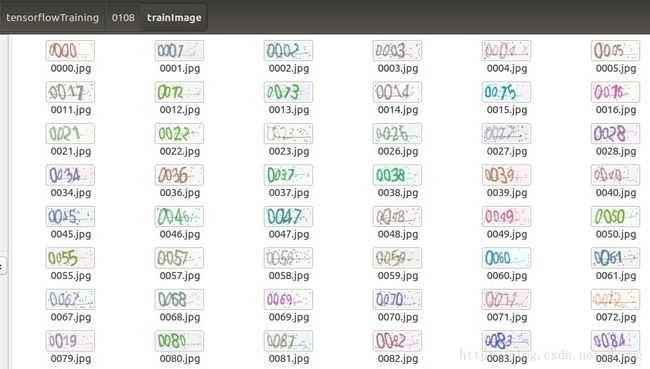
分别生成训练样本和测试样本,生成的样本图片如下:
使用tensorflow执行训练:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import os
import random
import time
# number
number = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
# 图像大小
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 60 # 80
IMAGE_WIDTH = 160 # 160
MAX_CAPTCHA = 4
char_set = number
CHAR_SET_LEN = len(char_set) #
image_filename_list = []
total = 0
train_path = './trainImage'
valid_path = './trainImage'
def get_image_file_name(imgFilePath):
fileName = []
total = 0
for filePath in os.listdir(imgFilePath):
captcha_name = filePath.split('/')[-1]
fileName.append(captcha_name)
total += 1
random.seed(time.time())
# 打乱顺序
random.shuffle(fileName)
return fileName, total
# 获取训练数据的名称列表
image_filename_list, total = get_image_file_name(train_path)
# 获取测试数据的名称列表
image_filename_list_valid, total = get_image_file_name(valid_path)
# 读取图片和标签
def gen_captcha_text_and_image(imageFilePath, image_filename_list, imageAmount):
num = random.randint(0, imageAmount - 1)
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(imageFilePath, image_filename_list[num]), 0)
img = cv2.resize(img, (160, 60))
img = np.float32(img)
text = image_filename_list[num].split('.')[0]
return text, img
# 文本转向量
# 例如,如果验证码是 ‘0296’ ,则对应的标签是
# [1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
# 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
# 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
def name2label(name):
label = np.zeros(MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN)
for i, c in enumerate(name):
idx = i * CHAR_SET_LEN + ord(c) - ord('0')
label[idx] = 1
return label
# label to name
def label2name(digitalStr):
digitalList = []
for c in digitalStr:
digitalList.append(ord(c) - ord('0'))
return np.array(digitalList)
# 文本转向量
def text2vec(text):
text_len = len(text)
if text_len > MAX_CAPTCHA:
raise ValueError('验证码最长4个字符')
vector = np.zeros(MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN)
def char2pos(c):
if c == '_':
k = 62
return k
k = ord(c) - 48
if k > 9:
k = ord(c) - 55
if k > 35:
k = ord(c) - 61
if k > 61:
raise ValueError('No Map')
return k
for i, c in enumerate(text):
idx = i * CHAR_SET_LEN + char2pos(c)
vector[idx] = 1
return vector
# 向量转回文本
def vec2text(vec):
char_pos = vec.nonzero()[0]
text = []
for i, c in enumerate(char_pos):
char_at_pos = i # c/63
char_idx = c % CHAR_SET_LEN
if char_idx < 10:
char_code = char_idx + ord('0')
elif char_idx < 36:
char_code = char_idx - 10 + ord('A')
elif char_idx < 62:
char_code = char_idx - 36 + ord('a')
elif char_idx == 62:
char_code = ord('_')
else:
raise ValueError('error')
text.append(chr(char_code))
return "".join(text)
# 生成一个训练batch
def get_next_batch(imageFilePath, image_filename_list=None, batch_size=128):
batch_x = np.zeros([batch_size, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
batch_y = np.zeros([batch_size, MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN])
def wrap_gen_captcha_text_and_image(imageFilePath, imageAmount):
while True:
text, image = gen_captcha_text_and_image(imageFilePath, image_filename_list, imageAmount)
if image.shape == (60, 160):
return text, image
for listNum in os.walk(imageFilePath):
pass
imageAmount = len(listNum[2])
for i in range(batch_size):
text, image = wrap_gen_captcha_text_and_image(imageFilePath, imageAmount)
batch_x[i, :] = image.flatten() / 255 # (image.flatten()-128)/128 mean为0
batch_y[i, :] = text2vec(text)
return batch_x, batch_y
####################################################################
# 占位符,X和Y分别是输入训练数据和其标签,标签转换成8*10的向量
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN])
# 声明dropout占位符变量
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # dropout
# 定义CNN
def crack_captcha_cnn(w_alpha=0.01, b_alpha=0.1):
# 把 X reshape 成 IMAGE_HEIGHT*IMAGE_WIDTH*1的格式,输入的是灰度图片,所有通道数是1;
# shape 里的-1表示数量不定,根据实际情况获取,这里为每轮迭代输入的图像数量(batchsize)的大小;
x = tf.reshape(X, shape=[-1, IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, 1])
# 搭建第一层卷积层
# shape[3, 3, 1, 32]里前两个参数表示卷积核尺寸大小,即patch;
# 第三个参数是图像通道数,第四个参数是该层卷积核的数量,有多少个卷积核就会输出多少个卷积特征图像
w_c1 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 32]))
# 每个卷积核都配置一个偏置量,该层有多少个输出,就应该配置多少个偏置量
b_c1 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([32]))
# 图片和卷积核卷积,并加上偏执量,卷积结果28x28x32
# tf.nn.conv2d() 函数实现卷积操作
# tf.nn.conv2d()中的padding用于设置卷积操作对边缘像素的处理方式,在tf中有VALID和SAME两种模式
# padding='SAME'会对图像边缘补0,完成图像上所有像素(特别是边缘象素)的卷积操作
# padding='VALID'会直接丢弃掉图像边缘上不够卷积的像素
# strides:卷积时在图像每一维的步长,是一个一维的向量,长度4,并且strides[0]=strides[3]=1
# tf.nn.bias_add() 函数的作用是将偏置项b_c1加到卷积结果value上去;
# 注意这里的偏置项b_c1必须是一维的,并且数量一定要与卷积结果value最后一维数量相同
# tf.nn.relu() 函数是relu激活函数,实现输出结果的非线性转换,即features=max(features, 0),输出tensor的形状和输入一致
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(x, w_c1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c1))
# tf.nn.max_pool()函数实现最大池化操作,进一步提取图像的抽象特征,并且降低特征维度
# ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1]定义最大池化操作的核尺寸为2*2, 池化结果14x14x32 卷积结果乘以池化卷积核
conv1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# tf.nn.dropout是tf里为了防止或减轻过拟合而使用的函数,一般用在全连接层;
# Dropout机制就是在不同的训练过程中根据一定概率(大小可以设置,一般情况下训练推荐0.5)随机扔掉(屏蔽)一部分神经元,
# 不参与本次神经网络迭代的计算(优化)过程,权重保留但不做更新;
# tf.nn.dropout()中 keep_prob用于设置概率,需要是一个占位变量,在执行的时候具体给定数值
conv1 = tf.nn.dropout(conv1, keep_prob)
# 原图像HEIGHT = 60 WIDTH = 160,经过神经网络第一层卷积(图像尺寸不变、特征×32)、池化(图像尺寸缩小一半,特征不变)之后;
# 输出大小为 30*80*32
# 搭建第二层卷积层
w_c2 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 32, 64]))
b_c2 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(conv1, w_c2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c2))
conv2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv2 = tf.nn.dropout(conv2, keep_prob)
# 原图像HEIGHT = 60 WIDTH = 160,经过神经网络第一层后输出大小为 30*80*32
# 经过神经网络第二层运算后输出为 16*40*64 (30*80的图像经过2*2的卷积核池化,padding为SAME,输出维度是16*40)
# 搭建第三层卷积层
w_c3 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 64]))
b_c3 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([64]))
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(conv2, w_c3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c3))
conv3 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv3 = tf.nn.dropout(conv3, keep_prob)
# 原图像HEIGHT = 60 WIDTH = 160,经过神经网络第一层后输出大小为 30*80*32 经过第二层后输出为 16*40*64
# 经过神经网络第二层运算后输出为 16*40*64 ; 经过第三层输出为 8*20*64,这个参数很重要,决定量后边全连接层的维度
# 搭建全连接层
# 二维张量,第一个参数8*20*64的patch,这个参数由最后一层卷积层的输出决定,第二个参数代表卷积个数共1024个,即输出为1024个特征
w_d = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([8 * 20 * 64, 1024]))
# 偏置项为1维,个数跟卷积核个数保持一致
b_d = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([1024]))
# w_d.get_shape()作用是把张量w_d的形状转换为元组tuple的形式,w_d.get_shape().as_list()是把w_d转为元组再转为list形式
# w_d 的 形状是[ 8 * 20 * 64, 1024],w_d.get_shape().as_list()结果为 8*20*64=10240 ;
# 所以tf.reshape(conv3, [-1, w_d.get_shape().as_list()[0]])的作用是把最后一层隐藏层的输出转换成一维的形式
dense = tf.reshape(conv3, [-1, w_d.get_shape().as_list()[0]])
# tf.matmul(dense, w_d)函数是矩阵相乘,输出维度是 -1*1024
dense = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(dense, w_d), b_d))
dense = tf.nn.dropout(dense, keep_prob)
# 经过全连接层之后,输出为 一维,1024个向量
# w_out定义成一个形状为 [1024, 8 * 10] = [1024, 80]
w_out = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([1024, MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN]))
b_out = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN]))
# out 的输出为 8*10 的向量, 8代表识别结果的位数,10是每一位上可能的结果(0到9)
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(dense, w_out), b_out)
# out = tf.nn.softmax(out)
# 输出神经网络在当前参数下的预测值
return out
# 训练
def train_crack_captcha_cnn():
output = crack_captcha_cnn()
# loss
# loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(output, Y))
# tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits()函数计算交叉熵,输出的是一个向量而不是数;
# 交叉熵刻画的是实际输出(概率)与期望输出(概率)的距离,也就是交叉熵的值越小,两个概率分布就越接近
# tf.reduce_mean()函数求矩阵的均值
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=output, labels=Y))
# optimizer 为了加快训练 learning_rate应该开始大,然后慢慢减小
# tf.train.AdamOptimizer()函数实现了Adam算法的优化器
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.001).minimize(loss)
predict = tf.reshape(output, [-1, MAX_CAPTCHA, CHAR_SET_LEN])
max_idx_p = tf.argmax(predict, 2)
max_idx_l = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(Y, [-1, MAX_CAPTCHA, CHAR_SET_LEN]), 2)
correct_pred = tf.equal(max_idx_p, max_idx_l)
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
step = 0
while True:
batch_x, batch_y = get_next_batch(train_path, image_filename_list, 64)
_, loss_ = sess.run([optimizer, loss], feed_dict={X: batch_x, Y: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.75})
print(step, loss_)
# 每100 step计算一次准确率
if step % 100 == 0:
batch_x_test, batch_y_test = get_next_batch(valid_path, image_filename_list_valid, 128)
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={X: batch_x_test, Y: batch_y_test, keep_prob: 1.})
print(step, acc)
# 训练结束条件
if acc > 0.98 or step > 6000:
saver.save(sess, "./model/crack_capcha.model", global_step=step)
break
step += 1
def predict_captcha(captcha_image):
output = crack_captcha_cnn()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('.'))
predict = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(output, [-1, MAX_CAPTCHA, CHAR_SET_LEN]), 2)
text_list = sess.run(predict, feed_dict={X: [captcha_image], keep_prob: 1})
text = text_list[0].tolist()
vector = np.zeros(MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN)
i = 0
for n in text:
vector[i * CHAR_SET_LEN + n] = 1
i += 1
return vec2text(vector)
# 执行训练
train_crack_captcha_cnn()
print "训练完成,请开始测试…"
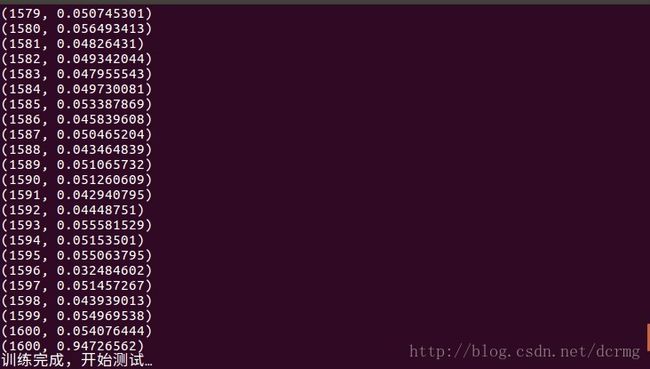
大约执行1600轮迭代(batchsize=128)之后训练完成:
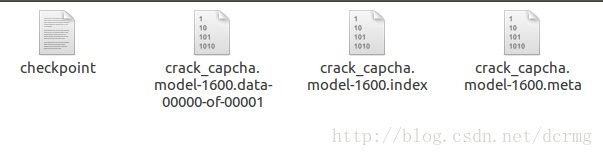
训练结果在model文件夹下生成4个文件:
测试单张验证码图片:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import os
import random
import time
import sys
number = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
# 图像大小
IMAGE_HEIGHT = 60
IMAGE_WIDTH = 160
MAX_CAPTCHA = 4
char_set = number
CHAR_SET_LEN = len(char_set)
model_path = './model/'
image_path = './validImage'
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, IMAGE_HEIGHT * IMAGE_WIDTH])
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN])
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) # dropout
# 定义CNN
def crack_captcha_cnn(w_alpha=0.01, b_alpha=0.1):
x = tf.reshape(X, shape=[-1, IMAGE_HEIGHT, IMAGE_WIDTH, 1])
# 3 conv layer
w_c1 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 1, 32]))
b_c1 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([32]))
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(x, w_c1, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c1))
conv1 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv1 = tf.nn.dropout(conv1, keep_prob)
w_c2 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 32, 64]))
b_c2 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([64]))
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(conv1, w_c2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c2))
conv2 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv2 = tf.nn.dropout(conv2, keep_prob)
w_c3 = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([3, 3, 64, 64]))
b_c3 = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([64]))
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(tf.nn.conv2d(conv2, w_c3, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME'), b_c3))
conv3 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv3, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv3 = tf.nn.dropout(conv3, keep_prob)
# Fully connected layer
w_d = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([8 * 20 * 64, 1024]))
b_d = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([1024]))
dense = tf.reshape(conv3, [-1, w_d.get_shape().as_list()[0]])
dense = tf.nn.relu(tf.add(tf.matmul(dense, w_d), b_d))
dense = tf.nn.dropout(dense, keep_prob)
w_out = tf.Variable(w_alpha * tf.random_normal([1024, MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN]))
b_out = tf.Variable(b_alpha * tf.random_normal([MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN]))
out = tf.add(tf.matmul(dense, w_out), b_out)
# out = tf.nn.softmax(out)
return out
# 向量转回文本
def vec2text(vec):
char_pos = vec.nonzero()[0]
text = []
for i, c in enumerate(char_pos):
char_at_pos = i # c/63
char_idx = c % CHAR_SET_LEN
if char_idx < 10:
char_code = char_idx + ord('0')
elif char_idx < 36:
char_code = char_idx - 10 + ord('A')
elif char_idx < 62:
char_code = char_idx - 36 + ord('a')
elif char_idx == 62:
char_code = ord('_')
else:
raise ValueError('error')
text.append(chr(char_code))
return "".join(text)
def predict_captcha(captcha_image):
output = crack_captcha_cnn()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint(model_path))
predict = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(output, [-1, MAX_CAPTCHA, CHAR_SET_LEN]), 2)
text_list = sess.run(predict, feed_dict={X: [captcha_image], keep_prob: 1})
text = text_list[0].tolist()
vector = np.zeros(MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN)
i = 0
for n in text:
vector[i * CHAR_SET_LEN + n] = 1
i += 1
return vec2text(vector)
if not os.path.exists(image_path):
print('Image does not exist, please check!, path:"{}"'.format(os.path.abspath(image_path)))
sys.exit()
image_list = os.listdir(image_path)
output = crack_captcha_cnn()
saver = tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint(model_path))
predict = tf.argmax(tf.reshape(output, [-1, MAX_CAPTCHA, CHAR_SET_LEN]), 2)
for image_ in image_list:
text_ = image_.split('.')[0]
image_p = os.path.join(image_path, image_)
# 单张图片预测
image = np.float32(cv2.imread(image_p, 0))
image = image.flatten() / 255
text_list = sess.run(predict, feed_dict={X: [image], keep_prob: 1})
text = text_list[0].tolist()
vector = np.zeros(MAX_CAPTCHA * CHAR_SET_LEN)
i = 0
for n in text:
vector[i * CHAR_SET_LEN + n] = 1
i += 1
predict_text= vec2text(vector)
print("真实值: {0} 预测值: {1}".format(text_, predict_text))
time.sleep(1)
由于captcha生成的验证码条件相对单一,使用训练出来的模型即便只有0.94的精度也比人工识别的精度要高了。预测结果正确:
识别过程中加载测试图片注意进行精度转换(np.float32())。
这里可以下载训练好的模型文件: http://download.csdn.net/download/dcrmg/10195217