sklearn:梯度提升正则化
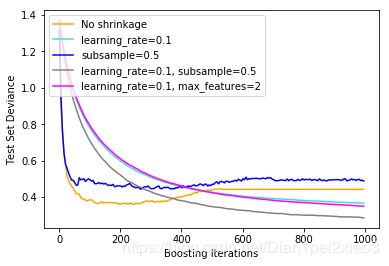
不同正则化策略对梯度提升效果的说明。 该示例取自Hastie等人2009。
使用的损失函数是二项式偏差。 通过收缩的规则化(learning_rate <1.0)可以显着提高性能。 与收缩相结合,随机梯度增强(子样本<1.0)可以通过减少包装的方差来产生更准确的模型。 没有收缩的子采样通常效果不佳。 减少方差的另一种策略是通过对随机森林中的随机分割类似的特征进行二次采样(通过max_features参数)。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import ensemble
from sklearn import datasets
X, y = datasets.make_hastie_10_2(n_samples=12000, random_state=1)
X = X.astype(np.float32)
# map labels from {-1, 1} to {0, 1}
labels, y = np.unique(y, return_inverse=True)
X_train, X_test = X[:2000], X[2000:]
y_train, y_test = y[:2000], y[2000:]
original_params = {'n_estimators': 1000, 'max_leaf_nodes': 4, 'max_depth': None, 'random_state': 2,
'min_samples_split': 5}
plt.figure()
for label, color, setting in [('No shrinkage', 'orange',
{'learning_rate': 1.0, 'subsample': 1.0}),
('learning_rate=0.1', 'turquoise',
{'learning_rate': 0.1, 'subsample': 1.0}),
('subsample=0.5', 'blue',
{'learning_rate': 1.0, 'subsample': 0.5}),
('learning_rate=0.1, subsample=0.5', 'gray',
{'learning_rate': 0.1, 'subsample': 0.5}),
('learning_rate=0.1, max_features=2', 'magenta',
{'learning_rate': 0.1, 'max_features': 2})]:
params = dict(original_params)
params.update(setting)
clf = ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier(**params)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# compute test set deviance
test_deviance = np.zeros((params['n_estimators'],), dtype=np.float64)
for i, y_pred in enumerate(clf.staged_decision_function(X_test)):
# clf.loss_ assumes that y_test[i] in {0, 1}
test_deviance[i] = clf.loss_(y_test, y_pred)
plt.plot((np.arange(test_deviance.shape[0]) + 1)[::5], test_deviance[::5],
'-', color=color, label=label)
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.xlabel('Boosting Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Test Set Deviance')
plt.show()