LeakCanary检测内存泄漏,BlockCanary优化代码结构
今天和大家分享的是第三方的框架,可以用来检测应用内存泄漏和代码阻塞相关问题,接下来我们就进入正题吧。
(1)LeakCanary的使用
详细了解在GitHub上LeakCanary
/*内存泄漏检测*/
debugCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android:1.5.1'
releaseCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.5.1'
testCompile 'com.squareup.leakcanary:leakcanary-android-no-op:1.5.1'//Application中引用
LeakCanary.install(this);调用单例,两种引用都会导致内存泄露,第一种是Context引用泄露,第二种是子控件引用泄露,避免方式是在onDestroy中,清除引用。
我们来模拟一个内存泄漏的实例。
public class LeakSingle {
private Context mContext;
private TextView mTextView;
private static LeakSingle sInstance;
private LeakSingle(Context context) {
mContext = context;
}
public static LeakSingle getInstance(Context context) {
if (sInstance == null) {
sInstance = new LeakSingle(context);
}
return sInstance;
}
// 内存泄露
public void setRetainedTextView(TextView tv) {
mTextView = tv;
mTextView.setText(mContext.getString(R.string.app_name));
}
// 删除引用, 防止泄露
public void removeRetainedTextView() {
mTextView = null;
}
}public class LeakBlockActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView text;
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.leakblock_activity);
text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.text);
//(1)Context引用泄露
//LeakSingle.getInstance(this).setRetainedTextView(text);
//(2)子控件引用泄露
LeakSingle.getInstance(this.getApplication()).setRetainedTextView(text);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
//(3)清楚TextView引用
LeakSingle.getInstance(this.getApplication()).removeRetainedTextView();
}
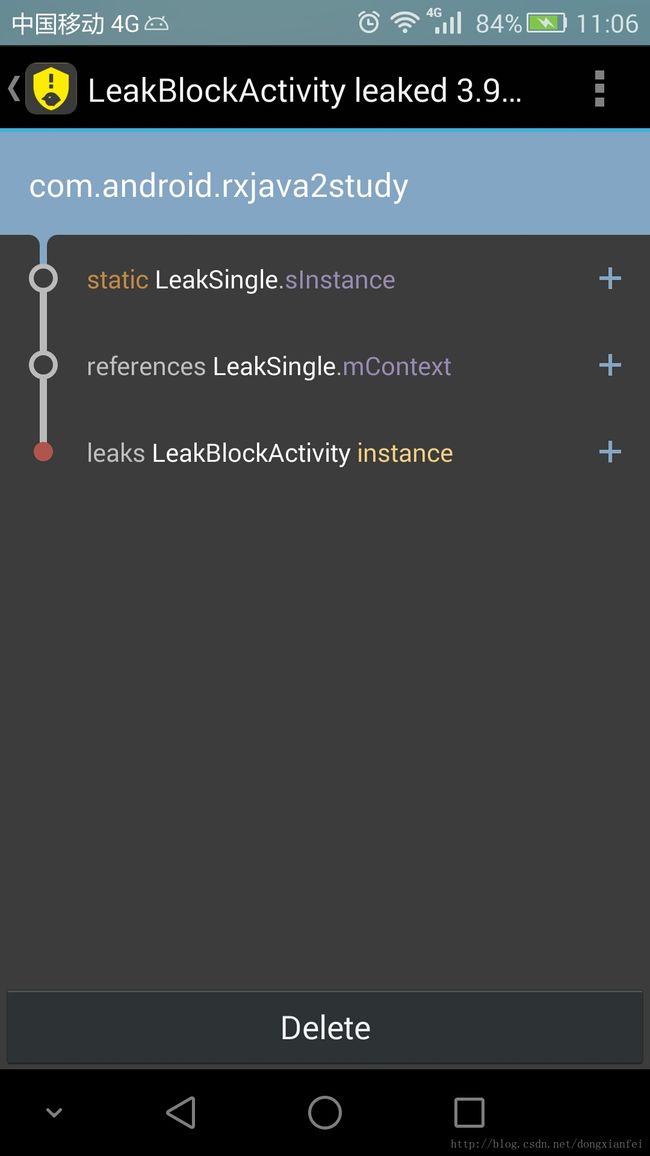
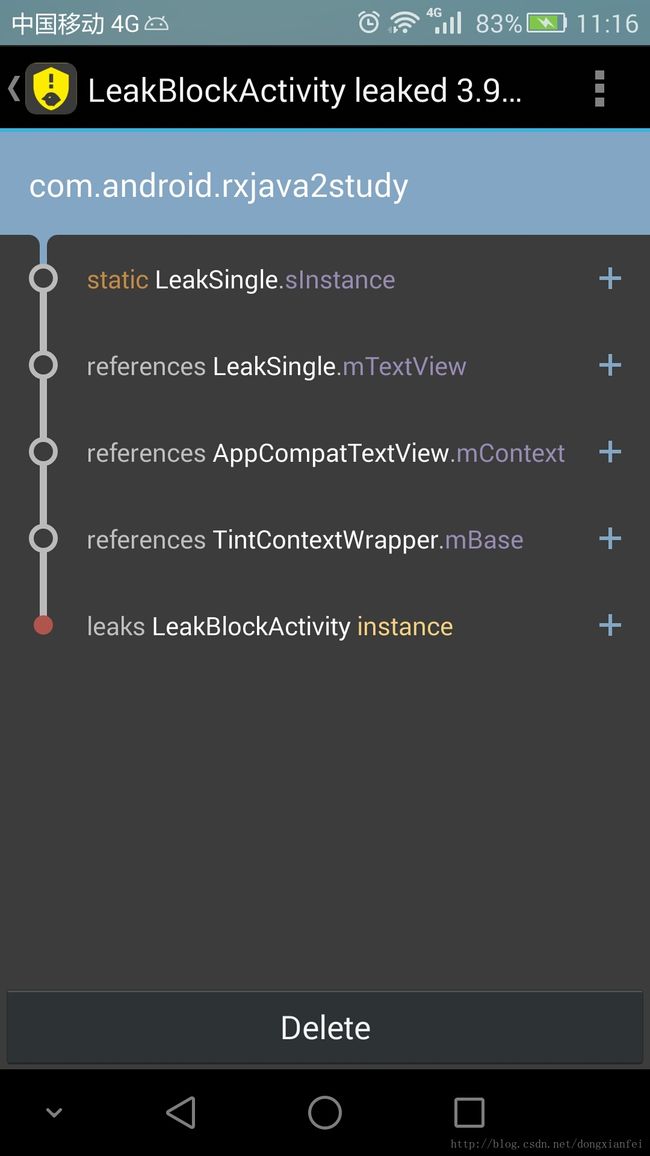
}我们看一下每种内存泄漏方式的提示:
LeakCanary的内存泄露提示一般会包含三个部分:
第一部分(LeakSingle类的sInstance变量)引用第二部分(LeakSingle类的mContext变量), 导致第三部分(LeakBlockActivity类的实例instance)泄露。
一般泄漏产生的主要原因:
生命周期较长的类使用Activity的Context,导致Activity被引用,无法被及时回收。除了需要Activity页面支持的控件类,如Dialog等, 其他全部使用应用的Context替换Activity的Context, 即Context.getApplicationContext()。还有就是单例不要持有页面的控件, 单例持有控件, 控件附属页面, 最终页面得不到释放, 单例可以使用回调修改页面, 内部仅仅保留处理数据部分。
(2)BlockCanary优化代码
详细了解在GitHub上BlockCanary
/*应用卡顿检测*/
debugCompile 'com.github.markzhai:blockcanary-android:1.5.0'
releaseCompile 'com.github.markzhai:blockcanary-no-op:1.5.0'//Application中配置
BlockCanary.install(this, new AppBlockCanaryContext()).start();blockCanary的配置需要自定义一个类继承BlockCanaryContext,并重写其部分方法来配置。
public class AppBlockCanaryContext extends BlockCanaryContext {
@Override
public String provideQualifier() {
return "com.android.rxjava2study";
}
@Override
public String provideNetworkType() {
return "Wifi";
}
@Override
public int provideBlockThreshold() {
return 500;
}
@Override
public String providePath() {
return "/blockcanary/log";
}
}接下来我们模拟一个阻塞的代码。
public class LeakBlockActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.leakblock_activity);
//卡顿
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
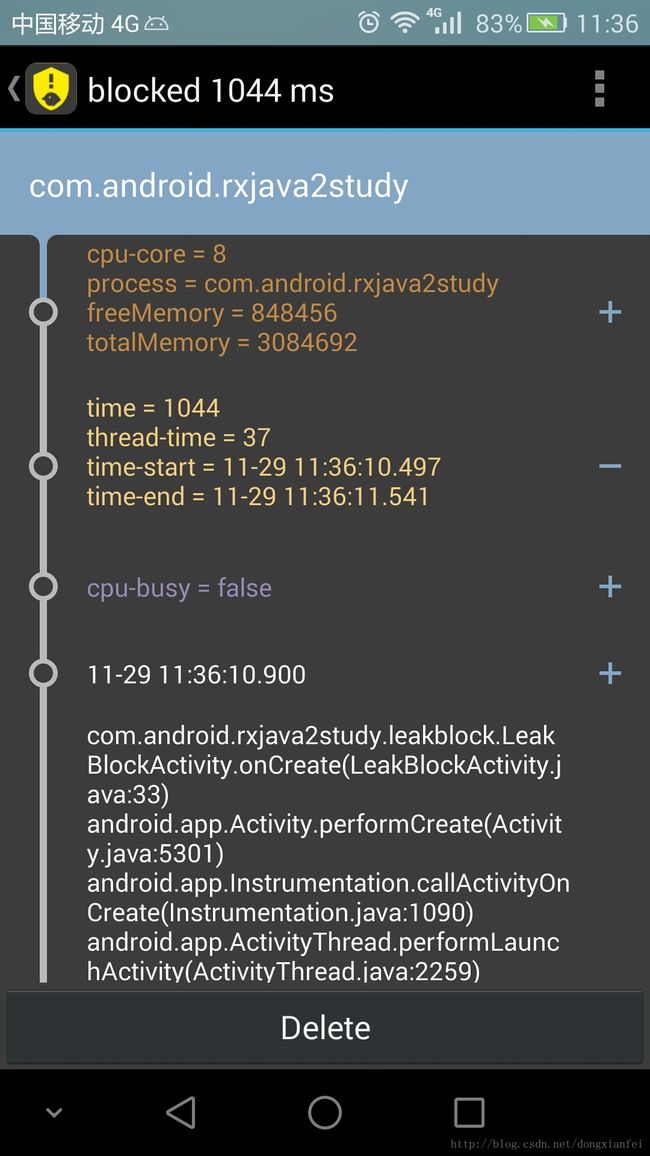
}看一下系统提示的卡顿结果。
系统准确的定位到Thread.sleep(1000);这句代码这里。
好啦,大家可以将其添加到自己的项目中试试吧。