Python刷题--Tree(最大深度/叶节点数/非叶节点数/第K层节点数/平衡二叉树/完全二叉树/镜像树/LCA公共祖先/BFS/DFS/二叉堆/堆排序/递归,非递归实现前序中序后序遍历)
堆排序小灰
堆排序
# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*-
import collections
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = None
self.right = None
def maxDepth(root):
if root is None:
return 0
left = maxDepth(root.left)
right = maxDepth(root.right)
return max(left, right) + 1
def minDepth(root):
if root is None:
return 0
leftDepth = minDepth(root.left)
rightDepth = minDepth(root.right)
if root.left is None or root.right is None:
return max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1
return min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1
def numOfTreeNode(root):
if root is None:
return 0
left = numOfTreeNode(root.left)
right = numOfTreeNode(root.right)
return left + right + 1
def numsOfNoChildNode(root):
if root is None:
return 0
if (root.left is None and root.right is None):
return 1
return numsOfNoChildNode(root.left) + numsOfNoChildNode(root.right)
def numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root, k):
if root is None or k < 1:
return 0
if k == 1:
return 1
numsLeft = numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root.left, k - 1)
numsRight = numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root.right, k - 1)
return numsLeft + numsRight
def isBalanced(root):
return maxDeath2(root) != -1
def maxDeath2(root):
if root is None:
return 0
left = maxDeath2(root.left)
right = maxDeath2(root.right)
if (left == -1 or right == -1 or abs(left - right) > 1):
return -1
return max(left, right) + 1
def isCompleteTreeNode(root):
if root is None:
return False
queue = collections.deque()
queue.append(root)
result = True
hasNoChild = False
while (queue):
current = queue.popleft()
if (hasNoChild):
if (current.left != None or current.right != None):
result = False
break
else:
if (current.left != None and current.right != None):
queue.append(current.left)
queue.append(current.right)
elif (current.left != None and current.right == None):
queue.append(current.left)
hasNoChild = True
elif (current.left == None and current.right != None):
result = False
break
else:
hasNoChild = True
return result
def isSameTreeNode(t1, t2):
if (t1 is None and t2 is None):
return True
elif (t1 is None or t2 is None):
return False
if (t1.val != t2.val):
return False
left = isSameTreeNode(t1.left, t2.left)
right = isSameTreeNode(t1.right, t2.right)
return left and right
def mirrorTreeNode(root):
if root is None:
return 0
left = mirrorTreeNode(root.left)
right = mirrorTreeNode(root.right)
root.left = right
root.right = left
return root
# def getLastCommonParent(root, t1, t2):
# if (findNode(root.left, t1)):
# if (findNode(root.right, t2)):
# return root
# else:
# return getLastCommonParent(root.left, t1, t2)
# else:
# if (findNode(root.left, t2)):
# return root
# else:
# return getLastCommonParent(root.right, t1, t2)
#
#
# def findNode(root, node):
# if (root is None or node is None):
# return False
# if (root == node):
# return True
# found = findNode(root.left, node)
# if (not found):
# found = findNode(root.right, node)
# return found
"""
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
_______6______
/ \
___2__ ___8__
/ \ / \
0 _4 7 9
/ \
3 5
For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes 2 and 8 is 6. Another example is LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
"""
"""注意这里是一个二叉搜索树,根结点的右子树上所有的点的值都比根结点大,左子树上所有点的值都比根结点的值小
因此分为四种情况,
1、如果两个节点一个值比节点大,一个小,那么二者的公共节点肯定是根结点,
2、如果两个节点中有一个与根结点的值同样大,那么二者的公共节点同样是根结点
3、如果两个节点的值都比根结点小,那么二者的公共节点出现在根结点的左子树中,递归查询
4、如果两个节点的值都比根结点大,那么二者的公共节点出现在根结点的右子树中,递归查询
"""
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if (p.val - root.val) * (q.val - root.val) <= 0:
return root
if p.val < root.val and q.val < root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
if p.val > root.val and q.val > root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)
# 广度优先遍历算法
def level_queue(root):
if root is None:
return
my_queue = collections.deque()
node = root
my_queue.append(node)
while my_queue:
node = my_queue.popleft()
print(node.val)
if node.left is not None:
my_queue.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
my_queue.append(node.right)
# 深度优先遍历算法
def depth_tree(tree_node):
if tree_node is not None:
print(tree_node.val)
if tree_node.left is not None:
depth_tree(tree_node.left)
if tree_node.right is not None:
depth_tree(tree_node.right)
"""
二叉堆本质上是一种完全二叉树,它分为两个类型:
1.最大堆
2.最小堆
对于二叉堆,如下有几种操作:
1.插入节点
2.删除节点
3.构建二叉堆 : 本质上就是让所有非叶子节点依次下沉。
1
/ \
3 2
/ \ / \
6 5 7 8
/\
9 10
==> 1 3 2 6 5 7 8 9 10
假设父节点的下标是parent,那么它的左孩子下标就是 2*parent+1;它的右孩子下标就是 2*parent+2 。
举例 小根堆:
"""
def unAdjust(array):
childIndex = len(array) - 1
parentIndex = childIndex / 2
temp = array[childIndex]
while (childIndex > 0 and temp < array[parentIndex]):
array[childIndex] = array[parentIndex]
childIndex = parentIndex
parentIndex = parentIndex / 2
array[parentIndex] = temp
def downAdjust(array, parentIndex, length):
temp = array[parentIndex]
childIndex = 2 * parentIndex + 1
while (childIndex < length):
if childIndex + 1 < length and array[childIndex + 1] < array[childIndex]:
childIndex += 1
if temp <= array[childIndex]:
break
array[parentIndex] = array[childIndex]
parentIndex = childIndex
childIndex = 2 * childIndex + 1
array[parentIndex] = temp
def buildHeap(array):
for i in range(len(array) / 2)[::-1]:
downAdjust(array, i, len(array))
"""
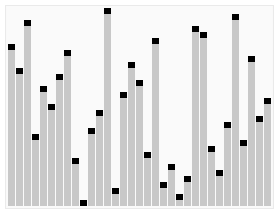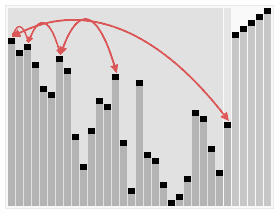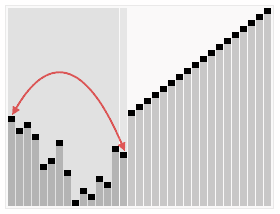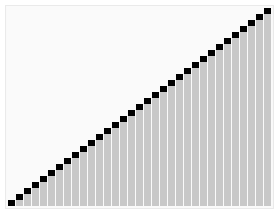
堆排序算法的步骤:
1. 把无序数组构建成二叉堆。
2. 循环删除堆顶元素,移到集合尾部,调节堆产生新的堆顶。
大根堆
"""
def downAdjustBig(array, parentIndex, length):
temp = array[parentIndex]
childIndex = 2 * parentIndex + 1
while (childIndex < length):
if childIndex + 1 < length and array[childIndex + 1] > array[childIndex]:
childIndex += 1
if temp >= array[childIndex]:
break
array[parentIndex] = array[childIndex]
parentIndex = childIndex
childIndex = 2 * childIndex + 1
array[parentIndex] = temp
def heapSort(array):
# 1.构建二叉堆
for i in range(len(array) / 2)[::-1]:
downAdjustBig(array, i, len(array))
print(array)
# 2.循环删除堆顶元素,移到集合尾部,调节堆产生新的堆顶
for i in range(len(array))[::-1]:
temp = array[i]
array[i] = array[0]
array[0] = temp
downAdjustBig(array, 0, i)
def inorderTraversal_recur(root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root:
return []
return inorderTraversal_recur(root.left) + [root.val] + inorderTraversal_recur(root.right)
def preorderTraversal_recur(root): ##前序遍历
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root:
return []
return [root.val] + preorderTraversal_recur(root.left) + preorderTraversal_recur(root.right)
def postorderTraversal_recur(root): ##后序遍历
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[int]
"""
if not root:
return []
return postorderTraversal_recur(root.left) + postorderTraversal_recur(root.right) + [root.val]
"""
当前结点curr不为None时,每一次循环将当前结点curr入栈;
当前结点curr为None时,则出栈一个结点,且打印出栈结点的value值。
整个循环在stack和curr皆为None的时候结束。"""
def inorderTraversal(self, root):
stack = []
sol = []
curr = root
while stack or curr:
if curr:
stack.append(curr)
curr = curr.left
else:
curr = stack.pop()
sol.append(curr.val)
curr = curr.right
return sol
"""
由于前序遍历的顺序是中左右,所以我们每次先打印当前结点curr,并将右子结点push到栈中,然后将左子结点设为当前结点。
入栈和出栈条件(当前结点curr不为None时,每一次循环将当前结点curr入栈;
当前结点curr为None时,则出栈一个结点)以及循环结束条件
(整个循环在stack和curr皆为None的时候结束)与中序遍历一模一样。
"""
def preorderTraversal(self, root): ## 前序遍历
stack = []
sol = []
curr = root
while stack or curr:
if curr:
sol.append(curr.val)
stack.append(curr.right)
curr = curr.left
else:
curr = stack.pop()
return sol
"""
代码的主体部分基本就是.right和.left交换了顺序,
且后序遍历在最后输出的时候进行了反向(因为要从 中右左 变为 左右中 )
"""
def postorderTraversal(self, root): ## 后序遍历
stack = []
sol = []
curr = root
while stack or curr:
if curr:
sol.append(curr.val)
stack.append(curr.left)
curr = curr.right
else:
curr = stack.pop()
return sol[::-1]
# 前序 中序 构建树
def getTreePreMid(pre, mid):
if len(pre) == 0:
return None
if len(pre) == 1:
return TreeNode(pre[0])
root = TreeNode(pre[0])
root_index = mid.index(pre[0])
root.left = getTreePreMid(pre[1:root_index + 1], mid[:root_index])
root.right = getTreePreMid(pre[root_index + 1:], mid[root_index + 1:])
return root
# 前序 中序 构建后序
def getAfterFromPreMid(pre, mid, res):
if len(pre) == 0:
return
if len(pre) == 1:
res.append(pre[0])
return
root = pre[0]
root_index = mid.index(root)
getAfterFromPreMid(pre[1:root_index + 1], mid[:root_index], res)
getAfterFromPreMid(pre[root_index + 1:], mid[root_index + 1:], res)
res.append(root)
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
"""
0
/ \
1 3
/ \
4 5
/ \
6
/ \
8 7
"""
root = TreeNode(0)
a = TreeNode(1)
b = TreeNode(3)
c = TreeNode(4)
d = TreeNode(5)
e = TreeNode(6)
f = TreeNode(7)
g = TreeNode(8)
root.left = a
root.right = b
a.left = c
a.right = d
c.left = e
e.right = f
e.left = g
# print maxDepth(root)
# print minDepth(root)
# print(numOfTreeNode(root))
# print(numsOfNoChildNode(root))
# print(numsOfkLevelTreeNode(root, 4))
# print(isBalanced(root))
# print(maxDeath2(root))
# print(isCompleteTreeNode(c))
# print getLastCommonParent(root, a, b)
print("##" * 20)
# level_queue(root)
# print depth_tree(root)
array = [7, 1, 3, 10, 5, 2, 8, 9, 6]
buildHeap(array)
print(array)
print("##" * 20)
arr = [1, 3, 2, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0]
heapSort(arr)
print(arr)
print("--" * 20)
res = inorderTraversal(root)
print(res)