SSD的学习笔记
Intuition
对于一个feature map(例如 38×38 )应用 3×3 的卷积层生成与feature map同等大小( 38×38 )的结果。对于一个这样的卷积层,输出结果是与之匹配的default boxes的Location的offset(xmin或xmax或ymin或ymax)或者是某个类别的confidence(21个类别)。
feature maps是多尺度的。
没有region proposal产生的过程,Single Shot = Single Network。
摘要
Our approach, named SSD, discretizes the output space of bounding boxes into a set of default boxes over different aspect ratios and scales per feature map location.
把bounding boxes离散化成每个特征图上拥有不同长宽比或不同尺度的原始boxes。
特点:
网络对每个原始boxes中是否存在某个类别的物体进行打分的同时,对每个default boxes进行调整,使得其更好地match物体的形状。
同时进行分类和回归?是的,offsets是一个回归的问题,类别一直都是一个分类问题。对于yolo和ssd直接利用一个网络判断物体分类和位置,而不再像Rcnn家族训练分别训练一个分类器和一个bounding boxes的回归器。
可以handle一张图片中有不同尺寸物体的问题。
依旧需要resize图片,使用warp的方法。固定输入的size是 300×300
resize-mode:P.Resize.WARP(需要resize的原因:虽然没有全连接层,但是为了最后判断的时候输出固定。)
不需要生成proposal和随后的降采样过程针对RCNN,整个步骤整合为一个网络。是提高速度的原因
速度:
For 300×300 input, SSD achieves 69.8% mAP on VOC2007 test at 24 FPS on a GTX 980.
GTX980 | mAP |FPS|Video Memory |Batch Size
介绍
强调eliminating bounding box proposals and the subsequent pixel or feature resampling stage.
not the first one to do this work 相关:YOLO,OverFeat- 用一个小的卷积模板预测分类和bounding box location offsets的offsets
YOLO用了全连接层 - 实现多尺度的检测:在一个feature map上使用一组filters完成不同长宽比的检测,并且将这些filters应用到后来多级网络得到的不同的feature maps上。
这些使得输入一个低分辨率的图片就可以得到高准确率的检测结果。–>加速啊!
- 用一个小的卷积模板预测分类和bounding box location offsets的offsets
一句总结core:predicting category scores and box offsets for a fixed set of default bounding boxes using small convolutional filters applied to feature maps.
再强调一遍:In order to achieve high detection accuracy we produce predictions of different scales from feature maps of different scales, and explicitly separate predictions by aspect ratio.
主体部分
Framework
SSD是基于一个前馈的卷积网络,网络的输入是固定大小的图片,输出是固定大小的张量。张量中包括bounding boxes和在这些boxes中存在某个类别物体的可能性。之后再利用non-maximum suppression做最后的检测。
卷积网络结构:截取经典的分类网络,并称之为base work。在base work的基础上加上我们自己auxiliary structure。
截取分类层之前的网络是否有什么技巧?
VGGNetBody(net, from_layer='data', fully_conv=True, reduced=True, dilated=True,
dropout=False, freeze_layers=freeze_layers)
def VGGNetBody(net, from_layer, need_fc=True, fully_conv=False, reduced=False,
dilated=False, nopool=False, dropout=True, freeze_layers=[]):
kwargs = {
'param': [dict(lr_mult=1, decay_mult=1), dict(lr_mult=2, decay_mult=0)],
'weight_filler': dict(type='xavier'),
'bias_filler': dict(type='constant', value=0)}
assert from_layer in net.keys()
net.conv1_1 = L.Convolution(net[from_layer], num_output=64, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu1_1 = L.ReLU(net.conv1_1, in_place=True)
net.conv1_2 = L.Convolution(net.relu1_1, num_output=64, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu1_2 = L.ReLU(net.conv1_2, in_place=True)
if nopool:
name = 'conv1_3'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu1_2, num_output=64, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool1'
net.pool1 = L.Pooling(net.relu1_2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
net.conv2_1 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=128, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu2_1 = L.ReLU(net.conv2_1, in_place=True)
net.conv2_2 = L.Convolution(net.relu2_1, num_output=128, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu2_2 = L.ReLU(net.conv2_2, in_place=True)
if nopool:
name = 'conv2_3'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu2_2, num_output=128, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool2'
net[name] = L.Pooling(net.relu2_2, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
net.conv3_1 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=256, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu3_1 = L.ReLU(net.conv3_1, in_place=True)
net.conv3_2 = L.Convolution(net.relu3_1, num_output=256, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu3_2 = L.ReLU(net.conv3_2, in_place=True)
net.conv3_3 = L.Convolution(net.relu3_2, num_output=256, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu3_3 = L.ReLU(net.conv3_3, in_place=True)
if nopool:
name = 'conv3_4'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu3_3, num_output=256, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool3'
net[name] = L.Pooling(net.relu3_3, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
net.conv4_1 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu4_1 = L.ReLU(net.conv4_1, in_place=True)
net.conv4_2 = L.Convolution(net.relu4_1, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu4_2 = L.ReLU(net.conv4_2, in_place=True)
net.conv4_3 = L.Convolution(net.relu4_2, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu4_3 = L.ReLU(net.conv4_3, in_place=True)
if nopool:
name = 'conv4_4'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu4_3, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool4'
net[name] = L.Pooling(net.relu4_3, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
net.conv5_1 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu5_1 = L.ReLU(net.conv5_1, in_place=True)
net.conv5_2 = L.Convolution(net.relu5_1, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu5_2 = L.ReLU(net.conv5_2, in_place=True)
net.conv5_3 = L.Convolution(net.relu5_2, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, **kwargs)
net.relu5_3 = L.ReLU(net.conv5_3, in_place=True)
if need_fc:
if dilated:
if nopool:
name = 'conv5_4'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu5_3, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool5'
net[name] = L.Pooling(net.relu5_3, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
else:
if nopool:
name = 'conv5_4'
net[name] = L.Convolution(net.relu5_3, num_output=512, pad=1, kernel_size=3, stride=2, **kwargs)
else:
name = 'pool5'
net[name] = L.Pooling(net.relu5_3, pool=P.Pooling.MAX, kernel_size=2, stride=2)
if fully_conv:
if dilated:
if reduced:
net.fc6 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=1024, pad=6, kernel_size=3, dilation=6, **kwargs)
else:
net.fc6 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=4096, pad=6, kernel_size=7, dilation=2, **kwargs)
else:
if reduced:
net.fc6 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=1024, pad=3, kernel_size=3, dilation=3, **kwargs)
else:
net.fc6 = L.Convolution(net[name], num_output=4096, pad=3, kernel_size=7, **kwargs)
net.relu6 = L.ReLU(net.fc6, in_place=True)
if dropout:
net.drop6 = L.Dropout(net.relu6, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
if reduced:
net.fc7 = L.Convolution(net.relu6, num_output=1024, kernel_size=1, **kwargs)
else:
net.fc7 = L.Convolution(net.relu6, num_output=4096, kernel_size=1, **kwargs)
net.relu7 = L.ReLU(net.fc7, in_place=True)
if dropout:
net.drop7 = L.Dropout(net.relu7, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
else:
net.fc6 = L.InnerProduct(net.pool5, num_output=4096)
net.relu6 = L.ReLU(net.fc6, in_place=True)
if dropout:
net.drop6 = L.Dropout(net.relu6, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
net.fc7 = L.InnerProduct(net.relu6, num_output=4096)
net.relu7 = L.ReLU(net.fc7, in_place=True)
if dropout:
net.drop7 = L.Dropout(net.relu7, dropout_ratio=0.5, in_place=True)
# Update freeze layers.
kwargs['param'] = [dict(lr_mult=0, decay_mult=0), dict(lr_mult=0, decay_mult=0)]
layers = net.keys()
for freeze_layer in freeze_layers:
if freeze_layer in layers:
net.update(freeze_layer, kwargs)
return netauxiliary stucture
获得多尺度的特征图。卷积特征层被加到了被截断的base network后面,来实现多尺度的检测。每一个特征层上用来预测识别的卷积模型都不一样。【对比:YOLO和Overfeat在一个尺度图上做预测识别】
识别的卷积预测。每一个特征层上都可以利用一组卷积滤波器产生一组确定数目的识别预测。对于每一个特征图( m×n×p ),用( 3×3×p )的kernel,得到对某个类别的评分或者相对default box坐标的shape offset.The bounding box offset output values are measured relative to a default box postion relative to each feature map location.
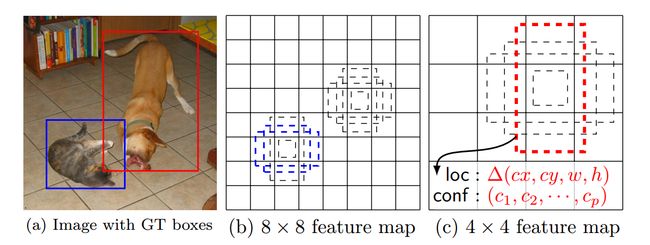
- Default Boxes:在一些不同尺度( 8×8或者4×4 )的特征图的每个位置上,我们给出(估计)一小组(4个)有着不同长宽比的原始boxes,如下图所示。对于每一个原始box,我们预测shape offsets和评估在这个box内中可能有的物体类别。具体来说,对于一个( m×n )大小的特征图,每一个位置上都有k个相应的default boxes,对于每个default box我们需要对c类物体的评估分和4个offsets,所以对于一个特征图需要(c+4)kmn个输出。这与anchor boxes
Faster Rcnn相似。【不一样的部分是SSD用在多尺度上】
Train
- Match default boxes和ground truth boxes。如上图所示。方法paper上很简略,看起来应该跟Faster Rcnn一毛一样。(阈值不同)
RCNN对照笔记
究极版RCNN–Faster Rcnn
1. 实现:
hypothesize bounding boxes->resample pixels or features for each box->apply a high-quality classfier
2. 优缺点:
* 优点:所有分类和检测大赛上的头名【use deep network–ResNetwork】
* 缺点:计算量大,不能实时。【具体数据7FPS-the basic Faster Rcnn】
3. 细节
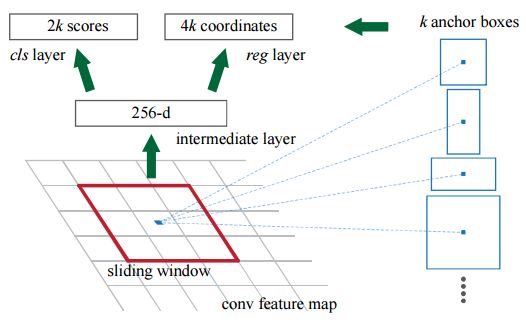 Faster Rcnn 中anchor的实现
Faster Rcnn 中anchor的实现
* anchor【default boxes】The k proposals are parameterized relative to k reference boxes, which we call anchors. An anchor is centered at the sliding window in question, and is associated with a scale and aspect ratio. 一般有三种尺度,三种长宽比。这里的sliding window 用 n×n 的卷积层实现,对于每一个被卷积层作用的卷积特征图( W×H )有 W×H×k 个anchors。
* anchor和计算proposal的方法具有平移不变性。如果一个物体在图像中平移,这个特征也相应的平移,并且相同的方法能够在任意位置预测出这个特征。【对比MultiBox的anchor就没有平移不变性】
* 提供一种多尺度预测的新方法。老方法一:基于图像\特征图的金字塔。老方法二:基于多尺度的sliding window\滤波器金字塔。anchor提供的方法是多尺度的anchor,most cost-efficient。
重大意义在于The design of multiscale anchors is a key component for sharing features without extra cost for addressing scales.
Faster Rcnn的loss function
1. 判断每个anchor中是否有物体。positive label两种情况(1)anchor和ground-truth box有最大的IOU(2)anchor和ground-truth box IOU值大于阈值(0.7) negative label的情况:non-positive anchor跟所有的ground-truth boxes的IOU小于一个阈值(0.3)非正也非负的anchors 不参与training
2. objective function
L(pi,ti)=1Ncls∑iLcls(pi,p∗i)+λ1Nreg∑ip∗iLreg(ti,t∗i)
p∗i=1 anchor为positive的时候。 pi 我们网络计算出来的anchor i中是物体的概率。
Lreg(ti,t∗i)=R(ti,t∗i) R is the robust loss function.
p∗iLreg 只有当anchor是positive的时候( p∗i=1 ),才有值。
bounding box regression
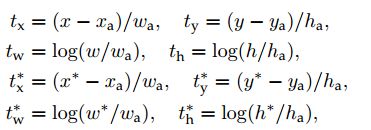
YOLO对照笔记
OverFeat对照笔记
SPP对照笔记
什么是crop和wrap?
Vocabulary
utilize 利用 prevail 盛行
albeit 即使,尽管 high-end 高档
truncate 截断 auxiliary 附加的
be fed into 送入 analogous相似的