https://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2007/09/04/880967.html
IHttpModule
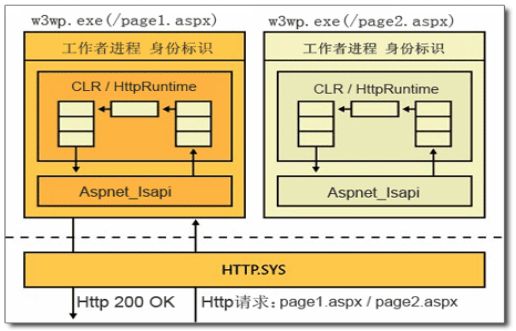
HTTPRuntime(运行时)。在一个控制台程序中,程序的入口是Program中的Main方法。那么,一个网站的入口在哪里呢?在最开始的ashx中,有个ProcessRequest方法,后来在WebForm中,在后台是一个不分类,继承自Page类,在Page_Load方法中去写代码。其实Page类型也有一个ProcessRequest的虚方法。![]()
都是这个ProcessRequest方法来处理请求的。在MVC中也是如此。在MVC中,任何一个Http请求,一定有一个IHttpHandler来处理,在这个接口中,定义了一个ProcessRequest方法。HttpApplication继承自IHttpHandler接口。任何一个Http请求就是一个HttpApplication对象来处理的,然后处理过程固定包含权限认证、缓存处理、Session处理、Cookie出库、生成html、输出客户端,与此同时,千千万万的开发者,又有各种各样的扩展诉求,任何一个环节都有可能扩展,如果是我们来设计,该怎么设计?
其实在MVC框架里面,用到的是观察者模式:
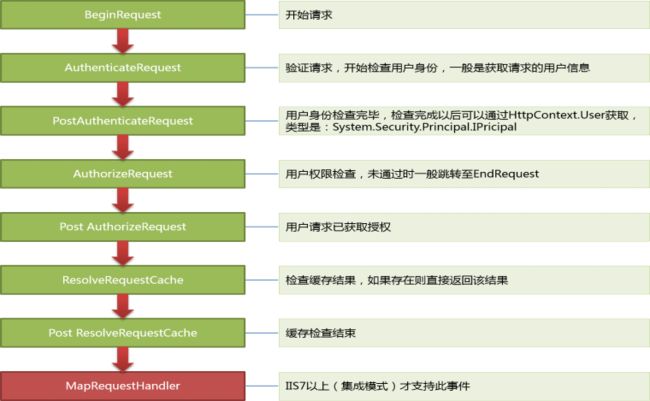
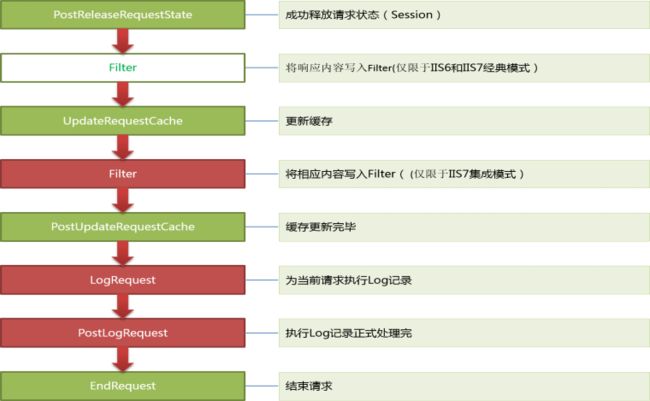
在HttpApplication类型,有这些事件:
// // 摘要: // Occurs just before ASP.NET sends HTTP headers to the client. public event EventHandler PreSendRequestHeaders; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the handler is selected to respond to the request. public event EventHandler MapRequestHandler; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the application is disposed. public event EventHandler Disposed; // // 摘要: // Occurs as the first event in the HTTP pipeline chain of execution when ASP.NET // responds to a request. public event EventHandler BeginRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when a security module has established the identity of the user. public event EventHandler AuthenticateRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when a security module has established the identity of the user. public event EventHandler PostAuthenticateRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when a security module has verified user authorization. public event EventHandler AuthorizeRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the user for the current request has been authorized. public event EventHandler PostAuthorizeRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET finishes an authorization event to let the caching modules // serve requests from the cache, bypassing execution of the event handler (for // example, a page or an XML Web service). public event EventHandler ResolveRequestCache; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET bypasses execution of the current event handler and allows // a caching module to serve a request from the cache. public event EventHandler PostResolveRequestCache; // // 摘要: // Occurs just before ASP.NET sends content to the client. public event EventHandler PreSendRequestContent; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET has mapped the current request to the appropriate event handler. public event EventHandler PostMapRequestHandler; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET has completed processing all the event handlers for the System.Web.HttpApplication.LogRequest // event. public event EventHandler PostLogRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the managed objects that are associated with the request have been // released. public event EventHandler RequestCompleted; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the request state (for example, session state) that is associated // with the current request has been obtained. public event EventHandler PostAcquireRequestState; // // 摘要: // Occurs just before ASP.NET starts executing an event handler (for example, a // page or an XML Web service). public event EventHandler PreRequestHandlerExecute; // // 摘要: // Occurs when the ASP.NET event handler (for example, a page or an XML Web service) // finishes execution. public event EventHandler PostRequestHandlerExecute; // // 摘要: // Occurs after ASP.NET finishes executing all request event handlers. This event // causes state modules to save the current state data. public event EventHandler ReleaseRequestState; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET has completed executing all request event handlers and the // request state data has been stored. public event EventHandler PostReleaseRequestState; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET finishes executing an event handler in order to let caching // modules store responses that will be used to serve subsequent requests from the // cache. public event EventHandler UpdateRequestCache; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET finishes updating caching modules and storing responses that // are used to serve subsequent requests from the cache. public event EventHandler PostUpdateRequestCache; // // 摘要: // Occurs just before ASP.NET performs any logging for the current request. public event EventHandler LogRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when ASP.NET acquires the current state (for example, session state) that // is associated with the current request. public event EventHandler AcquireRequestState; // // 摘要: // Occurs as the last event in the HTTP pipeline chain of execution when ASP.NET // responds to a request. public event EventHandler EndRequest; // // 摘要: // Occurs when an unhandled exception is thrown. public event EventHandler Error;
这里用的是观察者模式,把固定的步骤直接写在handler里面,在步骤前后分别放一个事件,然后开发者可以对事件注册动作,等着请求进来了,然后就可以按照顺讯执行一下。这种设计是不是很完美?但是仍有不完美的地方,就是每个请求都要执行这些事件,太多管闲事了。在.NET Core中出现了中间件,比这种更加完美。后续再详细介绍。
请见下列代码
public class HttpProcessDemo { public class HttpApplicationDemo : IHttpHandler { public bool IsReusable => true; public event Action BeginRequest; public event Action EndRequest; public event Action PreSomething1Handler; public event Action PostSomething1Handler; public event Action PreSomething2Handler; public event Action PostSomething2Handler; public event Action PreSomething3Handler; public event Action PostSomething3Handler; public event Action PreSomething4Handler; public event Action PostSomething4Handler; public event Action PreSomething5Handler; public event Action PostSomething5Handler; public event Action PreSomething6Handler; public event Action PostSomething6Handler; public void ProcessRequest(HttpContext context) { this.BeginRequest?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething1Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 1"); this.PostSomething1Handler?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething2Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 2"); this.PostSomething2Handler?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething3Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 3"); this.PostSomething3Handler?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething4Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 4"); this.PostSomething4Handler?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething5Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 5"); this.PostSomething5Handler?.Invoke(); this.PreSomething6Handler?.Invoke(); Console.WriteLine("Something 6"); this.PostSomething6Handler?.Invoke(); this.EndRequest?.Invoke(); } //任何请求进来,只能是 123456 //事件升级后,可以在程序启动时,实例化HttpApplicationDemo后,可以给事件注册动作,请求再进来时,处理不仅是123456了,还有多个事件里面的动作 }
对HttpApplication里面的事件进行动作注册,就叫IHttpModule。
自定义一个HttpModule+配置文件注册,然后任何一个请求都会执行Init里面注册给Application事件的动作。
public class CustomHttpModule : IHttpModule { public void Dispose() { Console.WriteLine(); } public event EventHandler CustomHttpModuleHandler; ////// 注册动作 /// /// public void Init(HttpApplication application) { application.BeginRequest += (s, e) => { this.CustomHttpModuleHandler?.Invoke(application, null); }; //application.EndRequest += (s, e) => //{ // HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("CustomHttpModule.EndRequest"); //}; #region 为每一个事件,都注册了一个动作,向客户端输出信息 application.AcquireRequestState += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format(" 来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "AcquireRequestState ")); application.AuthenticateRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "AuthenticateRequest ")); application.AuthorizeRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "AuthorizeRequest ")); application.BeginRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "BeginRequest ")); application.Disposed += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "Disposed ")); application.EndRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "EndRequest ")); application.Error += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "Error ")); application.LogRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "LogRequest ")); application.MapRequestHandler += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "MapRequestHandler ")); application.PostAcquireRequestState += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostAcquireRequestState ")); application.PostAuthenticateRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostAuthenticateRequest ")); application.PostAuthorizeRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostAuthorizeRequest ")); application.PostLogRequest += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostLogRequest ")); application.PostMapRequestHandler += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostMapRequestHandler ")); application.PostReleaseRequestState += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostReleaseRequestState ")); application.PostRequestHandlerExecute += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostRequestHandlerExecute ")); application.PostResolveRequestCache += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostResolveRequestCache ")); application.PostUpdateRequestCache += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PostUpdateRequestCache ")); application.PreRequestHandlerExecute += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PreRequestHandlerExecute ")); application.PreSendRequestContent += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PreSendRequestContent ")); application.PreSendRequestHeaders += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "PreSendRequestHeaders ")); application.ReleaseRequestState += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "ReleaseRequestState ")); application.RequestCompleted += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "RequestCompleted ")); application.ResolveRequestCache += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "ResolveRequestCache ")); application.UpdateRequestCache += (s, e) => application.Response.Write(string.Format("来自MyCustomModule 的处理,{0}请求到达 {1}
", DateTime.Now.ToString(), "UpdateRequestCache ")); #endregion } }
访问下页面,就是这样的结果:
正常流程下,会按照顺序执行19个事件。
学完HttpModule,我们可以做点什么有用的扩展?
任何一个请求都会执行HttpModuleInit里面注册给Application的事件
1、日志-性能监控
2、权限
3、缓存
4、页面加点东西
5、请求过滤
6、MVC就是一个Module的扩展
不适合的:不是针对全部请求的,就不太适合用Module,因为有性能损耗
1、多语言,根据Cookie信息去查询不同的数据做不同的展示,如果是全部一套处理,最后HttpModule拦截+处理,适合httpModule
2、跳转到不同界面,也不合适
3、防盗链,针对一类的后缀来处理的,而不是全部请求---判断----再防盗链
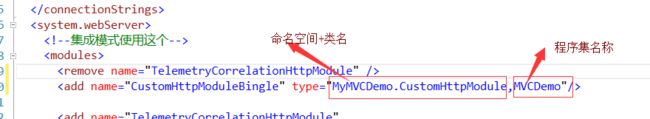
在HttpModule里面发布一个CustomHttpModuleHandler,在Global增加一个动作CustomHttpModuleBingle_CustomHttpModuleHandler(配置文件module名称_module里面事件名称),请求响应时,该事件会执行
protected void CustomHttpModuleBingle_CustomHttpModuleHandler(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.logger.Info("this is CustomHttpModuleBingle_CustomHttpModuleHandler");
}
HttpModule是对HttpApplication的事件动作注册动作,Global是对HttpModule里面的事件注册动作。