配置文件
配置文件yolov3.cfg定义了网络的结构
....
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=64
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=64
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[shortcut]
from=-3
activation=linear
.....配置文件描述了model的结构.
yolov3 layer
yolov3有以下几种结构
- Convolutional
- Shortcut
- Upsample
- Route
- YOLO
Convolutional
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=64
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leakyShortcut
[shortcut]
from=-3
activation=linear 类似于resnet,用以加深网络深度.上述配置的含义是shortcut layer的输出是前一层和前三层的输出的叠加.
resnet skip connection解释详细见https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/28124810
Upsample
[upsample]
stride=2通过双线性插值法将N*N的feature map变为(stride*N) * (stride*N)的feature map.模仿特征金字塔,生成多尺度feature map.加强小目标检测效果.
Route
[route]
layers = -4
[route]
layers = -1, 61以上述配置为例:
当layers只有一个值,代表route layer输出的是router layer - 4那一层layer的feature map.
当layers有2个值时,代表route layer的输出为route layer -1和第61 layer的feature map在深度方向连接起来.(比如说3*3*100,3*3*200add起来变成3*3*300)
yolo
[yolo]
mask = 0,1,2
anchors = 10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326
classes=80
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .5
truth_thresh = 1
random=1yolo层负责预测. anchors是9个anchor,事先聚类得到,表示最有可能的anchor形状.
mask表示哪几组anchor被使用.比如mask=0,1,2代表使用10,13 16,30 30,61这几组anchor. 在原理篇里说过了,每个cell预测3个boudingbox. 三种尺度,总计9种.
Net
[net]
# Testing
batch=1
subdivisions=1
# Training
# batch=64
# subdivisions=16
width= 320
height = 320
channels=3
momentum=0.9
decay=0.0005
angle=0
saturation = 1.5
exposure = 1.5
hue=.1定义了model的输入,batch等等.
现在开始写代码:
解析配置文件
这一步里,做配置文件的解析.把每一块的配置内容存储于一个dict.
def parse_cfg(cfgfile):
"""
Takes a configuration file
Returns a list of blocks. Each blocks describes a block in the neural
network to be built. Block is represented as a dictionary in the list
"""
file = open(cfgfile, 'r')
# store the lines in a list
lines = file.read().split('\n')
# get read of the empty lines
lines = [x for x in lines if len(x) > 0]
lines = [x for x in lines if x[0] != '#'] # get rid of comments
# get rid of fringe whitespaces
lines = [x.rstrip().lstrip() for x in lines]
block = {}
blocks = []
for line in lines:
if line[0] == "[": # This marks the start of a new block
# If block is not empty, implies it is storing values of previous block.
if len(block) != 0:
blocks.append(block) # add it the blocks list
block = {} # re-init the block
block["type"] = line[1:-1].rstrip()
else:
key, value = line.split("=")
block[key.rstrip()] = value.lstrip()
blocks.append(block)
return blocks用pytorch创建各个layer
逐个layer创建.
def create_modules(blocks):
# Captures the information about the input and pre-processing
net_info = blocks[0]
module_list = nn.ModuleList()
prev_filters = 3 #卷积的时候需要知道卷积核的depth.卷积核的size在配置文件里定义了.depeth就是上一层的output的depth.
output_filters = [] #用以保存每一个layer的输出的feature map
#index代表了当前layer位于网络的第几层
for index, x in enumerate(blocks[1:]):
#生成每一个layer
module_list.append(module)
prev_filters = filters
output_filters.append(filters)
return(net_info,module_list) - 卷积层
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=32
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky除了卷积之外实际上还包括了bn和leaky.batchnormalize基本成了标配了现在,用来解决梯度消失的问题(反向传播梯度越乘越小).leaky是激活函数RLU.
所以用到了nn.Sequential()
module = nn.Sequential()
module.add_module("conv_{0}".format(index), conv)
module.add_module("batch_norm_{0}".format(index), bn)
module.add_module("leaky_{0}".format(index), activn)卷积层创建完整代码
涉及到一个python语法enumerate. 就是为一个list中的每个元素添加一个index,形成新的list.
>>>seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
>>> list(enumerate(seasons))
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
>>> list(enumerate(seasons, start=1)) # 下标从 1 开始
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]卷积层创建
#index代表了当前layer位于网络的第几层
for index, x in enumerate(blocks[1:]):
module = nn.Sequential()
#check the type of block
#create a new module for the block
#append to module_list
if (x["type"] == "convolutional"):
#Get the info about the layer
activation = x["activation"]
try:
batch_normalize = int(x["batch_normalize"])
bias = False
except:
batch_normalize = 0
bias = True
filters= int(x["filters"])
padding = int(x["pad"])
kernel_size = int(x["size"])
stride = int(x["stride"])
if padding:
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
else:
pad = 0
#Add the convolutional layer
#prev_filters是上一层输出的feature map的depth.比如上层有64个卷积核,则输出为m*n*64
conv = nn.Conv2d(prev_filters, filters, kernel_size, stride, pad, bias = bias)
module.add_module("conv_{0}".format(index), conv)
#Add the Batch Norm Layer
if batch_normalize:
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(filters)
module.add_module("batch_norm_{0}".format(index), bn)
#Check the activation.
#It is either Linear or a Leaky ReLU for YOLO
if activation == "leaky":
activn = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace = True)
module.add_module("leaky_{0}".format(index), activn)- upsample层
#If it's an upsampling layer
#We use Bilinear2dUpsampling
elif (x["type"] == "upsample"):
stride = int(x["stride"])
upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor = 2, mode = "bilinear")
module.add_module("upsample_{}".format(index), upsample)- route层
[route]
layers = -4
[route]
layers = -1, 61首先是解析配置文件,然后将相应层的feature map 连接起来作为输出
#If it is a route layer
elif (x["type"] == "route"):
x["layers"] = x["layers"].split(',')
#Start of a route
start = int(x["layers"][0])
#end, if there exists one.
try:
end = int(x["layers"][1])
except:
end = 0
#Positive anotation
if start > 0:
start = start - index #start转换成相对于当前layer的偏移
if end > 0:
end = end - index #end转换成相对于当前layer的偏移
route = EmptyLayer()
module.add_module("route_{0}".format(index), route)
if end < 0: #route层concat当前layer前面的某2个layer,所以index>0是无意义的.
filters = output_filters[index + start] + output_filters[index + end]
else:
filters= output_filters[index + start]这里我们自定义了一个EmptyLayer
class EmptyLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EmptyLayer, self).__init__()这里定义EmptyLayer是为了代码的简便起见.在pytorch里定义一个自定义的layer.要写一个类,继承自nn.Module,然后实现forward方法.
关于如何定义一个自定义layer,参见下面的link.
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/examples_nn/two_layer_net_module.html
import torch
class TwoLayerNet(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, D_in, H, D_out):
"""
In the constructor we instantiate two nn.Linear modules and assign them as
member variables.
"""
super(TwoLayerNet, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(D_in, H)
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(H, D_out)
def forward(self, x):
"""
In the forward function we accept a Tensor of input data and we must return
a Tensor of output data. We can use Modules defined in the constructor as
well as arbitrary operators on Tensors.
"""
h_relu = self.linear1(x).clamp(min=0)
y_pred = self.linear2(h_relu)
return y_pred
# N is batch size; D_in is input dimension;
# H is hidden dimension; D_out is output dimension.
N, D_in, H, D_out = 64, 1000, 100, 10
# Create random Tensors to hold inputs and outputs
x = torch.randn(N, D_in)
y = torch.randn(N, D_out)
# Construct our model by instantiating the class defined above
model = TwoLayerNet(D_in, H, D_out)
# Construct our loss function and an Optimizer. The call to model.parameters()
# in the SGD constructor will contain the learnable parameters of the two
# nn.Linear modules which are members of the model.
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='sum')
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
for t in range(500):
# Forward pass: Compute predicted y by passing x to the model
y_pred = model(x)
# Compute and print loss
loss = criterion(y_pred, y)
print(t, loss.item())
# Zero gradients, perform a backward pass, and update the weights.
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
这里由于我们的route layer要做的事情很简单,就是concat两个layer里的feature map,调用torch.cat一行代码的事情,所以没必要定义一个RouteLayer了,直接在代表darknet的nn.Module的forward方法里做concat操作就可以啦.
- shorcut层
#shortcut corresponds to skip connection
elif x["type"] == "shortcut":
shortcut = EmptyLayer()
module.add_module("shortcut_{}".format(index), shortcut)和route层类似,这边也用个EmptyLayer替代.shortcut所做操作即对两个feature map做addition.
- yolo层
yolo层负责根据feature map做预测
首先是解析出有效的anchors.然后用我们自己定义的layer保存这些anchors.然后生成一个module.
涉及到一个python语法super
详细地看:http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-super.html 简单地说就是为了安全地继承.记住怎么用的就行了.没必要深究
#Yolo is the detection layer
elif x["type"] == "yolo":
mask = x["mask"].split(",")
mask = [int(x) for x in mask]
anchors = x["anchors"].split(",")
anchors = [int(a) for a in anchors]
anchors = [(anchors[i], anchors[i+1]) for i in range(0, len(anchors),2)]
anchors = [anchors[i] for i in mask]
detection = DetectionLayer(anchors)
module.add_module("Detection_{}".format(index), detection)
#我们自己定义了一个yolo层
class DetectionLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors):
super(DetectionLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
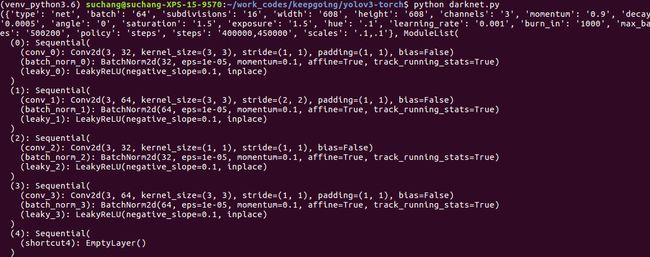
测试代码
blocks = parse_cfg("cfg/yolov3.cfg")
print(create_modules(blocks))完整代码如下:
#coding=utf-8
from __future__ import division
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
def parse_cfg(cfgfile):
"""
Takes a configuration file
Returns a list of blocks. Each blocks describes a block in the neural
network to be built. Block is represented as a dictionary in the list
"""
file = open(cfgfile, 'r')
# store the lines in a list
lines = file.read().split('\n')
# get read of the empty lines
lines = [x for x in lines if len(x) > 0]
lines = [x for x in lines if x[0] != '#'] # get rid of comments
# get rid of fringe whitespaces
lines = [x.rstrip().lstrip() for x in lines]
block = {}
blocks = []
for line in lines:
if line[0] == "[": # This marks the start of a new block
# If block is not empty, implies it is storing values of previous block.
if len(block) != 0:
blocks.append(block) # add it the blocks list
block = {} # re-init the block
block["type"] = line[1:-1].rstrip()
else:
key, value = line.split("=")
block[key.rstrip()] = value.lstrip()
blocks.append(block)
return blocks
class EmptyLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(EmptyLayer, self).__init__()
class DetectionLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, anchors):
super(DetectionLayer, self).__init__()
self.anchors = anchors
def create_modules(blocks):
# Captures the information about the input and pre-processing
net_info = blocks[0]
module_list = nn.ModuleList()
prev_filters = 3
output_filters = []
#index代表了当前layer位于网络的第几层
for index, x in enumerate(blocks[1:]):
module = nn.Sequential()
#check the type of block
#create a new module for the block
#append to module_list
if (x["type"] == "convolutional"):
#Get the info about the layer
activation = x["activation"]
try:
batch_normalize = int(x["batch_normalize"])
bias = False
except:
batch_normalize = 0
bias = True
filters= int(x["filters"])
padding = int(x["pad"])
kernel_size = int(x["size"])
stride = int(x["stride"])
if padding:
pad = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
else:
pad = 0
#Add the convolutional layer
#prev_filters是上一层输出的feature map的depth.比如上层有64个卷积核,则输出为m*n*64
conv = nn.Conv2d(prev_filters, filters, kernel_size, stride, pad, bias = bias)
module.add_module("conv_{0}".format(index), conv)
#Add the Batch Norm Layer
if batch_normalize:
bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(filters)
module.add_module("batch_norm_{0}".format(index), bn)
#Check the activation.
#It is either Linear or a Leaky ReLU for YOLO
if activation == "leaky":
activn = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace = True)
module.add_module("leaky_{0}".format(index), activn)
#If it's an upsampling layer
#We use Bilinear2dUpsampling
elif (x["type"] == "upsample"):
stride = int(x["stride"])
upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor = 2, mode = "bilinear")
module.add_module("upsample_{}".format(index), upsample)
#If it is a route layer
elif (x["type"] == "route"):
x["layers"] = x["layers"].split(',')
#Start of a route
start = int(x["layers"][0])
#end, if there exists one.
try:
end = int(x["layers"][1])
except:
end = 0
#Positive anotation
if start > 0:
start = start - index
if end > 0:
end = end - index
route = EmptyLayer()
module.add_module("route_{0}".format(index), route)
if end < 0:
filters = output_filters[index + start] + output_filters[index + end]
else:
filters= output_filters[index + start]
#shortcut corresponds to skip connection
elif x["type"] == "shortcut":
shortcut = EmptyLayer()
module.add_module("shortcut{}".format(index), shortcut)
#Yolo is the detection layer
elif x["type"] == "yolo":
mask = x["mask"].split(",")
mask = [int(x) for x in mask]
anchors = x["anchors"].split(",")
anchors = [int(a) for a in anchors]
anchors = [(anchors[i], anchors[i+1]) for i in range(0, len(anchors),2)]
anchors = [anchors[i] for i in mask]
detection = DetectionLayer(anchors)
module.add_module("Detection_{}".format(index), detection)
module_list.append(module)
prev_filter = filters
output_filters.append(filters)
return (net_info,module_list)
blocks = parse_cfg("/home/suchang/work_codes/keepgoing/yolov3-torch/cfg/yolov3.cfg")
print(create_modules(blocks))