最新项目中用到了些Material效果,在此对自己的学习做个小结。
首先养成良好的学习习惯-----看源码:
CoordinatorLayout
/**
* CoordinatorLayout is a super-powered {@link android.widget.FrameLayout FrameLayout}.
*
* CoordinatorLayout is intended for two primary use cases:
*
* - As a top-level application decor or chrome layout
* - As a container for a specific interaction with one or more child views
*
*
* By specifying {@link CoordinatorLayout.Behavior Behaviors} for child views of a
* CoordinatorLayout you can provide many different interactions within a single parent and those
* views can also interact with one another. View classes can specify a default behavior when
* used as a child of a CoordinatorLayout using the
* {@link CoordinatorLayout.DefaultBehavior DefaultBehavior} annotation.
*
* Behaviors may be used to implement a variety of interactions and additional layout
* modifications ranging from sliding drawers and panels to swipe-dismissable elements and buttons
* that stick to other elements as they move and animate.
*
* Children of a CoordinatorLayout may have an
* {@link CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams#setAnchorId(int) anchor}. This view id must correspond
* to an arbitrary descendant of the CoordinatorLayout, but it may not be the anchored child itself
* or a descendant of the anchored child. This can be used to place floating views relative to
* other arbitrary content panes.
*/
public class CoordinatorLayout extends ViewGroup implements NestedScrollingParent {
大概的翻译如下:
- CoordinateLayout是一个超级FrameLayout。
- CoordinateLayout原意是用于以下情况:
- 作为顶层布局。
- 作为一个容器,它的子View之间有特殊的相互作用(交互)。
- 通过为CoordinatorLayout的子views指定Behavior,在同一个父容器下可以提供不同的交互,并且那些子view可以和另一个子view相互作用,相互影响。通过@DefaultBehavior注释,CoordinatorLayout的子view可以使用一个默认的behavior。
- Behavior可以用来实现各种交互和 来自滑动抽屉、滑动删除元素和按钮关联其他元素产生的额外的布局修改。
- CoordinatorLayout的子view也许会有个anchor(锚点,即view显示在哪块区域),这个子view必须是CoordinatorLayout的直接子view,不能是孙子辈儿的view - -!
通过看CoordinatorLayout官方注释文档,了解到一个重要信息---Behavior,可以说CoordinatorLayout各种炫酷的交互效果,都是通过Behavior来控制的,除此之外,CoordinatorLayout类似于FrameLayout,那么接下来看重点:
Behavior:
/**
* Interaction behavior plugin for child views of {@link CoordinatorLayout}.
*
* A Behavior implements one or more interactions that a user can take on a child view.
* These interactions may include drags, swipes, flings, or any other gestures.
*
* @param The View type that this Behavior operates on
*/
public static abstract class Behavior {
老规矩:
- CoordinatorLayout的子view的交互行为插件。
- 一个Behavior可以实现一个或更多的交互,用户可以将这些交互用在CoordinatorLayout的子view上,这些交互包括:拖拽、滑动、飞速滑动、或者其他任何手势。
基本使用:
新建一个HelloWorld,选择BasicActivity,可以看到默认生成的布局中已经包含了CoordinatorLayout,说明Goolge官方非常推荐使用这种布局。
官方给出的Behavior实现类有4个:
- BottomSheetBehavior
- SwipeDismissBehavior
- FloatingActionButton中实现的Behavior
- ViewOffsetBehavior
BottomSheetBehavior
一般用于底部弹出框,类似于微信支付的效果,使用方法如下:
xml布局
Activity代码
scrollView = (NestedScrollView) findViewById(R.id.nestedScrollView);
FloatingActionButton fab = (FloatingActionButton) findViewById(R.id.fab);
fab.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
BottomSheetBehavior bottomSheetBehavior = BottomSheetBehavior.from(scrollView);
bottomSheetBehavior.setState(bottomSheetBehavior.getState() == BottomSheetBehavior.STATE_COLLAPSED?BottomSheetBehavior.STATE_EXPANDED:BottomSheetBehavior.STATE_COLLAPSED);
}
});
效果图:
实现的关键点:
- 根布局为 CoordinatorLayout;
- 为底部弹出框设置app:layout_behavior="@string/bottom_sheet_behavior";
- 在代码中得到BottomSheetBehavior,并动态改变它的状态;
- 至于FloatingActionButton跟随弹出框移动,关键点在于为FloatingActionButton设置app:layout_behavior="cn.lxf.behaviortext.FloatingBehavior";这是一个自定义的Behavior,文章后面会有讲解。
SwipeDismissBehavior
官方实现为Snackbar,已经封装好,唯一的条件是根布局必须为CoordinatorLayout,否则没有效果。
使用方式很简单:
Snackbar.make(view, "Replace with your own action", Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG).setAction("Action", null).show();
FloatingActionButton.Behavior
FloatingActionButton默认使用FloatingActionButton.Behavior,同Snackbar一样,唯一需要注意的是根布局必须为CoordinatorLayout。
@CoordinatorLayout.DefaultBehavior(FloatingActionButton.Behavior.class)
public class FloatingActionButton extends VisibilityAwareImageButton {
ViewOffsetBehavior
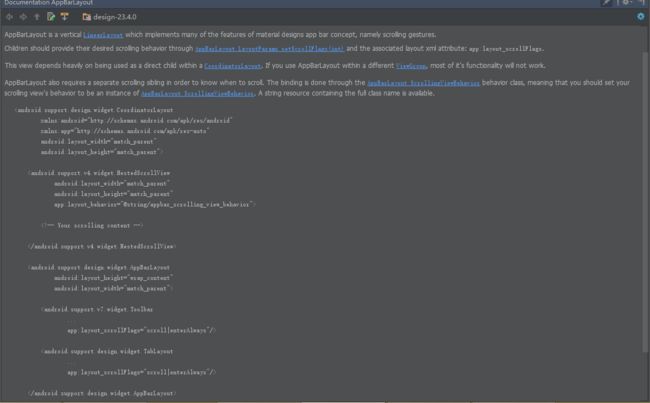
官方实现为AppBarLayout中的Beihavior。
挑重点:
- AppBarLayout是一个实现了很多Material设计风格的垂直的LinearLayout。
- 子view可以通过设置layout_scrollFlags来提供他们所需要的滚动方式。
- 你需要设置你的Scrolling view的behavior(app:layout_behavior)为AppBarLayout.ScrollingViewBehavior来提醒AppBarLayout什么时候滚动。
- 最下面为goolgle官方提供的一个例子。
话说第一次看到layout_scrollFlags属性的萌新必然会一脸懵逼,到底应该填什么呢(因为我当初就是这样...( ╯□╰ )),这里顺便介绍ScrollFlags的几个常量:
/**
* The view will be scroll in direct relation to scroll events. This flag needs to be
* set for any of the other flags to take effect. If any sibling views
* before this one do not have this flag, then this value has no effect.
*/
public static final int SCROLL_FLAG_SCROLL = 0x1;
/**
* When exiting (scrolling off screen) the view will be scrolled until it is
* 'collapsed'. The collapsed height is defined by the view's minimum height.
*
* @see ViewCompat#getMinimumHeight(View)
* @see View#setMinimumHeight(int)
*/
public static final int SCROLL_FLAG_EXIT_UNTIL_COLLAPSED = 0x2;
/**
* When entering (scrolling on screen) the view will scroll on any downwards
* scroll event, regardless of whether the scrolling view is also scrolling. This
* is commonly referred to as the 'quick return' pattern.
*/
public static final int SCROLL_FLAG_ENTER_ALWAYS = 0x4;
/**
* An additional flag for 'enterAlways' which modifies the returning view to
* only initially scroll back to it's collapsed height. Once the scrolling view has
* reached the end of it's scroll range, the remainder of this view will be scrolled
* into view. The collapsed height is defined by the view's minimum height.
*
* @see ViewCompat#getMinimumHeight(View)
* @see View#setMinimumHeight(int)
*/
public static final int SCROLL_FLAG_ENTER_ALWAYS_COLLAPSED = 0x8;
/**
* Upon a scroll ending, if the view is only partially visible then it will be snapped
* and scrolled to it's closest edge. For example, if the view only has it's bottom 25%
* displayed, it will be scrolled off screen completely. Conversely, if it's bottom 75%
* is visible then it will be scrolled fully into view.
*/
public static final int SCROLL_FLAG_SNAP = 0x10;
- SCROLL_FLAG_SCROLL:对应xml布局中的scroll,如果要设置其他的滚动flag,这个flag必须要设置,否则无效。
- SCROLL_FLAG_EXIT_UNTIL_COLLAPSED:对应xml布局中的exitUntilCollapsed,设置该flag的view在向上滑动退出屏幕时,不会完全退出,会保留collapsed height(minHeight)高度。
- SCROLL_FLAG_ENTER_ALWAYS:对应xml布局中的enterAlways,只要手指向下滑,设置该flag的view就会直接进入屏幕,不管NestedScrollView是否在滚动。
- SCROLL_FLAG_ENTER_ALWAYS_COLLAPSED :对应xml布局中的enterAlwaysCollapsed,是enterAlways的附加flag,使设置该flag的view在进入屏幕时最初只滑动显示到它的collapsed height(minHeight),一旦NestedScrollView滑到顶部,该view再滑动显示剩余的部分。
- SCROLL_FLAG_SNAP:对应xml布局中的snap,设置该flag的view在滚动停止时,如果没有完全显示,会自动滚到到最近的一个边界(顶端、中线和下线)。
自定义Behavior
自定义Behavior一般有两种情况:
- 某个view监听另一个view的状态变化,例如大小、位置、显示状态等。
- 某个view监听CoordinatorLayout里的滑动状态。
上面这两句话出自亓斌大神博客,然后我自己在学习过程中做了些实践。
首先看第一种,其实就是上面那个例子,FloatingActionButton怎么跟随自己的布局上下移动?很明显,这个效果类似于系统提供的FloatingActionButton+Snackbar的效果,看一下FloatingActionButton.Behavior源码(只贴了关键部分):
/**
* Determine whether the supplied child view has another specific sibling view as a
* layout dependency.
*
* This method will be called at least once in response to a layout request. If it
* returns true for a given child and dependency view pair, the parent CoordinatorLayout
* will:
*
* - Always lay out this child after the dependent child is laid out, regardless
* of child order.
* - Call {@link #onDependentViewChanged} when the dependency view's layout or
* position changes.
*
*
* @param parent the parent view of the given child
* @param child the child view to test
* @param dependency the proposed dependency of child
* @return true if child's layout depends on the proposed dependency's layout,
* false otherwise
*
* @see #onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout, android.view.View, android.view.View)
*/
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent,
FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
// We're dependent on all SnackbarLayouts (if enabled)
return SNACKBAR_BEHAVIOR_ENABLED && dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout;
}
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
View dependency) {
if (dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout) {
updateFabTranslationForSnackbar(parent, child, dependency);
} else if (dependency instanceof AppBarLayout) {
// If we're depending on an AppBarLayout we will show/hide it automatically
// if the FAB is anchored to the AppBarLayout
updateFabVisibility(parent, (AppBarLayout) dependency, child);
}
return false;
}
- layoutDependsOn(parent,child, dependency):决定一个child是否有一个其他特殊的兄弟view(dependency)作为布局依赖,听来比较拗口,其实就是指一个child是否会根据另一个view的参数和状态而改变。这个方法在初始化布局时最少会被调用一次,如果返回true,则父布局(CoordinatorLayout)会不断的调用onDependentViewChanged(parent,child, dependency)来改变该child的参数和状态。
- 然后系统会在onDependentViewChanged中判断dependency的类型,进而改变Fab的参数、状态。
下面我们来比葫芦画瓢:
public class FloatingBehavior extends FloatingActionButton.Behavior {
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
return super.layoutDependsOn(parent, child, dependency) || dependency instanceof NestedScrollView;
}
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton fab, View dependency) {
if (dependency instanceof NestedScrollView) {
CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams lp = (CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams) fab.getLayoutParams();
int fab_BM = lp.bottomMargin;
int distance = fab.getHeight() + fab_BM;
fab.setY(dependency.getY() - distance);
}
return super.onDependentViewChanged(parent, fab, dependency);
}
}
为Fab设置好改behavior后直接运行,发现报错:Could not inflate Behavior subclass cn.lxf.behaviortext.FloatingBehavior,不能实例化该behavior。一番求证后发现,自定义behavior时必须重写那个带2个参数的构造方法,因为在CoordinatorLayout中是通过反射这个构造方法来实例化behavior的,下面贴完整代码:
public class FloatingBehavior extends FloatingActionButton.Behavior {
public FloatingBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
return super.layoutDependsOn(parent, child, dependency) || dependency instanceof NestedScrollView;
}
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton fab, View dependency) {
if (dependency instanceof NestedScrollView) {
CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams lp = (CoordinatorLayout.LayoutParams) fab.getLayoutParams();
int fab_BM = lp.bottomMargin;
int distance = fab.getHeight() + fab_BM ;
fab.setY(dependency.getY() - distance);
}
return super.onDependentViewChanged(parent, fab, dependency);
}
}
再看第二种情况,某个view监听CoordinateLayout中的滑动状态,这里最好先了解一下android Lollipop版本之后新增的嵌套滑动机制,推荐我学习过的一篇文章https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002873657。
对于监听滑动状态,我们需要关注的总共有以下几个方法(由于篇幅原因,官方注释被我干掉了,加了简单的注解):
/**
* 当一个CoordinatorLayout的子view准备去开始一个嵌套滑动时调用
*
* @param coordinatorLayout 根布局coordinatorLayout
* @param child 这个behavior所关联的coordinatorLayout的子view
* @param directTargetChild 包含target 嵌套滚动操作的coordinatorLayout子view
* @param target 开始嵌套滑动的coordinatorLayout子view。
* @param nestedScrollAxes 嵌套滚动的轴线。See
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL},
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL}
* @return 如果behavior希望接受这个嵌套滚动,则返回true。
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onStartNestedScroll(View, View, int)
*/
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return false;
}
/**
* 当嵌套滑动已经被CoordinatorLayout接受时调用。
*
* 参数同上。
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedScrollAccepted(View, View, int)
*/
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child,
View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* 嵌套滚动结束时调用。
*
* 参数同上。
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onStopNestedScroll(View)
*/
public void onStopNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* target滑动之后调用
*
* @param coordinatorLayout 同上
* @param child 同上
* @param target 同上
* @param dxConsumed 水平方向target滑动的距离(消耗的距离px),左滑大于0,右滑小于0
* @param dyConsumed 垂直方向target滑动的距离(消耗的距离px),上滑大于0,下滑小于0
* @param dxUnconsumed 水平方向target未滑动的距离(但是被用户请求了)
* @param dyUnconsumed 垂直方向target未滑动的距离(但是被用户请求了)
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedScroll(View, int, int, int, int)
*/
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* target准备滑动时(滑动之前)调用
*
* @param coordinatorLayout 同上
* @param child 同上
* @param target 同上
* @param dx 水平方向target想要滑动的距离(用户请求的)
* @param dy 垂直方向target想要滑动的距离(用户请求的)
* @param consumed 需要我们自己传入。 consumed[0] 已经被消费的水平方向滑动的距离, consumed[1] 已经被消费的垂直方向滑动的距离
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreScroll(View, int, int, int[])
*/
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
// Do nothing
}
/**
* target在fling(飞速滚动)之后调用
*
* @param coordinatorLayout 同上
* @param child 同上
* @param target 同上
* @param velocityX 水平方向的速度
* @param velocityY 垂直方向的速度
* @param consumed child是否fling了
* @return behavior是否消费了这个fling
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedFling(View, float, float, boolean)
*/
public boolean onNestedFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed) {
return false;
}
/**
* target在fling(飞速滚动)之前调用
*
* 参数同onNestedFling方法。
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreFling(View, float, float)
*/
public boolean onNestedPreFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
float velocityX, float velocityY) {
return false;
}
还是看上面那个FloatingActionButton的例子,改成上滑消失,下滑显示,代码如下:
public class FloatingBehavior extends FloatingActionButton.Behavior {
private boolean isAniming;
public FloatingBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
}
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, FloatingActionButton child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return nestedScrollAxes == ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL;
}
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, FloatingActionButton child, View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
if (dyConsumed > 0 && !isAniming && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) {
hide(child);
} else if (dyConsumed < 0 && !isAniming && child.getVisibility() == View.INVISIBLE) {
show(child);
}
}
private void show(final View view){
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,1);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float f = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
view.setScaleX(f);
view.setScaleY(f);
}
});
animator.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
isAniming = true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
isAniming = false;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
isAniming = false;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) {
}
});
animator.start();
}
private void hide(final View view){
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1,0);
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float f = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
view.setScaleX(f);
view.setScaleY(f);
}
});
animator.addListener(new Animator.AnimatorListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
isAniming = true;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
view.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
isAniming = false;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
isAniming = false;
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) {
}
});
animator.start();
}
}
效果图:
Demo地址