课程总结
一,类的继承格式
1.在 Java 中通过 extends 关键字可以申明一个类是从另外一个类继承而来的,一般形式如下:
class 父类 {}
class 子类 extends 父类 {}2.可以通过子类扩展父类
3.只允许多层继承,不允许多重继承
二:方法的覆写和重载
覆写:就是指子类中定义了与父类中同名的方法,但是要考虑权限,被子类覆写的方法不能拥有比父类方法更严格的访问权限.
重载:同一个类中相同名称不同参数的方法
四.抽象类的基本概念
1.包含一个抽象方法的类必须是抽象类
2.抽象类和抽象方法都要使用abstract关键声明:
3.抽象方法只需要声明而不需要实现
实验报告
1.已知字符串:"this is a test of java".按要求执行以下操作:(要求源代码、结果截图。)
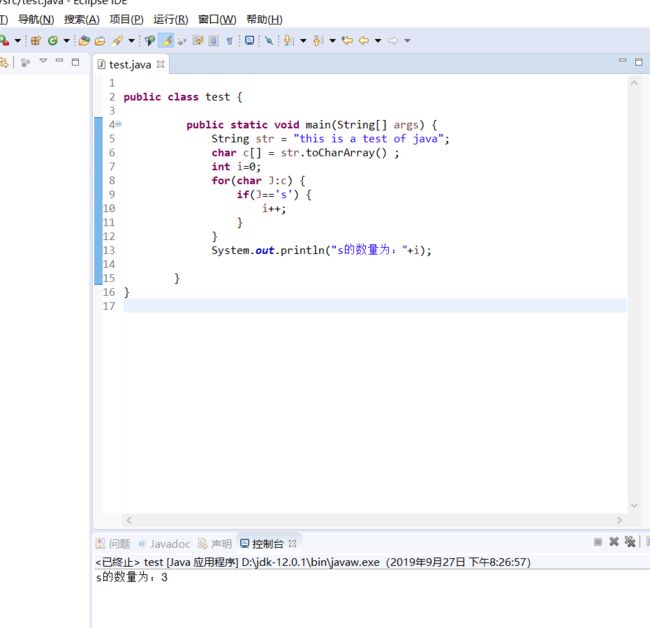
统计该字符串中字母s出现的次数。
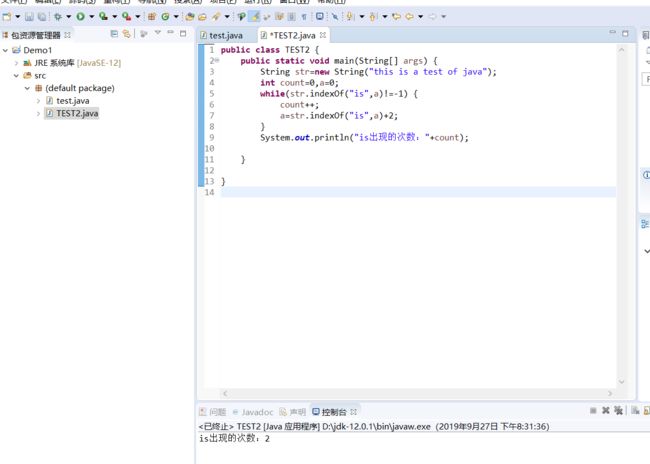
统计该字符串中子串“is”出现的次数。
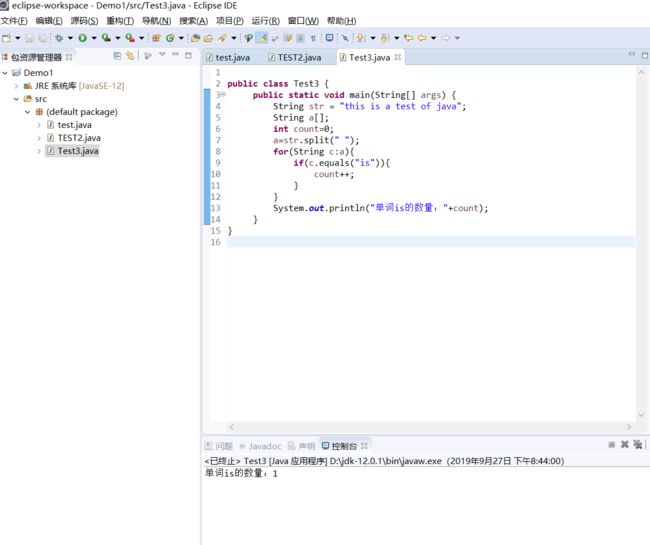
统计该字符串中单词“is”出现的次数。
实现该字符串的倒序输出。
(1)实验代码及截图
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a test of java";
char c[] = str.toCharArray() ;
int i=0;
for(char J:c) {
if(J=='s') {
i++;
}
}
System.out.println("s的数量为:"+i);
}
}public class TEST2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str=new String("this is a test of java");
int count=0,a=0;
while(str.indexOf("is",a)!=-1) {
count++;
a=str.indexOf("is",a)+2;
}
System.out.println("is出现的次数:"+count);
}
}(3)实验代码及截图
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "this is a test of java";
String a[];
int count=0;
a=str.split(" ");
for(String c:a){
if(c.equals("is")){
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("单词is的数量:"+count);
}
}(4)实验代码及截图
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer("this is a test of java");
System.out.println(str.reverse());
}
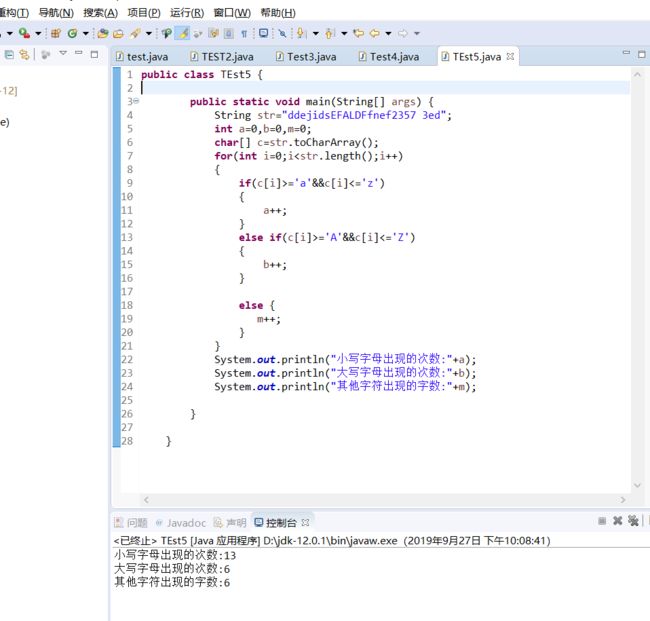
}3.已知字符串“ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed”。输出字符串里的大写字母数,小写英文字母数,非英文字母数。
实验代码及截图
public class TEst5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="ddejidsEFALDFfnef2357 3ed";
int a=0,b=0,m=0;
char[] c=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i='a'&&c[i]<='z')
{
a++;
}
else if(c[i]>='A'&&c[i]<='Z')
{
b++;
}
else {
m++;
}
}
System.out.println("小写字母出现的次数:"+a);
System.out.println("大写字母出现的次数:"+b);
System.out.println("其他字符出现的字数:"+m);
}
} 总结:
1.第二题不太会,第一题老师上课讲过大多数,书上有这些方法,很快就能解决,
2.课后要多看书。