网络是大端
发数据从低地址发, 先发的是 高位的数据。
收数据从高位收,先收到的数据存放到低地址。
TCP 是 流式的 所用套接字也是流式的
文件描述符
socket 是 IP 加 端口号
用到的函数:
int socket(int domain, int type, int protocol); int accept(int sockfd, struct sockaddr *addr, socklen_t *addrlen); #include#include #include int inet_aton(const char *cp, struct in_addr *inp); in_addr_t inet_addr(const char *cp); in_addr_t inet_network(const char *cp); char *inet_ntoa(struct in_addr in); struct in_addr inet_makeaddr(int net, int host); in_addr_t inet_lnaof(struct in_addr in);
查找头文件中的类型定义
grep -ER
练习代码:【服务器 阻塞式的 只能处理一个请求】
/****** * 阻塞式的 * * **********/ #include#include /* See NOTES */ #include #include #include #include //#include #define _PORT_ 9999 #define _BACKLOG_ 10 // 监听端口 队列长度 int main() { int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (sock < 0) { printf("create socket error, error is : %d, errstring is : %s\n", errno, strerror(errno)); return 1; } struct sockaddr_in server_socket; struct sockaddr_in client_socket; bzero(&server_socket, sizeof(server_socket)); server_socket.sin_family = AF_INET; server_socket.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); server_socket.sin_port = htons(_PORT_); if (bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&server_socket, sizeof(struct sockaddr_in)) < 0) { printf("bind error, error code is : %d, errno string is :%s\n", errno, strerror(errno)); close(sock); return 2; } if (listen(sock, _BACKLOG_) < 0) { printf("listen error , errno code is :%d, errno string is :%s\n", errno, strerror(errno)); close(sock); return 3; } printf("bind and listen success, wait accept...\n"); while (1) { socklen_t len = 0; int client_sock = accept(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&client_sock, &len); if (client_sock < 0) { perror("accept"); close(sock); return 4; } char buf[1024]; memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf)); inet_ntop(AF_INET, &client_socket.sin_addr, buf, sizeof(buf)); printf("get connect, ip is :%s port is : %d\n", buf,ntohs(client_socket.sin_port)); while (1) { memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf)); read(client_sock, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); printf("client : %s\n", buf); printf("server :"); memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf)); // fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); // buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0'; write(client_sock, buf, strlen(buf)+1); printf("please wait...\n"); } } close(sock); return 0; }
运行:
查看监听状态
[bozi@localhost ~]$ netstat -nltp (Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.) Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9999 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 10091/./server_1_si tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:60790 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 :::47946 :::* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 :::23 :::* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN - tcp 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN -
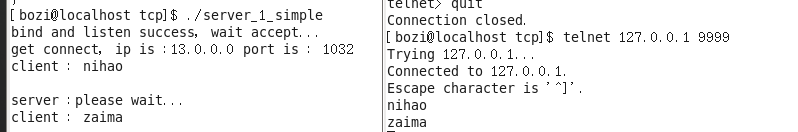
测试的时候 用 telnet
telnet CTRL+] 就可以进入命令行了
问题描述:服务器与 客户端连接后 马上 kill掉服务器 然后又启动服务器 出现 Address already in use的错误 linux中等上半分钟 就可以启动服务器了
[bozi@localhost tcp]$ ./server_1_simple
bind and listen success, wait accept...
get connect, ip is :13.0.0.0 port is : 1032
^C
[bozi@localhost tcp]$ ./server_1_simple
bind error, error code is : 98, errno string is :Address already in use
原因:
解决方法:
练习代码:【客户端 】
#include#include /* See NOTES */ #include #include #include #include #include #define SERVER_PORT 9999 //#define SERVER_IP "192.168.0.1" int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 2) { printf("usage:server IP\n"); return 1; } char* str_server_ip = argv[1]; char buf[1024]; memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf)); struct sockaddr_in server_sock; int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); bzero(&server_sock, sizeof(server_sock)); server_sock.sin_family = AF_INET; //inet_pton(AF_INET, str_server_ip, &server_sock.sin_addr); //别的 写法 server_sock.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(str_server_ip); server_sock.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT); int ret = connect(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&server_sock, sizeof(server_sock)); if (ret < 0) { perror("connect"); return 2; } printf("connect success...\n"); while (1) { printf("client:>"); fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); buf[strlen(buf) - 1] = '\0'; // 把'\n' 置成'\0' write(sock, buf, strlen(buf) + 1); printf("please wait ...\n"); } close(sock); return 0; }
练习代码:【线程的方式 服务器代码:可以同时处理多个客户请求】
#include#include /* See NOTES */ #include #include #include #include #include #include #define LISTEN_QUEUE_NUM 50 void* handler_data(void* arg) { int client_socket = (int)arg; printf("create a new thread...new socket:%d\n", client_socket); char buf[1024]; while (1) { ssize_t _s = read(client_socket, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; printf("client %s\n", buf); write(client_socket, buf, strlen(buf)); } else if (_s == 0) // client close { printf("client is close\n"); break; } else { break; } } close(client_socket); return (void*)0; } int main() { int listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (listen_sock < 0) { perror("socket"); exit(1); } struct sockaddr_in local; local.sin_family = AF_INET; local.sin_port = htons(9999); local.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); // local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("192.168.1.1"); // if (bind(listen_sock,(struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) { perror("bind"); exit(2); } if (listen(listen_sock, LISTEN_QUEUE_NUM) < 0) { perror("listen"); exit(3); } struct sockaddr_in peer; socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); // signal(SIGCHLD, collect_child); while (1) { int new_fd = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len); if (new_fd > 0) { pthread_t tid ; pthread_create(&tid, NULL, handler_data, (void*)new_fd); pthread_detach(tid); } } close(listen_sock); return 0; }
练习代码:【客户端代码】
#include#include /* See NOTES */ #include #include #include #include #include #include void usage(const char *proc) { printf("%s [ip] [port]\n", proc); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { if (argc != 3) { usage(argv[0]); return 3; } int conn = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (conn < 0) { perror("socket"); return 1; } struct sockaddr_in remote; remote.sin_family = AF_INET; remote.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); remote.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); if (connect(conn, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, sizeof(remote)) < 0) { perror("connect"); return 2; } char buf[1024]; while(1) { ssize_t _s = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { //buf[_s - 1] = '\0';// 去掉\n buf[_s] = '\0'; write(conn, buf, strlen(buf)); read(conn , buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); printf("server echo : %s\n", buf); } else { perror("read ----"); break; } } return 0; }
练习代码:【服务器 是 进程实现的】
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include void collect_child(int sig) { while (waitpid(-1, 0, WNOHANG) > 0) { printf("collect child done...\n"); } } int main() { int listen_sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM , 0); if (listen_sock < 0) { perror("listen "); exit(1); } struct sockaddr_in local; local.sin_family = AF_INET; local.sin_port = htons(9999); local.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY); if (bind(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) { perror("bind "); exit(2); } if (listen(listen_sock, 20) < 0) // backlog 20 { perror("listen"); exit(3); } struct sockaddr_in peer; socklen_t len = sizeof(peer); signal(SIGCHLD, collect_child); ////////////////////// while (1) { int new_fd = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len); if (new_fd < 0) { perror("accept"); exit(4); } pid_t id = fork(); if (id == 0) { // child printf("fork done... pid : %d, get a new client: socket >%s:%d\n", getpid(), inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr), ntohs(peer.sin_port)); char buf[1024]; while (1) { ssize_t _s = read(new_fd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; printf("client: %s\n", buf); write(new_fd,buf, strlen(buf) ); } else if (_s == 0) { printf("client is close\n"); break; } else { break; } } close(new_fd); exit(0); } else { // father close(new_fd); } } }
练习代码:【客户端】
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include void usage(const char *proc) { printf("%s [ip] [port]\n", proc); } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { if (argc != 3) { usage(argv[0]); return 3; } int conn = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); if (conn < 0) { perror("socket"); return 1; } struct sockaddr_in remote; remote.sin_family = AF_INET; remote.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); remote.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); if (connect(conn, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, sizeof(remote)) < 0) { perror("connect"); return 2; } char buf[1024]; while (1) { ssize_t _s = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; write(conn, buf, strlen(buf)); read(conn, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); printf("server echo:%s\n", buf); } else { exit(55); } } close(conn); return 0; }
运行结果:
[bozi@localhost tcp3]$ netstat -alpt Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name ............................................. tcp 0 0 localhost:distinct localhost:56683 ESTABLISHED 3451/./server tcp 0 0 localhost:56683 localhost:distinct ESTABLISHED 3450/./client tcp 1 0 192.168.174.158:60487 ip-42-99-128-139.pacne:http CLOSE_WAIT 2969/clock-applet tcp 0 0 localhost:56682 localhost:distinct ESTABLISHED 3411/./client tcp 0 0 localhost:distinct localhost:56682 ESTABLISHED 3412/./server
udp编程
UDP基础知识
UDP(User Datagram Protocol,用户数据报协议)是一个简单的、面向数据报的无连接协议,提供了快速但不一定可靠的传输服务。
UDP与TCP相比主要有以下区别。
1.UDP速度比TCP快
由于UDP不需要先与对方建立连接,也不需要传输确认,因此其数据传输速度比TCP快得多。
2.UDP有消息边界
使用UDP不需要考虑消息边界问题,使用上比TCP简单
3.UDP可以一对多传输
利用UDP可以使用广播或组播的方式同时向子网上的所有客户发送信息。这一点也比TCP方便。
4.UDP可靠性不如TCP
与TCP不同,UDP并不提供数据传送的保证机制。如果在从发送方到接收方的传递过程中出现数据报的丢失,协议本身并不能做出任何检测或提示。因此,通常人们把UDP称为不可靠的传输协议。
5.UDP不像TCP那样能保证有序传输
UDP不能确保数据的发送和接收顺序。对于突发性的数据报,有可能会乱序。事实上,UDP的这种乱序性基本上很少出现,通常只会在网络非常拥挤的情况下才有可能发生
UDP编程
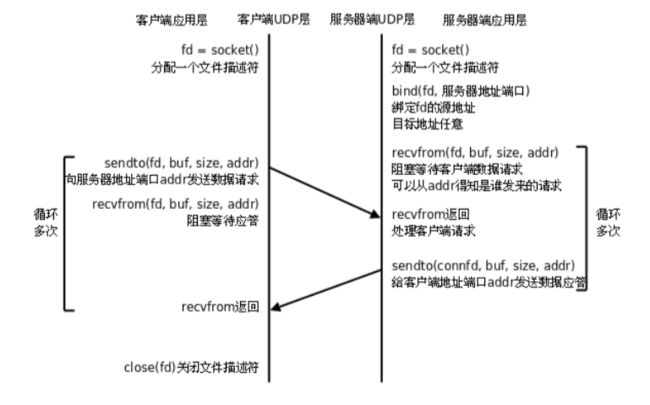
1)创建socket时,数据格式为:SOCK_DGRAM(数据块)
2)数据收发用recvfrom和sendto
ssize_t recvfrom(int socket,void *restrict buffer,size_t length,int flags,struct sockaddr * restrict address,socklen_t *restrict address_len);
restrict:类型限定符,限定约束指针。表明该指针是访问这个数据队形的唯一的方式
补充一点:
void *memcpy( void * restrict dest ,const void * restrict src,sizi_t n) 这是一个很有用的内存复制函数,由于两个参数都加了restrict限定,所以两块区域不能重叠,即 dest指针所指的区域,不能让别的指针来修改,即src的指针不能修改. 相对应的别一个函数 memmove(void *dest,const void * src,size_t)则可以重叠。
socket: 已连接的套接字
buffer:接收数据的缓冲区
length:缓冲区长度
flags :调用操作方式
address:指向装有源地址的缓冲区(传出型参数)
address_len:指向源地址缓冲区的实际长度(传入传出型参数)
ssize_t sendto(int socket,const void*buffer,size_t length,int flags,struct sockaddr* dest_addr,socklen_t len);
socket:已连接套接字
buffer:包含待发送数据的缓冲区
length:buffer缓冲区数据的长度
flags:调用方式标志位
dest_addr:指向目的套接字的地址
len:dest_addr所指地址的长度
练习代码:【服务器 】
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #define BF_SIZE 1024 int main(const int argc,const char* argv[]) { if (argc != 3) { printf("please enter %s [ip] [port]\n",argv[0]); exit(1); } int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM,0 );//SOCK_DGRAM 数据报套接口 if (fd < 0) { perror("socket"); exit(2); } struct sockaddr_in local; local.sin_family = AF_INET; local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); local.sin_port = htons(atoi(argv[2])); if (bind(fd, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0) { perror("bind"); return 2; } struct sockaddr_in remote; socklen_t len = sizeof(remote); while (1) { char buf[BF_SIZE]; memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf)); ssize_t _s = recvfrom(fd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, 0, (struct sockaddr *)&remote, &len);// 注意len取地址 sendto 中不用 if (_s > 0) { printf("client :[ip:%s][port:%d] %s", inet_ntoa(remote.sin_addr), ntohs(remote.sin_port), buf); } else if (_s == 0) { printf("read done...\n"); } else { break; } } close(fd); return 0; }
练习代码:【客户端】
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include int main(const int argc,const char* argv[] ) { if (argc != 3) { printf("please enter %s [ip] [port]\n", argv[0]); return 1; } int fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0); if (fd < 0) { perror("socket"); return 2; } int port = atoi(argv[2]); struct sockaddr_in remote; remote.sin_family = AF_INET; remote.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(argv[1]); remote.sin_port = htons(port); while (1) { char buf[1024]; ssize_t _s = read(0, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1); if (_s > 0) { buf[_s] = '\0'; } _s = sendto(fd, buf, strlen(buf),0, (struct sockaddr*)&remote, sizeof(remote)); } return 0; }
运行:
[bozi@localhost ~]$ netstat -atup Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name ....... udp 0 0 localhost:distinct32 *:* 4671/./server udp 0 0 *:60703 *:* 4673/./client