v-once指令
once:一旦,当...时候
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
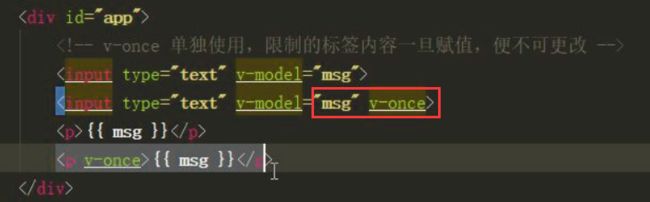
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="msg">
<input type="text" v-model="msg" v-once>
<p>{{ msg }}p>
<p v-once>{{ msg }}p>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: '初始值'
}
})
script>
html>
v-once,单独使用,限制的标签内容一旦被赋值,便不可修改,即使是data内的赋值.
v-colak指令:斗篷指令,掩盖
让页面在加载的时候,取消刷新带来的后端数据显示的闪烁效果.
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
[v-cloak] {
display: none; 先让页面默认不显示
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app" v-cloak>
{{ }}
{{ }}
{{ }}
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
})
script>
html>
处理的方法:也可以把vue.js环境加载在body代码执行之前.
条件指令
v-show:返回的是一个布尔值:flase/true
根据表达式之真假值,切换元素的 display CSS 属性。是否显示。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
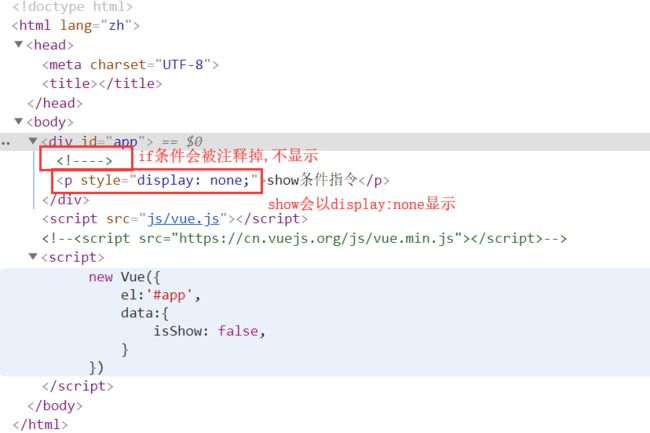
<div id="app">
<p v-if="isShow">if条件指令p>
<p v-show="isShow">show条件指令p>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
isShow: false,
}
})
script>
html>
总结:
两种都可以控制标签的显隐,绑定的值是布尔类型值,当都隐藏标签时
v-if是不渲染标签
v-show以 display:none 方式渲染
条件指令家族
if else-if else结合使用
例子:实现如下,点击红色就是显示红色方框图,点击黄色就显示黄色
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
.box {
width: 400px;
height: 300px;
}
.r { background-color: red; }
.y { background-color: yellow }
.b { background-color: blue; }
.active {
background-color: pink;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p v-if="0">ifififp> ="0"则不显示
<p v-else-if="0">elseifp>
<p v-else>elsep>
<div class="em">
<p>
<button @click="changeBox('rBox')" :class="{active: showName == 'rBox'}">红button>
<button @click="changeBox('yBox')" :class="{active: showName == 'yBox'}">黄button>
<button @click="changeBox('bBox')" :class="{active: showName == 'bBox'}">蓝button>
p>
<p>
<button @click="changeBox('rBox')" :class="showName == 'rBox' ? 'active' : ''">红button>
<button @click="changeBox('yBox')" :class="showName == 'yBox' ? 'active' : ''">黄button>
<button @click="changeBox('bBox')" :class="showName == 'bBox' ? 'active' : ''">蓝button>
p>
<div class="box r" v-if="showName == 'rBox'">div>
<div class="box y" v-else-if="showName == 'yBox'">div>
<div class="box b" v-else>div>
div>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
showName: 'rBox'
},
methods: {
changeBox(name) {
this.showName = name;
}
}
})
script>
html>
条件判断
首先绑定点击事件,映射好对应的关系,直接用"=="进行条件的判断是否成立.
原义指令
-- v-pre:指令可以在vue控制范围内,形成局部vue不控制区域 --
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ msg }}p>
<p v-pre>
{{ }}
<span v-if="hehe">span>
p>
div>
<p>
{{ }}
<span v-if="hehe">span>
p>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'message'
}
})
script>
html>
循环指令
v-for 配合key:
用法:基于源数据多次渲染元素或模板块。此指令之值,必须使用特定语法 alias in expression ,为当前遍历的元素提供别名:
<div v-for="item in items"> {{ item.text }} div>
v-for 默认行为试着不改变整体,而是替换元素。迫使其重新排序的元素,你需要提供一个 key 的特殊属性:
<div v-for="item in items" :key="item.id"> {{ item.text }} div
实例:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ str }}p>
<p>{{ str[0] }}p>
<div>
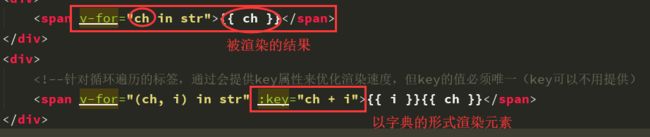
<span v-for="ch in str">{{ ch }}span>
div>
<div>
<span v-for="(ch, i) in str" :key="ch + i">{{ i }}{{ ch }}span>
div>
<div>
<p v-for="(ele, i) in arr">{{ i }}{{ ele }}p>
div>
<div>
<p v-for="ele in dic">{{ ele }}p>
div>
<div>
<p v-for="(ele, k) in dic">{{ k }}:{{ ele }}p>
div>
<div>
<p v-for="(ele, k, i) in dic">{{ i }}{{ k }}:{{ ele }}p>
div>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
str: 'abc123嘻嘻',
arr: [3, 4, 1, 2, 5],
dic: {
name: 'Jack',
age: 20,
gender: '哇塞',
}
}
})
script>
html>
渲染的结果:
todolist案例
留言实时更新,且可以删除.
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
li:hover {
color: red;
cursor: pointer;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>
<input type="text" v-model="userMsg">
<button type="button" @click="sendMsg">留言button>
p>
<ul>
<li v-for="(msg, index) in msgs" @click="deleteMsg(index)">
{{ msg }}
li>
ul>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msgs: localStorage.msgs ? JSON.parse(localStorage.msgs) : [], // 所有留言
userMsg: '', // 用户留言
},
methods: {
sendMsg() { // 留言事件
// 尾增
// this.msgs.push(this.userMsg);
// 首增
// this.msgs.unshift(this.userMsg);
let userMsg = this.userMsg;
if (userMsg) {
this.msgs.unshift(userMsg); // 渲染给页面
localStorage.msgs = JSON.stringify(this.msgs); // 同步到数据库
this.userMsg = ''; // 清空留言框
}
},
deleteMsg(index) {
// 开始索引 操作长度 操作的结果们
this.msgs.splice(index, 1)
}
}
})
script>
<script>
script>
html>
小结:
""" (1)、留言就是往留言数组中添加数据,删除留言就是从留言数组中移除数据 (2)、前台数据库:localstorage 和 sessionstorage localstorage永久保存数据 sessionstorage临时保存数据(当所属页面标签被关闭,数据被清空) (3)、前台localstorage 和 sessionstorage 数据库存储的值是字符串类型,所以要存放的 arr 、dic 等复杂数据需要Json转换。 """
实例成员-符合
插值表达式: delimiters: ['{[', ']}'],
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ msg }}
{[ msg ]}
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: '12345'
},
// delimiters: ['{{', '}}'],
delimiters: ['{[', ']}'],
})
script>
html>
实例成员-计算属性
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p @click="fn">{{ num }}p>
<p>十位:{{ parseInt(num / 10) }}p>
<p>个位:{{ num % 10 }}p>
十位:<input type="number" v-model="shi" min="0" max="9">
个位:<input type="number" v-model="ge" min="0" max="9">
结果:<b>{{ shi * 10 + +ge }}b>
结果:<b>{{ result }}b>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num: 99,
shi: '',
ge: '',
// result: 0,
},
methods: {
fn() {
this.num -= 3;
}
},
// 1) computed是用来声明 方法属性 的
// 2) 声明的方法属性不能在data中重复定义
// 3) 方法属性必须在页面中渲染使用,才会对内部出现的所有变量进行监听
computed: {
result() {
// console.log('该方法被调用了');
// this.shi;
// this.ge;
return this.shi * 10 + +this.ge
}
}
})
script>
html>
总结:
// 1) computed是用来声明 方法属性 的 // 2) 声明的方法属性不能在data中重复定义 // 3) 方法属性必须在页面中渲染使用,才会对内部出现的所有变量进行监听 // 4) 计算属性的值来源于监听方法的返回值
实例成员-属性监听
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p @click="fn">{{ num }}p>
<p>十位:{{ shi }}p>
<p>个位:{{ ge }}p>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
num: 99,
shi: 0,
ge: 0,
},
methods: {
fn() {
this.num -= 3;
}
},
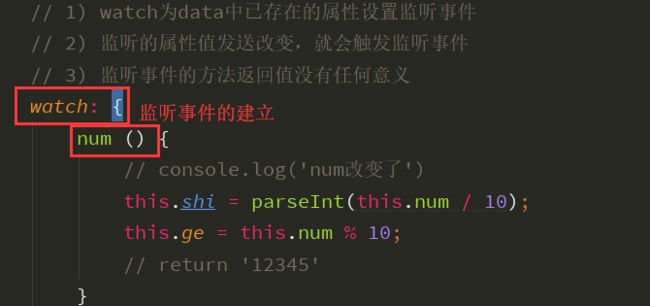
// 1) watch为data中已存在的属性设置监听事件
// 2) 监听的属性值发送改变,就会触发监听事件
// 3) 监听事件的方法返回值没有任何意义
watch: {
num () {
// console.log('num改变了')
this.shi = parseInt(this.num / 10);
this.ge = this.num % 10;
// return '12345'
}
}
})
script>
html>
总结:
""" (1)、watch为data中已存在的属性设置监听事件 (2)、监听的属性值发送改变,就会触发监听事件 (3)、监听事件的方法返回值没有任何意义 """
监听案例
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
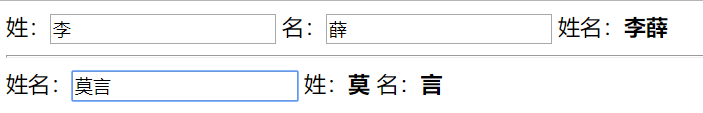
<div id="app">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="fName">
名:<input type="text" v-model="lName">
姓名:<b>{{ flName }}b>
<hr>
姓名:<input type="text" v-model="fullName">
姓:<b>{{ firstName }}b>
名:<b>{{ lastName }}b>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
fName: '',
lName: '',
fullName: '',
firstName: '',
lastName: '',
},
computed: {
flName(){
return this.fName + this.lName;
}
},
watch: {
fullName() {
nameArr = this.fullName.split('');
this.firstName = nameArr[0];
this.lastName = nameArr[1];
}
}
})
script>
html>
vue组件
关键字:template。
components:组件
组件的概念:
// 1) 组件:一个包含html、css、js独立的集合体,这样的集合体可以完成页面解构的代码复用 // 2) 分组分为根组件、全局组件与局部组件 // 根组件:所有被new Vue()产生的组件,在项目开发阶段,一个项目只会出现一个根组件 // 全局组件:不用注册,就可以成为任何一个组件的子组件 // 局部组件:必须注册,才可以成为注册该局部组件的子组件 // 3) 每一个组件都有自身的html结构,css样式,js逻辑 // 每一个组件其实都有自己的template,就是用来标识自己html结构的 // template模板中有且只有一个根标签 // 根组件一般不提供template,就由挂载点的真实DOM提供html结构 // 4) 除根组件的其他组件,数据要有局部作用域,保证组件复用时,各组件间数据的独立性 // 5) 在多组件共处时,在哪个组件模板中出现的变量,有当前组件组件提供
实例:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>{{ msg }}p>
div>
<div id="main">
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'message',
c1: 'red'
},
template: `
<div :style="{color: c1}" @click="fn">{{ msg }} {{ msg }}</div>
`,
methods: {
fn() {
alert(this.msg)
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: '#main',
data: {
msg: 'message'
}
})
script>
html>
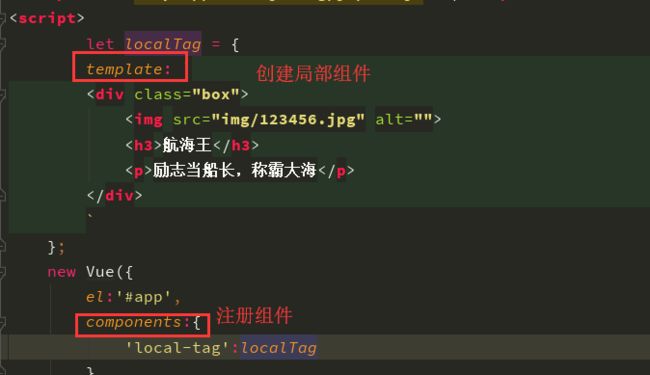
局部组件
使用的步骤:
// 1) 创建局部组件 // 2) 在父组件中注册该局部组件 // 3) 在父组件的template模板中渲染该局部组件
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
.box{
box-shadow:0 3px 5px 0 #0000FF;
width:240px;
height: 300px;
text-align: center;
padding:20px 0;
float:left;
margin: 5px;
}
.box img {
width: 200px;
}
style>
head>
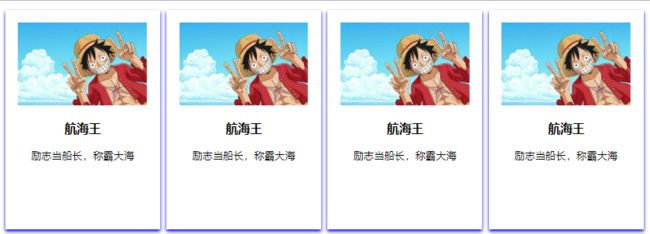
<body>
<div id="app">
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
div>
body>
<script src="https://cn.vuejs.org/js/vue.js">script>
<script>
let localTag = {
template: `
<div class="box">
<img src="img/123456.jpg" alt="">
<h3>航海王</h3>
<p>励志当船长,称霸大海</p>
</div>
`
};
new Vue({
el:'#app',
components:{
'local-tag':localTag
}
})
script>
html>
只需要在跟组件中添加绑定即可使用组件渲染的效果
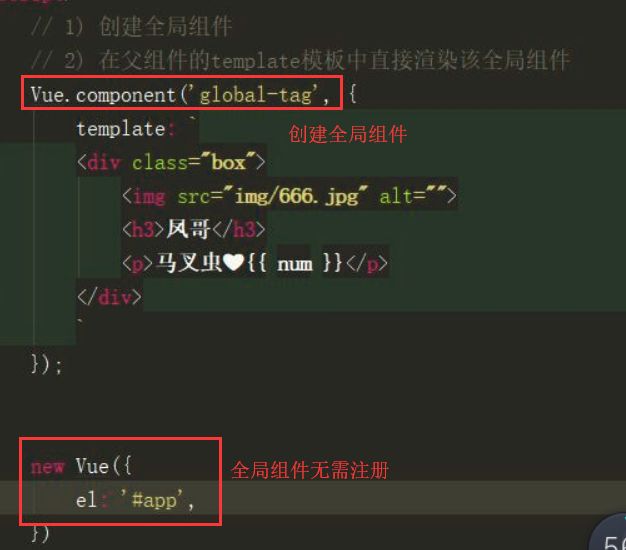
全局组件
//(1) 创建全局组件 //(2) 在父组件的template模板中直接渲染该全局组件,即可实现渲染效果
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
.box{
box-shadow:0 3px 5px 0 #0000FF;
width:240px;
height: 300px;
text-align: center;
padding:20px 0;
float:left;
margin: 5px;
}
.box img {
width: 200px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
<local-tag> local-tag>
div>
body>
<script src="https://cn.vuejs.org/js/vue.js">script>
<script>
Vue.component('global-tag',{
template:`
<div class="box" @click="action">
<img src="img/123456.jpg" alt="">
<h2>路飞</h2>
<p>搞笑可爱担当{{ num }}</p>
</div>>`,
data(){
return {
num:0
}
},
methods:{
action(){
this.num++;
}
}
});
new Vue({
el:'#app',
})
script>
html>
组件交互-父传子
数据的交互:父传子-通过绑定属性的方式
(1)父组件提供数据
(2) 在父组件模板中,为子组件标签设置自定义属性,绑定的值由父组件提供
(3) 在子组件实例中,通过props 实例成员获得自定义属性
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
.info {
text-align: center;
width: 200px;
padding: 3px;
box-shadow: 0 3px 5px 0 pink;
float: left;
margin: 5px;
}
.info img {
width: 200px;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<info v-for="info in infos" :key="info.image" :myinfo="info">info>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
let infos = [
{
image: 'img/001.png',
title: '小猫'
},
{
image: 'img/002.png',
title: '蛋糕'
},
{
image: 'img/003.png',
title: '蓝糕'
},
{
image: 'img/004.png',
title: '恶犬'
},
];
let info = {
template: `
<div class="info">
<img :src="myinfo.image" alt="">
<p><b>{{ myinfo.title }}</b></p>
</div>
`,
props: ['myinfo']
};
// 数据交互 - 父传子 - 通过绑定属性的方式
// 1) 父组件提供数据
// 2) 在父组件模板中,为子组件标签设置自定义属性,绑定的值有父组件提供
// 3) 在子组件实例中,通过props实例成员获得自定义属性
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
info,
},
data: {
infos,
}
})
script>
html>
先定义两个大字典info存放数据信息,然后由props创建组件之间的连接。
组件的交互-子传父
// 组件交互-子传父 // 1) 数据由子组件提供 // 2) 子组件内部通过触发系统事件,发送一个自定义事件,将数据携带出来 // 3) 父组件位子组件标签的自定义属性通过方法实现,就可以通过参数拿到子组件传递处理的参数
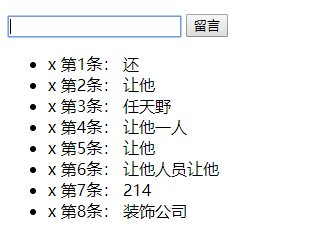
留言案例:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>title>
<style>
.close:hover {
cursor: pointer;
color: red;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<p>
<input type="text" v-model="userMsg">
<button @click="sendMsg">留言button>
p>
<ul>
<msg-li @remove_msg="removeAction" v-for="(msg, i) in msgs" :msg="msg" :index="i" :key="msg">msg-li>
ul>
div>
body>
<script src="js/vue.js">script>
<script>
let msgLi = {
template: `
<li>
<span class="close" @click="deleteMsg(index)">x </span>
<span>第{{ index + 1 }}条:</span>
<span>{{ msg }}</span>
</li>
`,
props: ['msg', 'index'],
methods: {
// 系统的click事件
deleteMsg(i) {
// $emit('自定义事件名', 参数们)
this.$emit('remove_msg', i);
this.$emit('myclick', 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
}
}
};
// 组件交互-子传父
// 1) 数据由子组件提供
// 2) 子组件内部通过触发系统事件,发送一个自定义事件,将数据携带出来
// 3) 父组件位子组件标签的自定义属性通过方法实现,就可以通过参数拿到子组件传递处理的参数
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msgs: [],
userMsg: ''
},
methods: {
sendMsg() {
if (this.userMsg) {
this.msgs.push(this.userMsg);
this.userMsg = "";
}
},
removeAction(i) {
this.msgs.splice(i, 1)
}
},
components: {
msgLi
}
})
script>
html>