团队的项目已经使用RN,有必要对React Native For Android有一个深入的了解,于是就写了这篇文章。注意本文分析的代码版本为:
- "react": "15.3.1",
- "react-native": "0.32.0"
环境配置
首先按照React Native的官方文档安装必要的环境并下载Demo程序,请参考Getting Started. 为了更方便的修改RN的源码,建议按照Building React Native from source配置一下。这篇文章第三步这是这样
从Demo入手
先把Demo跑起来看一下效果:
很简单,就是几个TextView. 我们来看一下JS是如何写的,在index.android.js中
...
class AwesomeProject extends Component {
render() {
return (
Welcome to React Native!
To get started, edit index.android.js
Double tap R on your keyboard to reload,{'\n'}
Shake or press menu button for dev menu
);
}
}
...
AppRegistry.registerComponent('AwesomeProject', () => AwesomeProject);
看着貌似很简单,那他们是怎么生成Android的页面呢。下面开始我们的分析之旅吧。
查看AwesomeProject下的android目录,发现只有MainActivity和MainApplication两个java文件。从MainActivity 入手
public class MainActivity extends ReactActivity {
/**
* Returns the name of the main component registered from JavaScript.
* This is used to schedule rendering of the component.
*/
@Override
protected String getMainComponentName() {
return "AwesomeProject";
}
}
内容也很简单,只有一个返回组件名字的函数。再关联到上面的js文件,Component名字是一样的。看一下ReactActvity的继承它就是一个Activity的子类。页面显示什么内容完全是由它控制的。先看一下它的启动时序图:
接下来就到源码里看看它的实现吧。
深入ReactAndroid
看了下ReactActivity的代码,发现在它只是一个空壳子,方法都是交给ReactActivityDelegate去处理的。这个delegate在ReactActivity的构造函数里就创建了。看一下它的onCreate最主要的就是调用loadApp().
protected void loadApp(String appKey) {
if (mReactRootView != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot loadApp while app is already running.");
}
mReactRootView = createRootView();
mReactRootView.startReactApplication(
getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager(),
appKey,
getLaunchOptions());
getPlainActivity().setContentView(mReactRootView);
}
最主要的是干了三件事:
- 创建ReactRootView
- 创建ReactInstanceManager
- 启动ReactApplication
接下来逐一分析。
1. 创建ReactRootView
protected ReactRootView createRootView() {
return new ReactRootView(getContext());
}
就是new了一个ReactRootView. 正如名字一样,它就是一个View,继承于FrameLayout。实现的功能包括,计算View的大小,监听手势、onTouch事件并交由JS处理,监听View大小变化和键盘变化。
2. 创建ReactInstanceManager
ReactInstanceManager是用来创建及管理CatalyInstance的实例的上层接口、控制开发调试,生命周期与ReactRootView所在activity保持一致。使用ReactInstanceManager.Builder创建,准备的参数包括:
ReactInstanceManager.Builder builder = ReactInstanceManager.builder()
.setApplication(mApplication)
.setJSMainModuleName(getJSMainModuleName())
.setUseDeveloperSupport(getUseDeveloperSupport())
.setRedBoxHandler(getRedBoxHandler())
.setUIImplementationProvider(getUIImplementationProvider())
.setInitialLifecycleState(LifecycleState.BEFORE_CREATE);
for (ReactPackage reactPackage : getPackages()) {
builder.addPackage(reactPackage);
}
String jsBundleFile = getJSBundleFile();
if (jsBundleFile != null) {
builder.setJSBundleFile(jsBundleFile);
} else {
builder.setBundleAssetName(Assertions.assertNotNull(getBundleAssetName()));
}
builder.build();
- Application :Android的Context
- Module Name : 对应index.android.js中的AppRegistry.registerComponent('Module Name'), 即是应用入口注册的模块名
- DeveloperSupport和RedBox: 调试相关
- UIImplementationProvider : 获取一个UIImplementation,这个类用于接收JS命令,然后处理Android的View
- ReactPackage: 包含一些Native和JS模块,RN自己提供了一个MainPackage
- BundleFile : JS代码和资源,文件的位置如何确定稍后会介绍
build之后会生成XReactInstanceManagerImpl。
到此startReactApplication的所有参数都已经准备好了,来看一下它的实现
if (!mReactInstanceManager.hasStartedCreatingInitialContext()) {
mReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground();
}
主要实现就是判断ReactContext是否已经创建,没有就在后台线程创建
3. 创建ReactContext
/**
* @return instance of {@link ReactContext} configured a {@link CatalystInstance} set
*/
private ReactApplicationContext createReactContext(
JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
mSourceUrl = jsBundleLoader.getSourceUrl();
NativeModuleRegistry.Builder nativeRegistryBuilder = new NativeModuleRegistry.Builder();
JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder jsModulesBuilder = new JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder();
final ReactApplicationContext reactContext = new ReactApplicationContext(mApplicationContext);
if (mUseDeveloperSupport) {
reactContext.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(mDevSupportManager);
}
try {
CoreModulesPackage coreModulesPackage =
new CoreModulesPackage(this, mBackBtnHandler, mUIImplementationProvider);
processPackage(coreModulesPackage, reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
}
for (ReactPackage reactPackage : mPackages) {
try {
processPackage(reactPackage, reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
}
}
NativeModuleRegistry nativeModuleRegistry;
try {
nativeModuleRegistry = nativeRegistryBuilder.build();
} finally {
}
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler != null
? mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler
: mDevSupportManager;
CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder catalystInstanceBuilder = new CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder()
.setReactQueueConfigurationSpec(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault())
.setJSExecutor(jsExecutor)
.setRegistry(nativeModuleRegistry)
.setJSModuleRegistry(jsModulesBuilder.build())
.setJSBundleLoader(jsBundleLoader)
.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler);
ReactMarker.logMarker(CREATE_CATALYST_INSTANCE_START);
try {
catalystInstance = catalystInstanceBuilder.build();
} finally {
}
if (mBridgeIdleDebugListener != null) {
catalystInstance.addBridgeIdleDebugListener(mBridgeIdleDebugListener);
}
try {
catalystInstance.getReactQueueConfiguration().getJSQueueThread().callOnQueue(
new Callable() {
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
reactContext.initializeWithInstance(catalystInstance);
try {
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
} finally {
}
return null;
}
}).get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return reactContext;
}
需要两个参数:JavaScriptExecutor和JSBundleLoader,都是之前创建的,具体作用后续用到会解释,先看一下继承关系:
它就是一个普通的Android Context子类,使用的是Application Context.
这个方法的重点不是创建Context,而是创建CatalystInstance,用于链接Java与JS引擎。
这两个方法调用了两次processPackage。�
-
CoreModulesPackage
- AndroidInfoModule : 获取Android版本号和ServerHost
- DeviceEventManagerModule:事件处理
- ExceptionsManagerModule :异常处理
- Timing :Timer,会监听屏幕每帧的变化,做一些处理
- SourceCodeModule: 可以获取到Bundle的地址
- UIManagerModule:UI管理器,允许JS创建和修改native的View
- 一些debug相关的模块
还有一些JS Module接口,和JS模块的名字一致,还没有看JS代码,具体功能就不描述了,看名字应该能猜出来: - RCTDeviceEventEmitter
- JSTimersExecution
- RCTEventEmitter
- RCTNativeAppEventEmitter
- AppRegistry
- Systrace
- HMRClient
- SamplingProfiler
- RCTDebugComponentOwnership
-
MainPackage
- AppStateModule :获取App前后台状态
- AsyncStorageModule:操作数据库,保存的是catalyst的一些状态
- CameraRollManager :获取设备相册的照片
- ClipboardModule : 允许JS操作剪贴板
- DatePickerDialogModule :JS可以调起native的日期控件
- DialogModule:JS调起native的对话框
- FrescoModule:Fresco库初始化和清理数据
- I18nManagerModule :国际化相关
- ImageEditingManager :图片裁剪
- ImageLoaderModule:图片加载器
- ImageStoreManager :图片内存缓存
- IntentModule : 打开其他的URL或Activity
- LocationModule:提供JS获取位置信息
- NativeAnimatedModule :创建、管理Native的动画
- XMLHttpRequest :实现了JS的XMLHttpRequest接口
- NetInfoModule :获取网络状态信息
- PermissionsModule : Android权限管理
- ShareModule :Android自带的分享
- StatusBarModule :改变状态栏样式
- TimePickerDialogModule : 调起Android选择时间控件
- ToastModule : 使用Android Toast
- VibrationModule : 管理设备震动
- WebSocketModule:基于OkHttp的ws实现
该模块中还一些ViewManager(创建管理Android的View),具体功能 先不介绍了,之后再专门写一篇关于View的文章 - ARTRenderableViewManager
- ARTRenderableViewManager
- ARTRenderableViewManager
- ARTSurfaceViewManager
- ReactDialogPickerManager
- ReactDrawerLayoutManager
- ReactDropdownPickerManager
- ReactHorizontalScrollViewManager
- ReactImageManager
- ReactModalHostManager
- ReactProgressBarViewManager
- ReactRawTextManager
- ReactScrollViewManager
- ReactSliderManager
- ReactSwitchManager
- FrescoBasedReactTextInlineImageViewManager
- ReactTextInputManager
- ReactTextViewManager
- ReactToolbarManager
- ReactViewManager
- ReactViewPagerManager
- ReactVirtualTextViewManager
- ReactWebViewManager
- RecyclerViewBackedScrollViewManager
- SwipeRefreshLayoutManager
列出上面这些是为了方便查看,以后开发时看能不能复用。回到先面说的processPackage,会把上面列出的module分别放到NativeModuleRegistry和JavaScriptModuleRegistry的map中。接下来就该创建CatalystInstance.来看一下它的构造函数:
private CatalystInstanceImpl(
final ReactQueueConfigurationSpec ReactQueueConfigurationSpec,
final JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
final NativeModuleRegistry registry,
final JavaScriptModuleRegistry jsModuleRegistry,
final JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader,
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler) {
mHybridData = initHybrid();
mReactQueueConfiguration = ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create(
ReactQueueConfigurationSpec,
new NativeExceptionHandler());
mBridgeIdleListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
mJavaRegistry = registry;
mJSModuleRegistry = jsModuleRegistry;
mJSBundleLoader = jsBundleLoader;
mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler = nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler;
mTraceListener = new JSProfilerTraceListener(this);
initializeBridge(
new BridgeCallback(this),
jsExecutor,
mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread(),
mReactQueueConfiguration.getNativeModulesQueueThread(),
mJavaRegistry.getModuleRegistryHolder(this));
mMainExecutorToken = getMainExecutorToken();
}
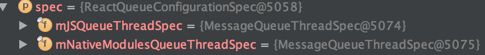
终于看到一些核心点的东西了。先介看下第一个参数: ReactQueueConfigurationSpec,是用于配置执行消息的线程的,其它的参数上面都看到过。
从这里猜测JS与Native之间交互,双工通讯都有一个线程,每个线程有一个对列,特别像Android的Handler机制。看了一下ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create的实现,确实是使用了Android的Handler机制,其准备好了三个线程:Android UI线程,JS 线程和NativeModulesQueue线程,后两个后强线程并结合looper使用。第一线程很明显是更新UI的,JS线程是JSCExecutor使用,native调用js会在这个线程执行,Native线程是执行JS调用native。
这里还有一个关键参数: ModuleRegistryHolder
mJavaRegistry.getModuleRegistryHolder(this)
这个要创建一个ModuleRegistryHolder对象,并把所有Native Module传递给c++层。
4. Module处理
执行到这里Native Module放在NativeModuleRegistry,JS Module放在JavaScriptModuleRegistry中,先来看一下它们相关的类图
Native Module的信息在Java和C ++中都保存了一份。
JS Module只在Java中保存。在JS代码里应该会有Module的处理,这些Module真正的实现在JS中,Native调用只需要传递类名和方法名就可以。
JS Module在Native中只是一个接口,并未真正的实现
5. Native初始化
所有的参数准备好了之后,就需要初始化Bridge,这是JS与Native通讯的关键,是个native函数(注意这块native的含意,对于RN来说,native是指Android或iOS,而在java或Android中Native就是指c/c++).
这里有一个细节,initializeBridge是一个jni方法,CatalystInstanceImpl.cpp只是一个空壳子,真的实现是在Instance.cpp中,应该是为了Android和iOS能复用。查看c++代码,最终走到这里
void Instance::initializeBridge(
std::unique_ptr callback,
std::shared_ptr jsef,
std::shared_ptr jsQueue,
std::unique_ptr nativeQueue,
std::shared_ptr moduleRegistry) {
callback_ = std::move(callback);
jsQueue->runOnQueueSync(
[this, &jsef, moduleRegistry, jsQueue,
nativeQueue=folly::makeMoveWrapper(std::move(nativeQueue))] () mutable {
nativeToJsBridge_ = folly::make_unique(
jsef.get(), moduleRegistry, jsQueue, nativeQueue.move(), callback_);
});
CHECK(nativeToJsBridge_);
}
其实就是在上面创建的JS线程是创建一个c++层的NativeToJsBridge的对象,来看一下它的构造函数
NativeToJsBridge::NativeToJsBridge(
JSExecutorFactory* jsExecutorFactory,
std::shared_ptr registry,
std::shared_ptr jsQueue,
std::unique_ptr nativeQueue,
std::shared_ptr callback)
: m_destroyed(std::make_shared(false))
, m_mainExecutorToken(callback->createExecutorToken())
, m_delegate(
std::make_shared(
this, registry, std::move(nativeQueue), callback)) {
std::unique_ptr mainExecutor =
jsExecutorFactory->createJSExecutor(m_delegate, jsQueue);
// cached to avoid locked map lookup in the common case
m_mainExecutor = mainExecutor.get();
registerExecutor(m_mainExecutorToken, std::move(mainExecutor), jsQueue);
}
在对象初始化时还创建了一个JsToNativeBridge对象,通过代码里的注释我们可以知道:
- JsToNativeBridge :管理JS调用Native
- NativeToJsBridge : 管理Native调用JS,也管理相关的线程
先创建一个JSExecutor,来看一下实现
std::unique_ptr JSCExecutorFactory::createJSExecutor(
std::shared_ptr delegate, std::shared_ptr jsQueue) {
return std::unique_ptr(
new JSCExecutor(delegate, jsQueue, m_cacheDir, m_jscConfig));
}
创建了一个JSCExecutor对象
JSCExecutor::JSCExecutor(std::shared_ptr delegate,
std::shared_ptr messageQueueThread,
const std::string& cacheDir,
const folly::dynamic& jscConfig) throw(JSException) :
m_delegate(delegate),
m_deviceCacheDir(cacheDir),
m_messageQueueThread(messageQueueThread),
m_jscConfig(jscConfig) {
initOnJSVMThread();
SystraceSection s("setBatchedBridgeConfig");
folly::dynamic nativeModuleConfig = folly::dynamic::array();
{
SystraceSection s("collectNativeModuleNames");
std::vector names = delegate->moduleNames();
for (auto& name : delegate->moduleNames()) {
nativeModuleConfig.push_back(folly::dynamic::array(std::move(name)));
}
}
folly::dynamic config =
folly::dynamic::object
("remoteModuleConfig", std::move(nativeModuleConfig));
SystraceSection t("setGlobalVariable");
setGlobalVariable(
"__fbBatchedBridgeConfig",
folly::make_unique(detail::toStdString(folly::toJson(config))));
setGlobalVariable(
"__fbBatchedBridgeSerializeNativeParams",
folly::make_unique(""));
}
这里把之前传到c++的NativeModule列表遍历一下,弄到一个数据里,然后生成一个JSON串。
void JSCExecutor::setGlobalVariable(std::string propName, std::unique_ptr jsonValue) {
try {
SystraceSection s("JSCExecutor.setGlobalVariable",
"propName", propName);
auto globalObject = JSContextGetGlobalObject(m_context);
String jsPropertyName(propName.c_str());
String jsValueJSON = jsStringFromBigString(*jsonValue);
auto valueToInject = JSValueMakeFromJSONString(m_context, jsValueJSON);
JSObjectSetProperty(m_context, globalObject, jsPropertyName, valueToInject, 0, NULL);
} catch (...) {
std::throw_with_nested(std::runtime_error("Error setting global variable: " + propName));
}
}
先来看一下__fbBatchedBridgeConfig的值是什么
{
"remoteModuleConfig":[
["ImageStoreManager"],
["ImageEditingManager"],
["LocationObserver"],
["Networking"],
["SourceCode"],
["NetInfo"],
["ShareModule"],
["ImageLoader"],
["FrescoModule"],
["ToastAndroid"],
["Timing"],
["Vibration"],
["UIManager"],
["DatePickerAndroid"],
["AsyncSQLiteDBStorage"],
["I18nManager"],
["AppState"],
["NativeAnimatedModule"],
["CameraRollManager"],
["PermissionsAndroid"],
["TimePickerAndroid"],
["AndroidConstants"],
["StatusBarManager"],
["ExceptionsManager"],
["AnimationsDebugModule"],
["DialogManagerAndroid"],
["IntentAndroid"],
["WebSocketModule"],
["Clipboard"],
["DeviceEventManager"]
]
}
这些就是我们上面列出的Module名字.
setGlobalVariable像是扔到一个全局的配置中,至此initializeBridge分析完了。
回到createReactContext中,看一下剩下部分
try {
catalystInstance.getReactQueueConfiguration().getJSQueueThread().callOnQueue(
new Callable() {
@Override
public Void call() throws Exception {
reactContext.initializeWithInstance(catalystInstance);
Systrace.beginSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE, "runJSBundle");
try {
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
ReactMarker.logMarker(RUN_JS_BUNDLE_END);
}
return null;
}
}).get();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
这段代码最主要就是在JS的线种队列中添加一个Callable,然后执行,最终调用到CatalystInstanceImpl.loadScriptFromFile(这里有三种实现,FromFile, FromAssets, FromOptimizedBundle,本次分析就选择从File中加载,其原理是一样的),也就是要加载JS代码了。这是一个native方法,经过几次调用会走到下面的方法
void JSCExecutor::loadApplicationScript(std::unique_ptr script, std::string sourceURL) throw(JSException) {
...
String jsScript = jsStringFromBigString(*script);
...
String jsSourceURL(sourceURL.c_str());
evaluateScript(m_context, jsScript, jsSourceURL);
bindBridge();
flush();
ReactMarker::logMarker("CREATE_REACT_CONTEXT_END");
}
evaluateScript应该是调用了JavaScriptCore中的方法,验证JS文件是否有效u并解析执行,bindBridge从__fbBatchedBridge中取出几个属性:
- callFunctionReturnFlushedQueue
- invokeCallbackAndReturnFlushedQueue
- flushedQueue
这三个都是MessageQueue.js中的方法,把它们当用c++的对象,保存在JSCExecutor中,关于这三个方法是如何设置的请参考React Native通讯原理。
void JSCExecutor::flush() {
auto result = m_flushedQueueJS->callAsFunction({});
try {
auto calls = Value(m_context, result).toJSONString();
m_delegate->callNativeModules(*this, std::move(calls), true);
} catch (...) {
std::string message = "Error in flush()";
try {
message += ":" + Value(m_context, result).toString().str();
} catch (...) {
// ignored
}
std::throw_with_nested(std::runtime_error(message));
}
}
先调用JS的flushedQueue,返回一个JS的一个队列(本次拿到的队列为空),对于RN如何把JS对象转换成Native的对象,之后再写篇文章分析。
至此createReactContext就完成了。
6. setupReactContext
创建ReactApplicationContext是在AsyncTask的doInBackground中执行的,�而在onPostExecute中只调用了setupReactContext,看一下它的实现
private void setupReactContext(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
...
CatalystInstance catalystInstance =
Assertions.assertNotNull(reactContext.getCatalystInstance());
catalystInstance.initialize();
mDevSupportManager.onNewReactContextCreated(reactContext);
mMemoryPressureRouter.addMemoryPressureListener(catalystInstance);
moveReactContextToCurrentLifecycleState();
for (ReactRootView rootView : mAttachedRootViews) {
attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(rootView, catalystInstance);
}
ReactInstanceEventListener[] listeners =
new ReactInstanceEventListener[mReactInstanceEventListeners.size()];
listeners = mReactInstanceEventListeners.toArray(listeners);
for (ReactInstanceEventListener listener : listeners) {
listener.onReactContextInitialized(reactContext);
}
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
- catalystInstance.initialize()会初始化所有Native Module
- 添加内存警告的回调
- 如果是Resumed状态,回调listener
- 给root view添加内容,重点看一下这个
private void attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(
ReactRootView rootView,
CatalystInstance catalystInstance) {
Systrace.beginSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE, "attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance");
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
// Reset view content as it's going to be populated by the application content from JS
rootView.removeAllViews();
rootView.setId(View.NO_ID);
UIManagerModule uiManagerModule = catalystInstance.getNativeModule(UIManagerModule.class);
int rootTag = uiManagerModule.addMeasuredRootView(rootView);
rootView.setRootViewTag(rootTag);
@Nullable Bundle launchOptions = rootView.getLaunchOptions();
WritableMap initialProps = Arguments.makeNativeMap(launchOptions);
String jsAppModuleName = rootView.getJSModuleName();
WritableNativeMap appParams = new WritableNativeMap();
appParams.putDouble("rootTag", rootTag);
appParams.putMap("initialProps", initialProps);
catalystInstance.getJSModule(AppRegistry.class).runApplication(jsAppModuleName, appParams);
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
设置RootView,然后获取AppRegistry的代理对象,因为所有的JSModule在Android中都是接口,无法直接调用,所以就使用了代理对象。这样也有一个好处就是,所有Native调用JS都会收敛到JavaScriptModuleInvocationHandler中,有一个统一的入口
public @Nullable Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, @Nullable Object[] args) throws Throwable {
ExecutorToken executorToken = mExecutorToken.get();
if (executorToken == null) {
FLog.w(ReactConstants.TAG, "Dropping JS call, ExecutorToken went away...");
return null;
}
NativeArray jsArgs = args != null ? Arguments.fromJavaArgs(args) : new WritableNativeArray();
mCatalystInstance.callFunction(
executorToken,
mModuleRegistration.getName(),
method.getName(),
jsArgs
);
return null;
}
从而得知,所有native调用js都是通过CatalystInstance的。在callFunction中会做一些容错处理,然后调用c++方法callJSFunction。
void NativeToJsBridge::callFunction(
ExecutorToken executorToken,
std::string&& module,
std::string&& method,
folly::dynamic&& arguments) {
...
runOnExecutorQueue(executorToken, [module = std::move(module), method = std::move(method), arguments = std::move(arguments), tracingName = std::move(tracingName), systraceCookie] (JSExecutor* executor) {
....
// This is safe because we are running on the executor's thread: it won't
// destruct until after it's been unregistered (which we check above) and
// that will happen on this thread
executor->callFunction(module, method, arguments);
});
}
------------------------------------------------
void JSCExecutor::callFunction(const std::string& moduleId, const std::string& methodId, const folly::dynamic& arguments) {
try {
auto result = m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS->callAsFunction({
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(moduleId)),
Value(m_context, String::createExpectingAscii(methodId)),
Value::fromDynamic(m_context, std::move(arguments))
});
auto calls = Value(m_context, result).toJSONString();
__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG,"zbljni","JSCExecutor::callFunction moduleId = %s, methodId = %s, result = %s" , moduleId.c_str(), methodId.c_str(), calls.c_str());
m_delegate->callNativeModules(*this, std::move(calls), true);
} catch (...) {
std::throw_with_nested(std::runtime_error("Error calling function: " + moduleId + ":" + methodId));
}
}
m_callFunctionReturnFlushedQueueJS (这个方法的作用参考React Native通讯原理) 就是当作一个函数指针然后调用JS的代码,也就是调用AppRegistry的runApplication,就是显示
AppRegistry.registerComponent('AwesomeProject', () => AwesomeProject);
这里的Component。这样JS代码就能显示到手机上了。UI相关的东西我们之后再单写文章进行分析。
先看一下执行的结果
D/zbljni (11286): JSCExecutor::callFunction moduleId = AppRegistry, methodId = runApplication, result = [[4,4],[9,9],["[2,[3,15]]","[1,[2]]"],21]
一堆数字,这是什么鬼,看一下是怎么回调native的
void callNativeModules(
JSExecutor& executor, std::string callJSON, bool isEndOfBatch) override {
ExecutorToken token = m_nativeToJs->getTokenForExecutor(executor);
m_nativeQueue->runOnQueue([this, token, callJSON=std::move(callJSON), isEndOfBatch] {
// An exception anywhere in here stops processing of the batch. This
// was the behavior of the Android bridge, and since exception handling
// terminates the whole bridge, there's not much point in continuing.
for (auto& call : react::parseMethodCalls(callJSON)) {
m_registry->callNativeMethod(
token, call.moduleId, call.methodId, std::move(call.arguments), call.callId);
}
if (isEndOfBatch) {
m_callback->onBatchComplete();
m_callback->decrementPendingJSCalls();
}
});
}
前面分析过有三个线程,这里就是在NativeModulesQueue线程中执行,里面有个parseMethodCalls,相信这是解析执行结果的,代码在MethodCall.cpp中的parseMethodCalls就不粘代码了, 先来解释下返回结果的含意:
- [4,4] : Module Id, 是c++层ModuleRegistry的modules_的索引
- [9,9] : Method Id,是Java层JavaModuleWrapper的mMethods的索引
- ["[2,[3,15]]","[1,[2]]"] : Request Params
- 21 : Request Call Id
根据返回结果创建一个c++的 std::vector
void ModuleRegistry::callNativeMethod(ExecutorToken token, unsigned int moduleId, unsigned int methodId,folly::dynamic&& params, int callId) {
...
modules_[moduleId]->invoke(token, methodId, std::move(params));
}
这里modules_是所有Native Module的集合, 至于moduleId是否对应__fbBatchedBridgeConfig中的module还不确定,invoke方法在父类BaseJavaModule中就是执行module中的@ReactMethod的方法,如果有多个应该是由methodid决定的。
通过debug代码,看到 4:对应的是UIManagerModule, 9 :对应的是setChildren,["[2,[3,15]]","[1,[2]]" :这些对应方法的参数
public void setChildren( int viewTag, ReadableArray childrenTags) {
...
}
还有�个疑问,在调用setChildren之前还调用了很多其他的方法,为什么runApplication的返回结果偏偏是它。由于对JS代码不熟悉,所以猜测在调用runApplication之后,JS开始调用native创建UI,这些操作都是添加到JS的工作队列中。由于时序问题,刚好runApplication执行完,队列中需要执行setChildren,所以就返回回来了。如果有了解的朋友欢迎解惑。
其实,runApplication的调用就是Native与JS通讯的流程。
这篇文章只是从代码的角度去分析,并未做相关的总结,之后会写相关的文章去介绍。如果有感兴趣的topic,欢迎留言。
已完成topic:
- React Native通讯原理