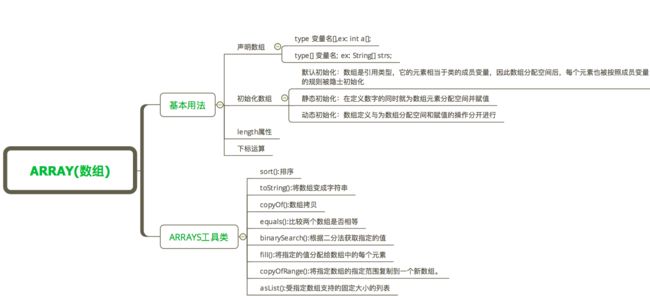
Java数组知识图如下:
数组基本用法
- 声明数组
声明数组语法格式:
type 变量名[]; ex: int a[];
type[] 变量名; ex: int[] a;
__ ps:声明数组时不能指定其长度(数组中元素的个数) __
- 初始化数组
Java中使用关键字new创建数组对象,语法格式:
1.默认初始化数组名 = new 数组元素的类型 [数组元素的个数] int[] a = new int[5];
__ ps:数组是引用类型,它的元素相当于类的成员变量,因此数组分配空间后,每个元素也被按照成员变量的规则被隐士初始化。 __public static void initAry(){ //初始化引用数据类型的数组,默认数组中的元素值为null String[] strAry = new String[5]; for (String str:strAry) { System.out.println(str); } //初始化基本数据类型的数组,如果是整型数组,则元素默认值为0,如果为浮点型,则元素默认值为0.0 byte[] byteAry = new byte[5]; for (byte be:byteAry) { System.out.println(be); } double[] doubleAry = new double[5]; for (double de:doubleAry) { System.out.println(de); } } - length属性
数组length属性是数组的长度,也是数组初始化时,指定数组内存储的元素个数。 - 下标运算
数组的下标运算,是根据数组的下标(索引)来获取数组中的元素
下标运算格式:
数组名[索引];
ex:
_ ps:数组的下标(索引)是从0开始 _public static void getElementOfIndex(){ int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; //获取a数组中的第五个元素 System.out.println(a[4]); //如果我们知道数组中的元素个数,初始化数组时,可以给数组分配容量大小 //这里的数字5代表这个数组中有5个位置可以放置元素 int[] intAry = new int[5]; System.out.println("intAry长度:"+intAry.length); //对数组中每个元素赋值 for (int i = 0; i < intAry.length; i++) { //根据数组的下标获取元素,并进行赋值操作 intAry[i] = i; } //遍历数组中的每个元素System.out.println("开始遍历数组"); for (int a:intAry) { System.out.println(a); } }
Arrays工具类(常用操作数组方法)
- sort():排序
ex:
//sort排序是优化过的快排算法实现的
public static void sortAry(){
int a[] = new int[]{1,4,5,4,2};
Arrays.sort(a);
for (int i:a) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
- toString():将数组转变成字符串
ex:
public static void aryToString(){
int[] intArray = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
String intArrayString = Arrays.toString(intArray);
// 打印得出的结果是引用值
System.out.println(intArray);
// [I@7150bd4d
System.out.println(intArrayString);
// [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
_ ps:说明了Java中数组的引用和值得区别,第三行直接打印intArray,输出的是乱码,因为intArray仅仅是一个地址引用。第4行输出的则是真正的数组值,因为它经过了Arrays.toString()的转化。_
- copyOf():数组拷贝
ex:
public static void aryCopyOf(){
int a[] = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
int b[] = Arrays.copyOf(a,2);
int c[] = Arrays.copyOf(a,6);
for (int i:b) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
- equals():比较两个数组是否相等
Arrays类中的equals()方法重写了Object(超类)的equals()方法
ex:
public static void equalsAry(){
int a[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
int b[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
boolean isTrue = a.equals(b);
System.out.println(a.hashCode());
System.out.println(b.hashCode());
System.out.println(isTrue);
//1846274136
//1639705018
//false
}
_ ps: 根据Arrays工具类内的equals()方法源码可以看出,数组比较的不是对象的值,而是对象所在内存空间中的地址_
- binarySearch():根据二分法获取指定的值
ex:
public static void binarySearchAry(){
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int[] b = {1,3,2};
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(a,2));
//在调用binarySearch()方法之前必须根据元素的自然顺序对范围进行升序排序
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(b,2));
}
_ ps:在调用binarySearch()方法之前必须根据元素的自然顺序对范围进行升序排序 _
- fill():将指定的值分配给数组中的每个元素
ex:
public static void fillAry(){
int[] a = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
Arrays.fill(a,0);
for(int i:a){
System.out.println(i);
//[0,0,0,0,0]
}
}
- copyOfRange():将指定的指定范围复制到一个新的数组
ex:
public static void copyOfRangeAry(){
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8};
int[] c = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,0,9);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c));
//[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,0]
}
- asList():将数组转化为集合
ex:
public static void aryAsList(){
String[] stringArray = { "a", "b", "c", "d", "e" };
List mn = Arrays.asList(stringArray);
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(stringArray));
System.out.println(mn);
System.out.println(arrayList);
}