wes定义: 全外显子组测序,是利用目标序列捕获技术, 将全基因组编码基因外显子区域的DNA捕获并富集后,进行高通量测序的基因组分析方法
通过测序可以找到大量的单核苷酸多态性位点(Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, SNP),插入缺失位点(Insertion/Deletion, InDel)、杂合性缺失(Loss of Heterozygosity, LOH)、拷贝数变异(Copy Number Variation, CNV)【拷贝数变异只针对肿瘤】
配合比较基因组学分析、群体遗传学分析、进化分析和计算生物学分析方法既可以用于深入探索疾病基因组的奥秘。
优点:但在同样的测序通量下,外显子组测序针对目标区段的测序深度以及覆盖度都高于全基因组重测序, 因此该技术对于发生在外显子区的常见和罕见的染色体变异具有很高的检测灵敏度。
wes流程首先要建立一个环境变量
然后在这个环境变量下安装会用到得软件,下载比对的参考基因组和数据库
先安装conda,用镜像下载快一些
Miniconda是conda轻量级,我们处理数据就够用了
conda命令详解:https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bb429659b34
Miniconda 安装包可以到 https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/miniconda/ 下载。
conda create -n wes python=2 #建立wes环境变量
conda install bwa
conda install sra-tools
conda install samtools
conda install bcftools vcftools snpeff
conda install multiqc qualimap
conda install gatk #这里需要了解gatk只是conda是不够的
提到gatk就不得不说一下java,生物信息很多软件都是用java写的,所以需要在linux上配置java运行环境。平台上的java 是1.7x的版本,但是一些生物信息软件(比如picard)需要更高级版本的java。
安装java
什么是GATK: stands for GenomeAnalysisToolkit
It is a collection of command-line tools for analyzing high-throughput sequencing data with a primary focus on variant discovery. The tools can be used individually or chained together into complete workflows. We provide end-to-end workflows, called GATK Best Practices
gatk4.0包含了picard工具,全部是基于illumina数据格式
下载地址:http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsa/wiki/index.php/Downloading_the_GATK
这个是已经编译好的版本,GATK是一个java程序,解开编译好的压缩包,我们可以看到下面有几个文件:
$ ls
AnalyzeCovariates.jar GenomeAnalysisTK.jar resources
两个后缀名为jar的文件和一个名为resources的文件夹,这两个.jar文件就是后面我们要用到java程序,主要要用的就是GenomeAnalysisTK.jar这个程序,resources文件夹里面有一些example的数据,可以用来测试。
在GATK使用过程中,有些步骤需要用到已知变异信息,对于这些已知变异,GATK只提供了人类的已知变异信息,可以在GATK的FTP站点下载(GATK resource bundle)
https://software.broadinstitute.org/gatk/download/bundle
GATK在进行BQSR和VQSR的过程中会使用到R软件绘制一些图,因此,在运行GATK之前最好先检查一下是否正确安装了R和所需要的包,所需要的包大概包括ggplot2、gplots、bitops、caTools、colorspace、gdata、gsalib、reshape、RColorBrewer等。如果画图时出现错误,会提示需要安装的包的名称。
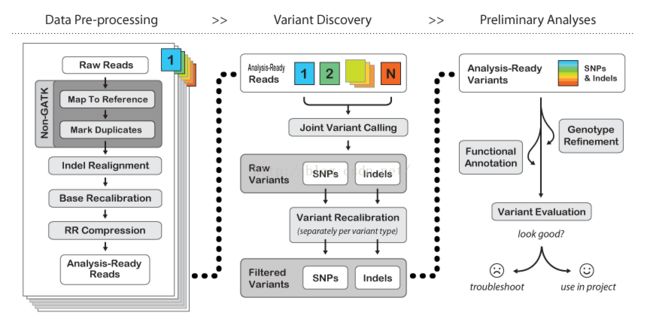
二、GATK的使用流程
GATK最佳使用方案:共3大步骤。原始数据的处理—变异检测—初步分析。
1.原始数据比对和过滤,就是illumina下机数据为fastq格式,推荐使用bwa进行mapping
BWA,即Burrows-Wheeler-Alignment Tool。
BWA 是一种能够将差异度较小的序列比对到一个较大的参考基因组上的软件包。它由三个不同的算法
1.BWA-backtrack: 是用来比对 Illumina 的序列的,reads 长度最长能到 100bp。
2.BWA-SW: 用于比对 long-read ,支持的长度为 70bp-1Mbp;同时支持剪接性比对。
3.BWA-MEM: 都支持较长的read长度,同时都支持剪接性比对(split alignments),但是BWA-MEM是更新的算法,也更快,更准确,且 BWA-MEM 对于 70bp-100bp 的 Illumina 数据来说,效果也更好些。选择这个算法,该算法先使用 MEM(maximal exact matches) 进行 seeding alignments,再使用 SW(affine-gap Smith-Waterman) 算法进行 seeds 的延伸。
BWA–MEM 算法执行局部比对和剪接性。可能会出现 query 序列的多个不同的部位出现各自的最优匹配,导致 reads 有多个最佳匹配位点。这对 long reads 的比对时比较重要的结果。但是却会和 Picard 的 markDuplicates 程序部兼容。
特别说明:
如果 mates.fq 缺省,且参数 –p 未设定,那么 reads.fq 被认为是 single-end;如果 mates.fq 存在,且参数 –p 未设定,那么 mem 命令会认为 read.fq 和 mates.fq 中的 i-th reads 组成一个read对 (a read pair),这个模式是常用的 paired-end mode。
如果参数 –p 被设定,那么, mem 命令会认为 read.fq 中的 第 2i-th 和 第 (2i + 1)-th 的 reads 组成一个 read 对 (a read pair),这种方式也被成为交错式的(interleaved paired-end)。 在这种情况下,即使有 mates.fq,也会被忽略。
bwa下载有2种方式,一种是我们前边介绍的conda,另一种可以直接下载二进制文件然后进行编译
$wget http://superb-sea2.dl.sourceforge.net/project/bio-bwa/bwa-0.7.12.tar.bz2
$tar jxf bwa-0.7.12.tar.bz2
$cd bwa-0.7.12
$make
$echo'PATH=$PATH:/your/bwa/path'>> ~/.bashrc
$source ~/.bashrc
应用bwa算法之前,需要利用 BWA 的 index 命令,构建出参考基因组的 FM-index
bwa index -a bwtsw hg38.fa #构建参考基因组索引
构建索引时需要注意的问题:bwa构建索引有两种算法,两种算法都是基于BWT的,这两种算法通过参数-a is 和-a bwtsw进行选择。 其中-a bwtsw对于短的参考序列是不工作的,必须要大于等于10Mb;-a is是默认参数,这个参数不适用于大的参考序列,必须要小于等于2G。
最后生成文件:hg19.fa.amb、hg19.fa.ann、hg19.fa.bwt、hg19.fa.pac和hg19.fa.sa。
bwa常用参数:
-t INT 线程数,默认是1。
-M 将 shorter split hits 标记为次优,以兼容 Picard’s markDuplicates 软件。
-p 若无此参数:输入文件只有1个,则进行单端比对;若输入文件有2个,则作为paired
reads进行比对。若加入此参数:则仅以第1个文件作为输入(输入的文件若有2个,则忽
略之),该文件必须是read1.fq和read2.fa进行reads交叉的数据。
-R STR 完整的read group的头部,可以用'\t'作为分隔符, 在输出的SAM文件中被解释为制
表符TAB. read group 的ID,会被添加到输出文件的每一个read的头部。
-T INT 当比对的分值比 INT 小时,不输出该比对结果,这个参数只影响输出的结果,不影响比
对的过程。
-a 将所有的比对结果都输出,包括 single-end和 unpaired paired-end的 reads,但是这些比
对的结果会被标记为次优。
比对命令如下:
$ bwa mem ref.fareads.fq> mem-se.sam
$ bwa mem ref.faread1.fqread2.fq> mem-pe.sam
$ bwa mem -t4-M -R"\@RG\tID:{library}\tLB:{library}\tPL:Illumina\tPU:{sample}\tSM:{sample}\" ref.fa read1.fastq read2.fastq > mem-pe.sam 2> ./mem-pe.log
2.寻找SA coordinates,确定reads在参考基因组上的坐标。
使用软件:BWA
使用命令: bwa aln
bwa aln -n 0.04 -o 1 -k 2 -t 20 reference.fa leftRead.fastq > leftRead.sai
bwa aln -n 0.04 -o 1 -k 2 -t 20 reference.fa rightRead.fastq > rightRead.sai
参数说明: -n :NUM Maximum edit distance if the value is INT, or the fraction of missing alignments given 2% uniform base error rate if FLOAT. In the latter case, the maximum edit distance is automatically chosen for different read lengths. [0.04]
-o:Maximum number of gap opens
-k:Maximum edit distance in the seed
-t:Number of threads (multi-threading mode)
将SA coordinates输出文件转换为sam格式
使用软件:BWA
使用命令:bwa sample
bwa sample -a 1000 -n 3 -N 10 reference.fa leftRead.sai leftRead.fastq > leftRead.sam
bwa sample -a 1000 -n 3 -N 10 reference.fa rightRead.sai rightread.fastq > rightRead.sam
参数说明: -a:Maximum insert size for a read pair to be considered being mapped properly. Since 0.4.5, this option is only used when there are not enough good alignment to infer the distribution of insert sizes.
-n:Maximum number of alignments to output in the XA tag for reads paired properly. If a read has more than INT hits, the XA tag will not be written.
-N:Maximum number of alignments to output in the XA tag for disconcordant read pairs (excluding singletons). If a read has more than INT hits, the XA tag will not be written.
将sam文件转换为bam文件
使用软件:samtools
使用命令:samtools view
samtools view -Sb leftRead.sam > leftRead.bam
samtools view -Sb rightRead.sam > rightRead.bam
参数说明: -S: input is SAM
默认下输入是 BAM 文件,若是输入是 SAM 文件,则最好加该参数,否则有时候会报错。
-b: output BAM
默认下输出是 SAM 格式文件,该参数设置输出 BAM 格式
但是为什么要把SAM文件转化成BAM文件,两者都存储了什么,是什么样的?
bwa、Bowtie2是现下最流行的短序列比对软件,SAM(Sequence Alignment/Map)格式是一种通用的比对格式,用来存储reads到参考序列的比对信息。SAM是一种序列比对格式标准,由sanger制定,是以TAB为分割符的文本格式。主要应用于测序序列mapping到基因组上的结果表示。
SAM文件官网:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SAM_%28file_format%29
SAM做的事情:
1. 非常多序列(read),mapping到多个参考基因组(reference)上;
2. 同一条序列,分多段(segment)比对到参考基因组上;
3. 无限量的,结构化信息表示,包括错配、删除、插入等比对信息;
行:除注释外,每一行是一个read。
@HD,说明符合标准的版本、对比序列的排列顺序;2@SQ,参考序列说明;3@RG,比对上的序列(read)说明;4@PG,使用的程序说明;5@CO,任意的说明信息。
比对结果部分(alignment section),每一行表示一个片段(segment)的比对信息,包括11个必须的字段(mandatory fields)和一个可选的字段,字段之间用tab分割。必须的字段有11个,顺序固定,不可用时,根据字段定义,可以为’0’或者’*’,这是11个字段包括:
比对结果详解:
SRR035022.2621862 163 16 59999 37 22S54M = 60102 179 CCAACCCAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCGACCCTCACCCTCACCC >AAA=>?AA>@@B@B?AABAB?AABAB?AAC@B?@AB@A?A>A@A?AAAAB??ABAB?79A?AAB;B?@?@<=8:8 XT:A:M XN:i:2 SM:i:37 AM:i:37 XM:i:0 XO:i:0 XG:i:0 RG:Z:SRR035022 NM:i:2 MD:Z:0N0N52 OQ:Z:CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCBCCCCCCBBCC@CCCCCCCCCCACCCCC;CCCBBC?CCCACCACA@
QNAME SRR035022.2621862
FLAG 163
RNAME 16
POS 59999
MAQ 37
CIGAR 22S54M
MRNM =
MPOS 60102
ISIZE 179
SEQ CCAACCCAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCCTAACCGACCCTCACCCTCACCC
QUAL >AAA=>?AA>@@B@B?AABAB?AABAB?AAC@B?@AB@A?A>A@A?AAAAB??ABAB?79A?AAB;B?@?@<=8:8TAG XT:A:M
TAG XN:i:2
TAG SM:i:37
TAG AM:i:37
TAG XM:i:0
TAG XO:i:0
TAG XG:i:0
TAG RG:Z:SRR035022
TAG NM:i:2
TAG MD:Z:0N0N52
TAG OQ:Z:CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCBCCCCCCBBCC@CCCCCCCCCCACCCCC;CCCBBC?CCCACCACA
必须的字段有11个,顺序固定,不可自行改动,根据字段定义,可以为’0‘或者’*‘,这是11个字段包括:
QNAME,比对片段的(template)的编号;
FLAG,位标识,template mapping情况的数字表示,每一个数字代表一种比对情况,这里的值是符合情况的数字相加总和;
(picard专门有一个工具解读sam的flag:http://broadinstitute.github.io/picard/explain-flags.html)
1The read is one of a pair read是pair中的一条(read表示本条read,mate表示pair中的另一条read)
2The alignment is one end of a proper paired-end alignment pair一正一负完美的比对上
4The read has no reported alignments 这条read没有比对上
8The read is one of a pair and has no reported alignments mate没有比对上
16The alignment is to the reverse reference strand 这条read反向比对
32The other mate in the paired-end alignment is aligned to the reverse reference strand mate反向比对
64The read is the first (#1) mate in a pair 这条read是read1
128The read is the second (#2) mate in a pair 这条read是read2
RNAME,参考序列的编号,如果注释中对SQ-SN进行了定义,这里必须和其保持一致,另外对于没有mapping上的序列,这里是’*‘;
POS,比对上的位置,注意是从1开始计数,没有比对上,此处为0;
MAPQ,mappint的质量;
CIGAR,简要比对信息表达式(Compact Idiosyncratic Gapped Alignment Report),其以参考序列为基础,使用数字加字母表示比对结果,比如3S6M1P1I4M,前三个碱基被剪切去除了,然后6个比对上了,然后打开了一个缺口,有一个碱基插入,最后是4个比对上了,是按照顺序的;
“M”表示 match或 mismatch;
“I”表示 insert;
“D”表示 deletion;
“N”表示 skipped(跳过这段区域);
“S”表示 soft clipping(被剪切的序列存在于序列中);
“H”表示 hard clipping(被剪切的序列不存在于序列中);
“P”表示 padding;
“=”表示 match;
“X”表示 mismatch(错配,位置是一一对应的);
RNEXT,下一个片段比对上的参考序列的编号,没有另外的片段,这里是’*‘,同一个片段,用’=‘;
PNEXT,下一个片段比对上的位置,如果不可用,此处为0;
TLEN,Template的长度,最左边得为正,最右边的为负,中间的不用定义正负,不分区段(single-segment)的比对上,或者不可用时,此处为0;
SEQ,序列片段的序列信息,如果不存储此类信息,此处为’*‘,注意CIGAR中M/I/S/=/X对应数字的和要等于序列长度;
QUAL,序列的质量信息,格式同FASTQ一样。read质量的ASCII编码。
可选字段(optional fields),格式如:TAG:TYPE:VALUE,其中TAG有两个大写字母组成,每个TAG代表一类信息,每一行一个TAG只能出现一次,TYPE表示TAG对应值的类型,可以是字符串、整数、字节、数组等。
2.bam和sam的区别与一致
sam是带有比对信息的序列文件(即告诉你这个reads在染色体上的位置等),用于储存序列数据(SAM format is a generic format for storing large nucleotide sequence alignments. )。
BAM is the compressed binary version of the Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) format. 生物信息中的二进制文件主要是为了节约空间,计算机机可读。可以用samtools工具实现sam和bam文件之间的转化。
二者都是fastq文件经过序列比对或者mapping后输出的格式(其储存的信息都是一致的)
在UCSC种对bam文件有详细介绍
BAM is the compressed binary version of the Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) format, a compact and index-able representation of nucleotide sequence alignments. Many next-generation sequencing and analysis tools work with SAM/BAM. For custom track display, the main advantage of indexed BAM over PSL and other human-readable alignment formats is that only the portions of the files needed to display a particular region are transferred to UCSC. This makes it possible to display alignments from files that are so large that the connection to UCSC would time out when attempting to upload the whole file to UCSC. Both the BAM file and its associated index file remain on your web-accessible server (http, https, or ftp), not on the UCSC server
Convert SAM to BAM using the samtools program:
```samtools view -S -b -o my.bam my.sam```
Sort and create an index for the BAM:
samtools sort my.bam my.sorted
samtools index my.sorted.bam
The sort command appends .bam to my.sorted, creating a BAM file of alignments ordered by leftmost position on the reference assembly. The index command generates a new file, my.sorted.bam.bai, with which genomic coordinates can quickly be translated into file offsets in my.sorted.bam
在UCSC浏览器中显示:
Move both the BAM file and index file (my.sorted.bam and my.sorted.bam.bai) to an http, https, or ftp location.
If the file URL ends with .bam, you can paste the URL directly into the custom track management page, click submit and view in the Genome Browser. The track name will then be the name of the file. If you want to configure the track name and descriptions, you will need to create a track line, as shown below in next step .
Construct a custom track using a single track line. The most basic version of the "track" line will look something like this:
track type=bam name="My BAM" bigDataUrl=http://myorg.edu/mylab/my.sorted.bam
Again, in addition to http://myorg.edu/mylab/my.sorted.bam, the associated index file http://myorg.edu/mylab/my.sorted.bam.bai must also be available at the same location.
Paste the custom track line into the text box in the custom track management page, click submit and view in the Genome Browser
其他信息可查看UCSC官网:http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/bam.html
通过bwa软件对fastqc文件比对结束,前边要做质控(fasqc和multiqc软件)过滤(trim_galore软件),下一步找变异,下一篇我们梳理一下GATK找变异的流程