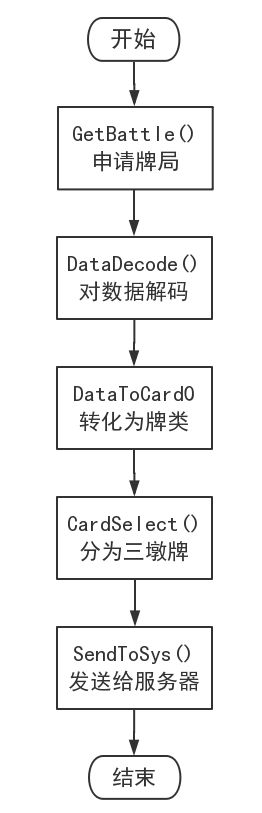
1、链接
队友链接(zxr)
出牌算法
2、分工
UI:zxr
出牌算法:zxr+zsy 当然是被队友带着养老了
3、PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 15 | 30 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 855 | 980 |
| Developm | 开发 | 240 | 360 |
| Analysis | 需求分析(包括学习新技术) | 20 | 20 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 60 | 60 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 30 | 30 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范(为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 10 | 10 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 240 | 360 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 240 | 360 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 60 | 60 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 420 | 420 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 0 | 0 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 0 | 0 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 0 | 0 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结,并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 | 855 | 980 |
4、解题思路描述与设计实现说明
思路描述
首先,数据规模为$n=13$很容易想到枚举算法(大概是$O(13^{5} * 8^{5}$)?貌似也没有限时),只要暴力枚举前中墩的情况即可,因为前中墩枚举结束后,剩余牌自动归为前墩。
其次,对于枚举结束之后的三墩,先进行合法性检测,即三墩需满足:前墩$\lt$中墩$\lt$后墩等号取不到
再者,对于合法的一组手牌,我们算出这组牌赢的概率的估计值。对,是概率的估计值,那么如何计算?因为我们偷到了一个权重数组,同时,我们维护一个大小为25的小根堆队友说25吉利,显然最后堆底的牌组就是我们考虑的最优组合。
最后,发到服务器,等待出分。
设计实现说明
1、爆搜或者10重for的嵌套。简单粗暴,除了久一点,没什么问题。
2、爆搜或者5重for,先选出后墩,再选出中墩。即后中墩是分开选择的。显然可以出解,而且比上一种方法快很多。但是,会出现倒水的情况,即无法保证三墩的大小关系。
3、先搜模式,匹配原始牌组,最后出牌。
4、AI算法,笔者没有头绪。
最后选择了方法3因为一开始写的是方法2,发现倒水了,就被队友说服去写方法3了,而至于为什么不写方法1,因为方法1时间复杂度太高了$O(!)$,关于方法3的实现,请看官移步开头链接查看。(文件名为:_AutoRecommend)
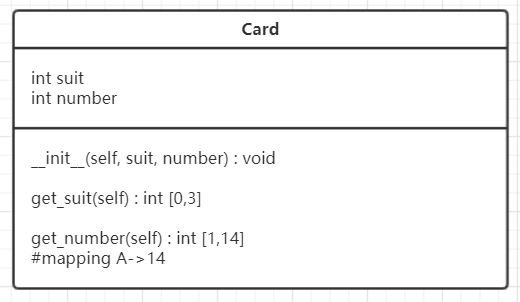
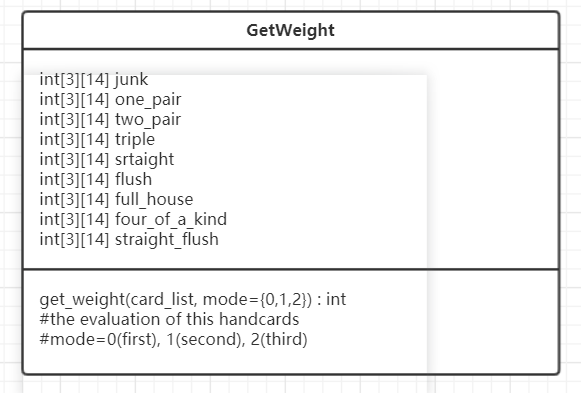
类图
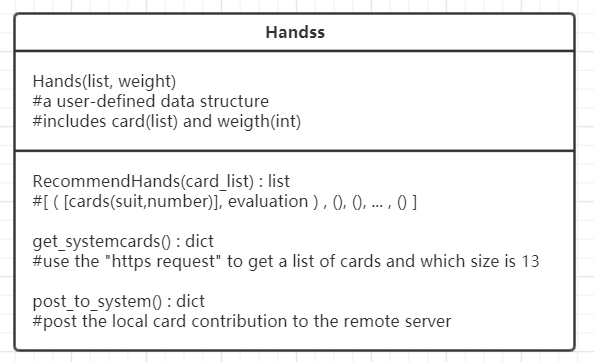
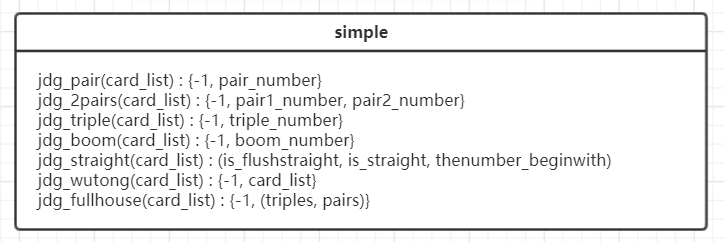
5、关键代码解释
没有python-style的python大概就是我这样的
def dfs(card_list, nw, state):
if ( nw == s ):
ct = 0
for i in range(len(state)):
if ( state[i] == 0 ):
state[i] = 1
hands.append(card_list[i])
state[i] = 0
ct += 1
print(hands)
header = hands[:f]
middle = hands[f:s]
tailer = hands[s:t]
#print(hands)
#print(header); print(middle); print(tailer)
ret = chk(header, middle, tailer)
if ( ret[0] == 1 ):
if ( len(q) >= hyper_n ):
if ( q[0].weight < ret[1] ):
heapq.heappushpop(q, HandCard(hands, ret[1]))
else:
heapq.heappush(q, HandCard(hands, ret[1]))
while (ct>0):
hands.pop()
ct -= 1
return
for i in range(len(state)):
if ( state[i] == 0 ):
state[i] = 1
hands.append(card_list[i])
dfs(card_list, nw+1, state)
hands.pop()
state[i] = 0
hyper_n = 10
f = 3
s = 8
t = 13
q = []
hands = []
heapq.heapify(q)
dfs(cards, 0, np.zeros(len(cards)))上述是一个简(T)单(到)粗(无)暴(边)的爆搜,直接否掉,这就不能算是个解决方案,实在是太缓慢了。而接下来是一个暴力+贪心的版本。
def RecommendHands( card_list ):
sz = len(card_list)
q = []
heapq.heapify(q)
nw_hands = []
#last O(n^5) using the brute force to enumerate the combination of the last hands
for i in range(0,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(card_list[i])
for j in range(i+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(card_list[j])
for k in range(j+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(card_list[k])
for g in range(k+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(card_list[g])
for t in range(g+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(card_list[t])
_c = nw_hands; _w = get_weight(_c, 2)
heapq.heappush(q, Hands(_c, -_w))
if len(q) > hyper_n:
_ = heapq.heappop(q)
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
last_hands = []; middle_hands = []; header_hands = []
while len(q)>0:
last_hands.append(heapq.heappop(q))
#last_hands = [ ([(1,1),(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(1,5)],weight), (), (), ... () ].dtype = Hands([(),()],w)
for _ in last_hands:
#fir every last_hands choose the middle_hands and header_hands
tp_card_list = card_list.copy()
for i in _.list:
for j in range(len(tp_card_list)):
if tp_card_list[j] == i:
tp_card_list.pop(j)
break
#now tp_card_list contain only 8 cards for middle and header
sz = len(tp_card_list)
for i in range(0,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(tp_card_list[i])
for j in range(i+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(tp_card_list[j])
for k in range(j+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(tp_card_list[k])
for g in range(k+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(tp_card_list[g])
for t in range(g+1,sz,1):
nw_hands.append(tp_card_list[t])
_c = nw_hands; _w = get_weight(_c, 1)
heapq.heappush(q, Hands(_c, -_w))
if len(q) > hyper_n:
_ = heapq.heappop(q)
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
nw_hands.pop()
while len(q)>0:
X = heapq.heappop(q)
middle_hands.append(X)
tp2_card_list = tp_card_list.copy()
szz = len(middle_hands)
for i in middle_hands[szz-1].list:
for j in range(len(tp2_card_list)):
if i == tp2_card_list[j]:
tp2_card_list.pop(j)
break
_c = tp2_card_list; _w = get_weight(tp2_card_list, 0)
header_hands.append(Hands(_c, -_w))
my_hands = []
for lst in last_hands:
for j in range(hyper_n):
my_hands.append( [(header_hands[j].list, header_hands[j].weight),
(middle_hands[j].list, middle_hands[j].weight),
(lst.list, lst.weight)] )
#for i in my_hands:
# print(i)
return my_hands
#middle O(n^5) using the brute force to enumrate the combination of the middle hands
#first the rest, no choise to choose最后是我们真正采用的算法。暴力枚举13张牌可能组成的牌型,从单张(junks)到顺子(straights),每种牌型从大到小排序,再从中枚举组合出后中前墩的可能出牌模式,最后枚举判断是否合法即可,如若合法则加入丢入小根堆中维护,最后小根堆弹出至空的最后一组出牌即为所求。因为每部分都不短,还请看官移步文首的仓库品鉴(文件名为:_AutoRecommend.py)
6、性能分析与改进
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall
64 0.001 0.000 15.890 0.248 Algorithm_fight.py:142(get_battle)
32 0.030 0.001 8.021 0.251 Algorithm_fight.py:155(decode_data)
32 0.001 0.000 3.058 0.096 Algorithm_fight.py:168(my_choose)
800 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Algorithm_fight.py:180()
32 0.001 0.000 7.483 0.234 Algorithm_fight.py:204(send_2_system)
32 0.055 0.002 26.529 0.829 Algorithm_fight.py:221(_start)
1 0.000 0.000 26.530 26.530 Algorithm_fight.py:239(main)
416 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Algorithm_fight.py:29(chg)
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Algorithm_fight.py:37(Hands)
50944 0.019 0.000 0.025 0.000 Algorithm_fight.py:38(__init__)
292872 0.034 0.000 0.034 0.000 Algorithm_fight.py:42(__lt__)
32 0.125 0.004 3.056 0.096 Algorithm_fight.py:49(RecommendHands)
1 0.000 0.000 26.767 26.767 Algorithm_fight.py:7()
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 GetWeight.py:7()
50944 0.240 0.000 2.790 0.000 GetWeight.py:99(get_weight) 参数解释:
ncalls:表示函数调用的次数。
tottime:表示指定函数的总的运行时间,除掉函数中调用子函数的运行时间。
percall:(第一个 percall)等于 tottime/ncalls。
cumtime:表示该函数及其所有子函数的调用运行的时间,即函数开始调用到返回的时间。
percall:(第二个 percall)即函数运行一次的平均时间,等于 cumtime/ncalls。
filename:lineno(function):每个函数调用的具体信息
其实,撇开网络请求,自我感觉完成得还是不错的,当然仅指完成层面。
改进方面:虽然是偷的权重数组,但是也和队友商量了挺久,以及讨论爆搜的剪枝(chk),也实现了一些讨论的方案。
7、单元测试
class UnitTest(unittest.TestCase):
@classmethod
def setUpClass(self):
pass
@classmethod
def tearDownClass(self):
pass
def tst_jdg_pair(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
ct += 1
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_pair(nw))
def tst_jdg_2pairs(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_2pairs(nw))
def tst_jdg_triple(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_triple(nw))
def tst_jdg_boom(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_boom(nw))
def tst_jdg_straight(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_boom(nw))
def tst_jdg_flush(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_flush(nw))
def tst_jdg_fullhouse(self):
ct = 0
for i in open('./UnitTest-in.txt').readlines():
nw = []; cards = i.split()
for j in cards:
nw.append((suit_sa[j[0]],number_sa[j[1:len(j)]]))
#print(nw)
ct += 1
print("card %d " % (ct), end="")
print(jdg_fullhouse(nw))
test_lists = ["tst_jdg_pair","tst_jdg_2pairs","tst_jdg_triple","tst_jdg_boom","tst_jdg_straight","tst_jdg_flush","tst_jdg_fullhouse"]
if __name__ == "__main__":
for i in test_lists:
suit = unittest.TestSuite()
suit.addTest(UnitTest(i))
runner = unittest.TextTestRunner()
runner.run(suit)8、贴出Github的代码签入记录
9、遇到的代码模块异常或结对困难及解决方法
问题描述
- 结对没有尽早开始写代码,拖延得比较后面。
国庆当然是快乐 - 关于算法结果有冲突。
倒水我是不想重写的,队友一开始的思路我是不解的
做过哪些尝试
- 意识到快来不及了,马上动工
233 - 队友说得对,就重写吧。
是否解决
- 较好地解决。显然我们完成了作业,我也解决了倒水。
有何收获
- 队友是个好队友,我就不知道了,我都差点跟队友吵起来。
还好队友的算法思路够真 - 学了一下python自带堆heapq的使用。
写模拟更强了
10、评价你的队友
值得学习的地方
儒雅随和,不紧不慢。
需要改进的地方
学前端太慢了。。在我看来,找到直接开抄就行。。
11、学习进度条
| 周数 | 新增代码(行) | 累计代码(行) | 本周学习消耗(小时) | 累计学习消耗(小时) | 重要成长 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 21 | AxureRp的学习与制作 |
| 7 | 800+ | 800+ | 0.4 | 21.4 | python的自带堆(heapq)调用,以及gitignore的编写 |
心得:
1、感谢我的队友,考虑到我的各种原因,包揽了前端,还写了特殊牌型得判断,最后放我来写我自己最熟悉的算法部分,同时队友也非常体谅我的进度。平心而论,如果这次是个人作业,我可能就完成不了了,或者说只会做出一个非常丑陋的UI界面。
2、一开始想写爆搜,怕爆栈就丢了for上去,确实除了慢点没什么问题,剪了剪枝也没有非常出乎意料的提升。暴力出奇迹,这是我写过最暴力的工程代码,但是却有着极低的编程复杂度。
3、最后被算法思路极真的队友,喊去写了我们最后使用的算法,不得不说,先找模式确实快很多。