这一周的课程内容比较难,而且比较不容易理解,所有学习的很吃力,现在接触的知识越来越多,也越来越难了,还是要多对照书本来进行学习!
这周主要学的有:
一、抽象类
1.Java中可以创建一种类专门用来当作父类,这种类称为“抽象类”。
2.抽象类的作用类似“模版”,其目的是要设计者依据它的格式来修改并创建新的类。
二、抽象类的定义及使用规则
1.包含一个抽象方法的类必须是抽象类;
2.抽象类和抽象方法都要使用abstract关键字声明;
3.抽象方法只需要声明而不需要实现;
4.抽象类必须被子类继承,子类(如果不是抽象类)必须覆写抽象类中的全部抽象方法。
实验四 类的继承
实验内容
(一)抽象类的使用
设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
实验源码:
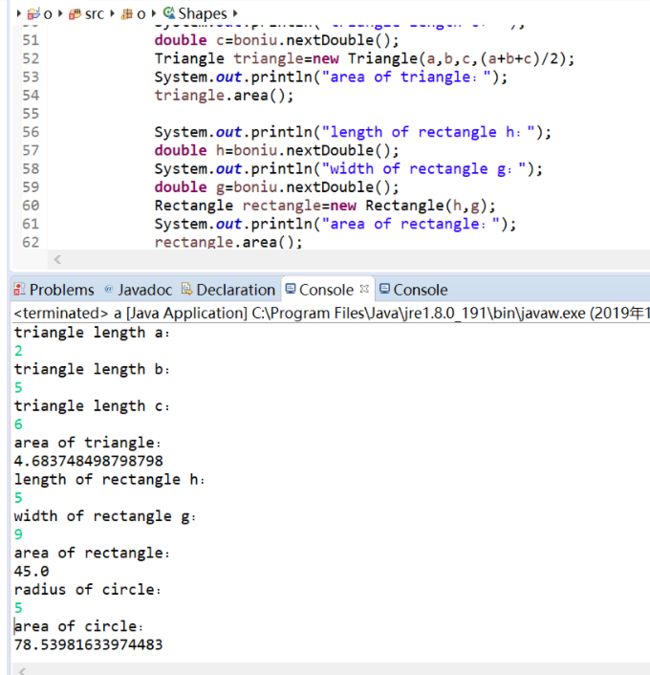
package first; import java.util.Scanner; abstract class Shapes { public abstract void area();} class Triangle extends Shapes{ private double a,b,c; private double p; Triangle(double a, double b, double c, double p){ this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; this.p = (a+b+c)/2;} public void area() { System.out.println(Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c))); } } class Rectangle extends Shapes{ private double h,g; Rectangle(double h, double g){ this.h = h; this.g = g; } public void area() { System.out.println(h*g); } } class Cricle extends Shapes{ private double r; Cricle(double r){ this.r=r; } public void area() { System.out.println(Math.pow(r,2)*Math.PI); } } public class a{ public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner boniu=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("triangle length a:" ); double a=boniu.nextDouble(); System.out.println("triangle length b:" ); double b=boniu.nextDouble(); System.out.println("triangle length c:" ); double c=boniu.nextDouble(); Triangle triangle=new Triangle(a,b,c,(a+b+c)/2); System.out.println("area of triangle:"); triangle.area(); System.out.println("length of rectangle h:"); double h=boniu.nextDouble(); System.out.println("width of rectangle g:"); double g=boniu.nextDouble(); Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle(h,g); System.out.println("area of rectangle:"); rectangle.area(); System.out.println("radius of circle:"); double r=boniu.nextDouble(); Cricle cricle=new Cricle(r); System.out.println("area of circle:"); cricle.area(); } }
实验结果:
实验源码:
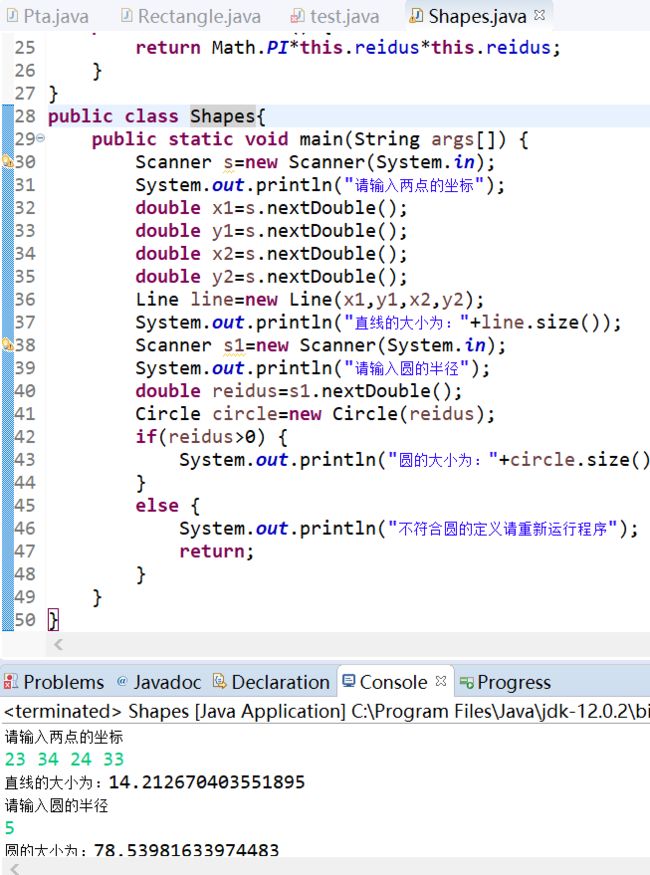
package first; import java.util.Scanner; interface Shape1{ public double size(); } class Line implements Shape1{ private double x1,x2,y1,y2; public Line(double x1,double x2,double y1,double y2) { this.x1=x1; this.x2=x2; this.y1=y1; this.y2=y2; } public double size() { return Math.sqrt((x2-x1)*(x2-x1)+(y2-y1)*(y2-y1)); } } class Circle implements Shape1{ private double reidus; public Circle(double reidus) { this.reidus=reidus; } public double size() { return Math.PI*this.reidus*this.reidus; } } public class Shape{ public static void main(String args[]) { Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入两点的坐标"); double x1=s.nextDouble(); double y1=s.nextDouble(); double x2=s.nextDouble(); double y2=s.nextDouble(); Line line=new Line(x1,y1,x2,y2); System.out.println("直线的大小为:"+line.size()); Scanner s1=new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入圆的半径"); double reidus=s1.nextDouble(); Circle circle=new Circle(reidus); if(reidus>0) { System.out.println("圆的大小为:"+circle.size()); } else { System.out.println("不符合圆的定义请重新运行程序"); return; } } }
实验结果:
总结:这周的题目比较难,写的也十分的困难,对新知识不够理解,也忘了一些以前的知识点,接下来还是要加强对知识点的巩固!!